Building a Word Search with PHP and MariaDB: Fetching Search Results Using FULLTEXT, LIKE, and LOCATE/POSITION
In this beginner-level tutorial, we’ll walk you through creating a simple word search application using PHP and MariaDB. This will allow users to search for specific words in a database using three different search methods: FULLTEXT, LIKE, and LOCATE/POSITION. We’ll also implement the Fetch API to dynamically display the search results in real-time without needing to reload the page.
Along the way, we’ll cover how to set up your MariaDB database, create a simple PHP script to handle the search functionality, and explore best practices for querying a database. Let’s get started!
Setting Up the MariaDB Database
Before we dive into the PHP code, let’s set up the database and table. We will create a posts table to store some sample text data for the word search.
CREATE DATABASE blog_db;
USE blog_db;
CREATE TABLE posts (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
content TEXT NOT NULL,
FULLTEXT(title, content)
);
-- Insert sample data into the table
INSERT INTO posts (title, content) VALUES
('First Post', 'This is the first post. It talks about PHP and MariaDB.'),
('Learning PHP', 'PHP is a powerful server-side language used for web development.'),
('WordPress and PHP', 'WordPress uses PHP for creating dynamic content on websites.'),
('MariaDB Introduction', 'MariaDB is a popular relational database management system.');
This SQL code creates a table called posts with two columns: title and content. We’ve also added a FULLTEXT index on both columns, which will help with the FULLTEXT search method.
Creating the HTML Structure
Now, let’s create a simple HTML form with an input field for the user to type a search query and options to choose the type of search method they prefer.
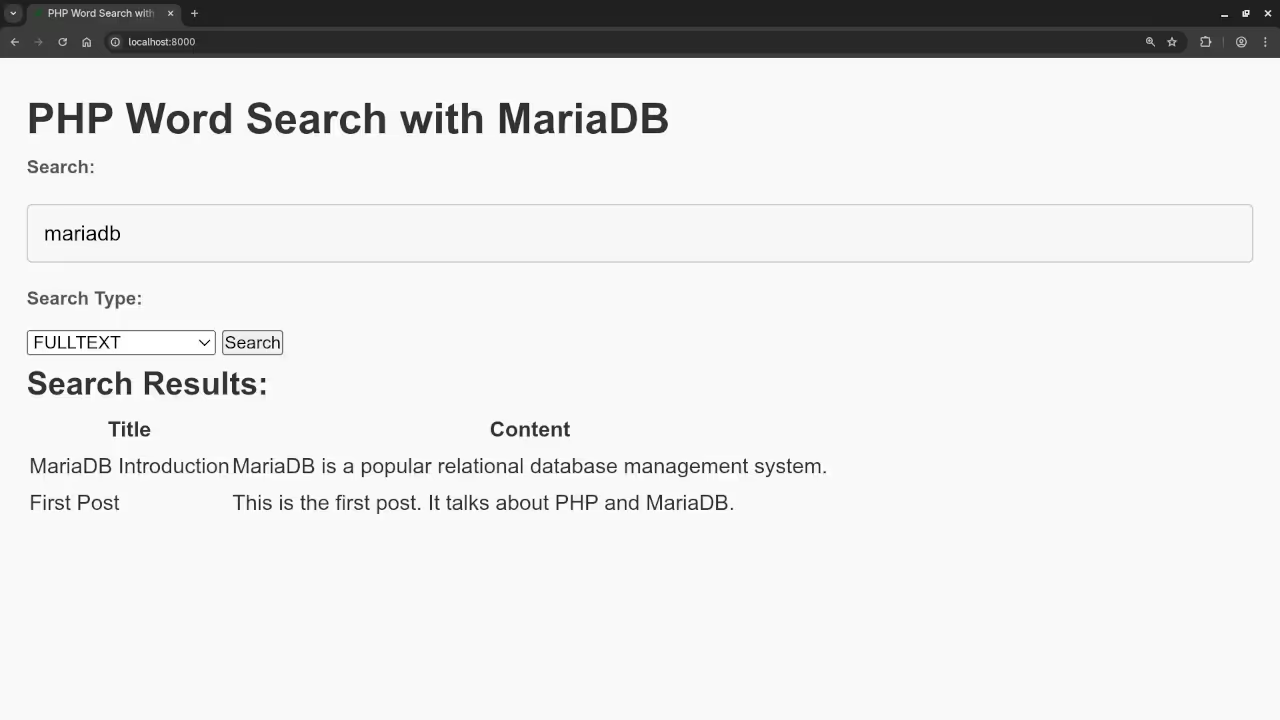
<h1>PHP Word Search with MariaDB</h1>
<label for="searchInput">Search:</label>
<input type="text" id="searchInput" placeholder="Enter a search term">
<label for="searchType">Search Type:</label>
<select id="searchType">
<option value="fulltext">FULLTEXT</option>
<option value="like">LIKE</option>
<option value="locate">LOCATE/POSITION</option>
</select>
<button id="searchButton">Search</button>
<h2>Search Results:</h2>
<table id="resultsTable">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Title</th>
<th>Content</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!-- Results will be displayed here -->
</tbody>
</table>
<script src="script.js"></script>
Here, we’ve created an input field where users can type their search query, a dropdown to select the search type, and a button to initiate the search. The results will be displayed in a table below the input.
Writing the JavaScript for Fetch API
Now, let’s write the JavaScript code that will handle the user’s search request. This script will make use of the Fetch API to send the user’s input to a PHP script without reloading the page.
document.getElementById('searchButton').addEventListener('click', function() {
const searchInput = document.getElementById('searchInput').value;
const searchType = document.getElementById('searchType').value;
if (searchInput === '') {
alert('Please enter a search term.');
return;
}
fetch('search.php', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
searchInput: searchInput,
searchType: searchType
})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
let resultsHTML = '';
data.forEach(post => {
resultsHTML += `<tr><td>${post.title}</td><td>${post.content}</td></tr>`;
});
document.querySelector('#resultsTable tbody').innerHTML = resultsHTML;
})
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));
});
This script listens for a click on the search button, grabs the input values (search term and search type), and sends them via a POST request to the search.php file. When the response is received, it populates the search results in the table.
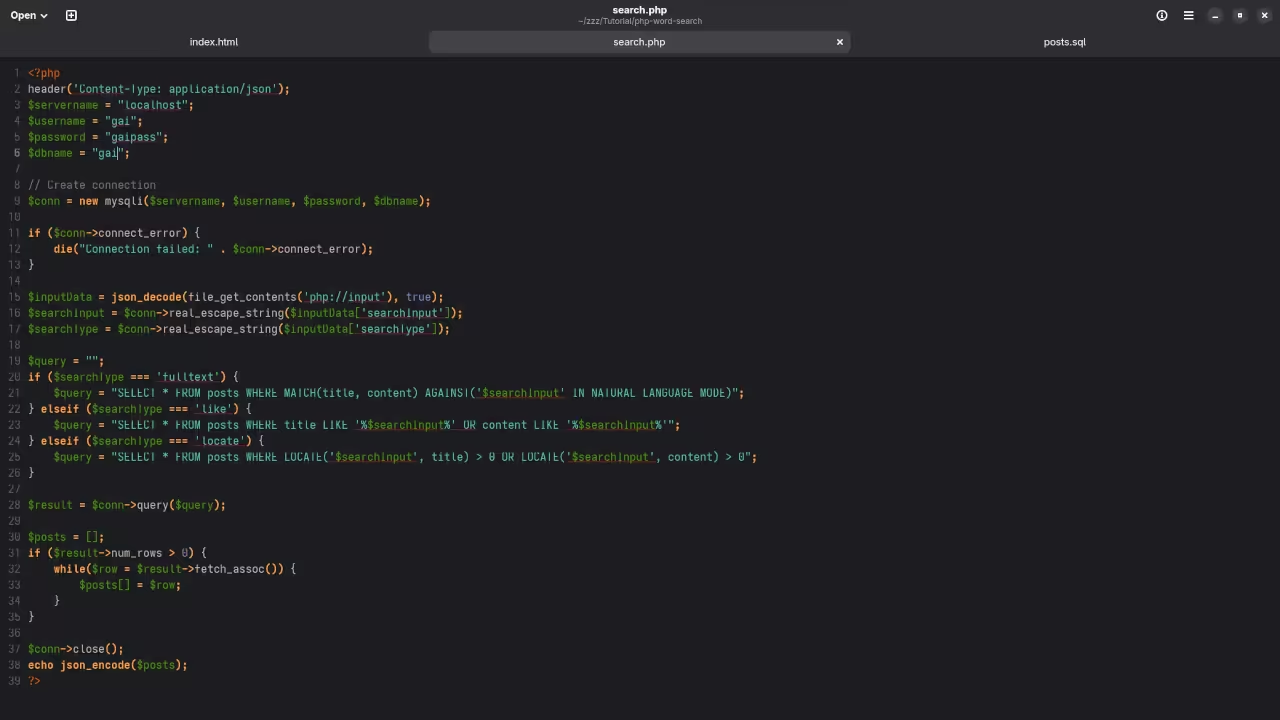
PHP Script to Handle the Search
Next, let’s create the search.php file that will process the search query and return the results from the database based on the selected search type.
header('Content-Type: application/json');
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$dbname = "blog_db";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$inputData = json_decode(file_get_contents('php://input'), true);
$searchInput = $conn->real_escape_string($inputData['searchInput']);
$searchType = $conn->real_escape_string($inputData['searchType']);
$query = "";
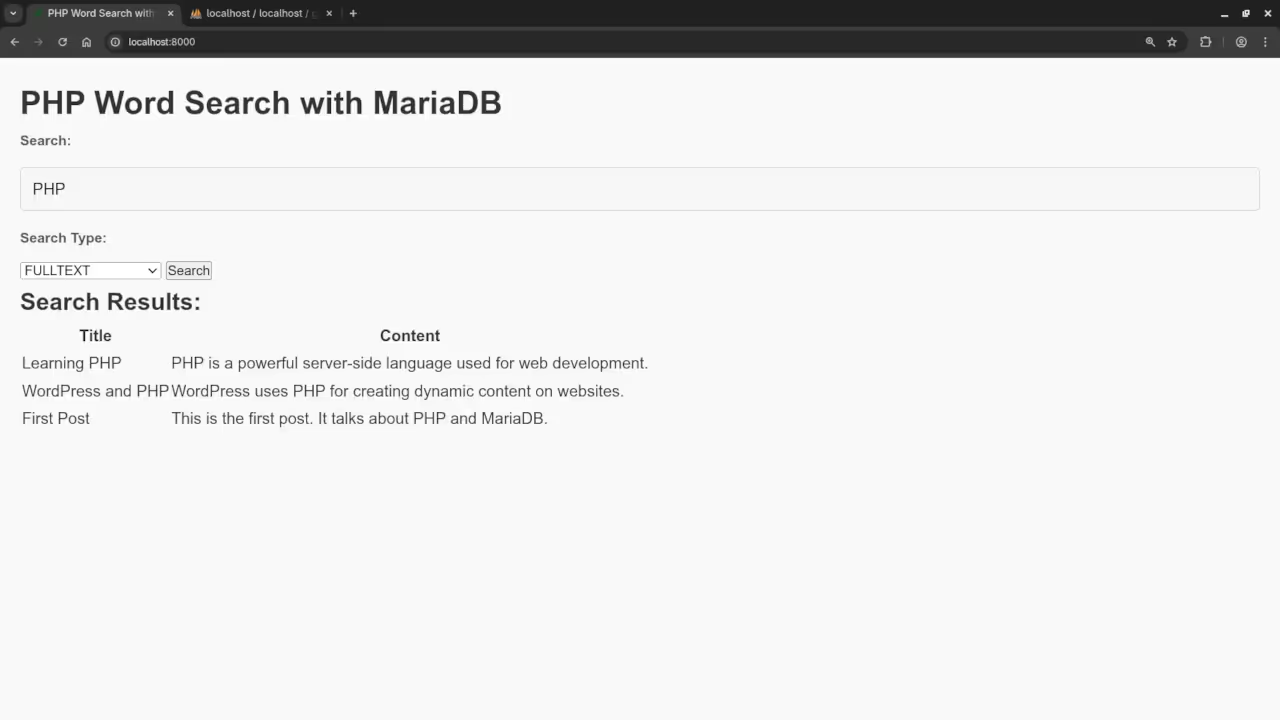
if ($searchType === 'fulltext') {
$query = "SELECT * FROM posts WHERE MATCH(title, content) AGAINST('$searchInput' IN NATURAL LANGUAGE MODE)";
} elseif ($searchType === 'like') {
$query = "SELECT * FROM posts WHERE title LIKE '%$searchInput%' OR content LIKE '%$searchInput%'";
} elseif ($searchType === 'locate') {
$query = "SELECT * FROM posts WHERE LOCATE('$searchInput', title) > 0 OR LOCATE('$searchInput', content) > 0";
}
$result = $conn->query($query);
$posts = [];
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
$posts[] = $row;
}
}
$conn->close();
echo json_encode($posts);
This PHP script connects to the MariaDB database, retrieves the search input, and runs the appropriate SQL query based on the search method selected by the user. It then returns the results as a JSON object, which is handled by the JavaScript to update the page with the results.
Best Practices for Word Search
When implementing search functionality in a web application, here are a few best practices to keep in mind:
- Indexing: Use FULLTEXT indexes to optimize searches on large text fields like titles and content.
- Prepared Statements: Always use prepared statements or sanitize inputs to prevent SQL injection.
- Efficient Querying: Choose the correct query type based on your use case. LIKE can be slow on large datasets, while FULLTEXT is optimized for larger text fields.
Screenshots And Screencast


Learn More
If you’re interested in learning more about PHP and database interaction, I recommend checking out my book Learning PHP, which covers PHP fundamentals and much more.
Additionally, if you prefer learning through video tutorials, I’ve created a course called Learning PHP, which is perfect for anyone looking to improve their PHP skills.
If you need personalized help, I offer one-on-one programming tutorials, as well as services for updating or migrating PHP applications. Feel free to reach out via my contact page.
Conclusion
That’s it! You’ve now built a simple PHP-based word search application using MariaDB and learned how to search using different query methods. This can be expanded with more advanced features such as pagination, fuzzy search, or filtering results based on different criteria.
Happy coding!
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.