Graphical User Interface For Git
Perform Git workflows that streamline your software development process and ensure smooth collaboration.
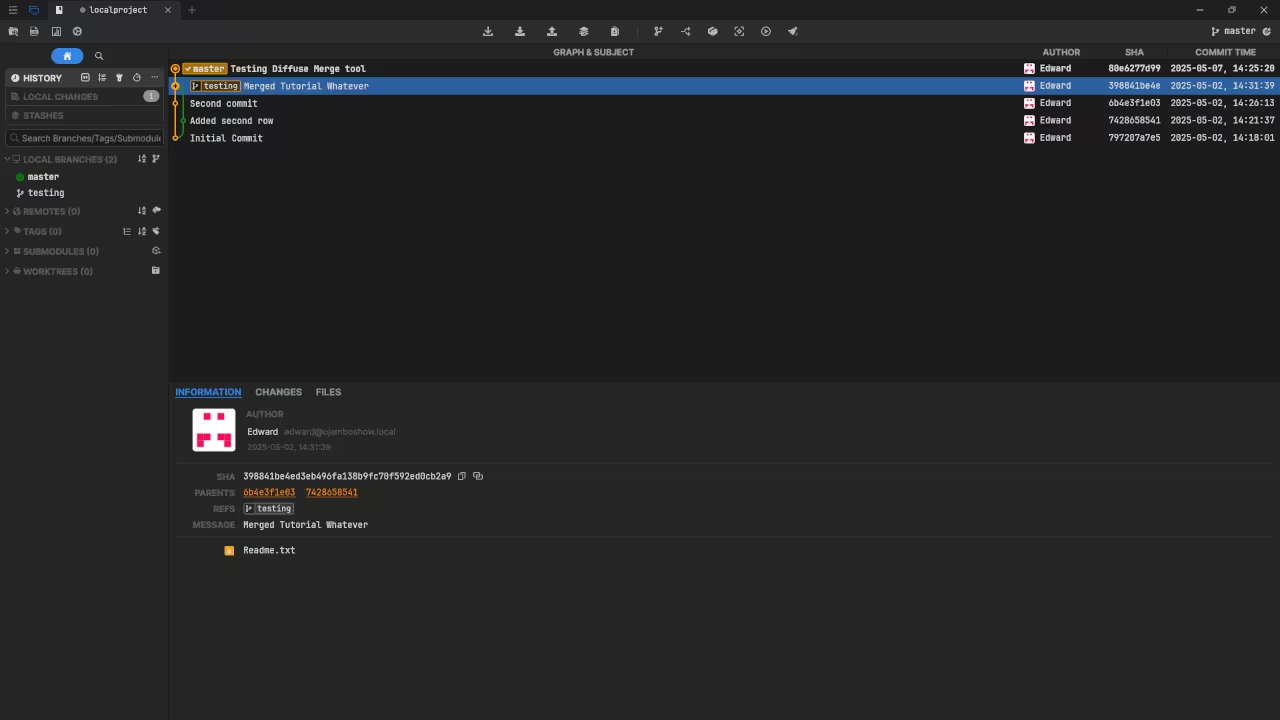
Use Git source code management (SCM) via a GUI called SourceGit. Commit, merge, add and remove remotes for staging and pushing. More Git commands, AI services, and external tools are supported.
The focus of this tutorial will be on a Git local repository with 2 branches.
- View a previously created local repository.
- Making changes, staging files, and committing with meaningful messages.
- Add a remote repository
- Pushing your changes to a remote repository.
Requirements For Using Git GUI
Glossary:
Distributed Version Control System
(DVCS) tracks versions of files.
Software Collaboration
Teams working together on projects.
Repository
Project storage space where all changes to files are tracked.
Branch
Enables developers to work on different versions of the project.
Stage
Prepare for a commit by adding files to a staging area.
Commit
Captures staged changes as a snapshot to add to repository’s history.
Clone
Clones a repository into a newly created folder.
Fetch
Fetches branches, tags (refs) from one or mote repositories.
Pull
Incorporate changes from remote repository into current branch.
Push
Updates remote refs using local refs.
References
Refs point to an object name or another ref (symbolic ref).
Merge
Integrates changes from one branch into another.
Rebase
Replay changes from one line of work onto another in the order they were introduced.
Reset
Undo commits that have not been pushed to a remote repository to rewind history without changing local files.
Revert
Undo changes made in a specific commit, by creating a new commit that reverses the changes.
Cherry-Pick
Selectively applying changes from a specific commit (or commits) in one branch to another.
Amend
Modify the most recent commit.
Reword
Change the most recent commit message via git commit --amend.
Remote
Manage set of repositories (“remotes”) whose branches you track.
Tag
Create, list, delete or verify a tag object signed with GPG.
Stash
Save uncommitted changes (both staged and unstaged), for later use, and then reverts them from your working copy.
Diff
Show changes between the working tree and the index or a tree.
Blame
Ignore changes made by the revision when assigning blame, as if the change never happened.
LFS
Git Large File Storage (LFS) replaces large files such as rich media.
Tools
| Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Text editor | For creating and editing source code | Apache Netbeans IDE |
| SSH | Secure Shell Client | OpenSSH |
| Shell Access | Access to the command line. | Terminal |
| Git | Distributed version control system. | Git |
| SourceGit | Graphical user interface for Git. | sourcegit |
| Name | Description | Example |
Create Local Repository
# Create New Project Folder If Applicable # mkdir localproject # Enter Project Folder # cd localproject # Initialize Local Repository As Working Folder # git init
Add New File To Local Repository
# Create New File # echo "Did you know that Ojambo.com has a donate button" > Readme.txt # Start Tracking A Specific File (Stage) With Git # git add Readme.txt # Add A Message And Commit Changes With Git # git commit -m "Initial Commit"
Create New Testing Branch
# Create New Branch # git branch testing # Switch To Testing Branch # git checkout testing
Create New File Testing Branch
# Create New File # echo "Did you know that Ojambo.com has live streams" > New.txt # Start Tracking A Specific File (Stage) With Git # git add New.txt # Add A Message And Commit Changes With Git # git commit -m "Testing file" # Check Status # git status
Explanation:
- The local repository is created without bare because a working folder is needed.
- The add command stages the desired files.
- The commit command will record a snapshot.
- The status command displays the state of the working folder and staging area.
The remote repository is normally hosted on a remote location and accessed through SSH or a platform-specific method. During the commit, a message that clearly explains the changes made and why they were made helps future developers understand the context.
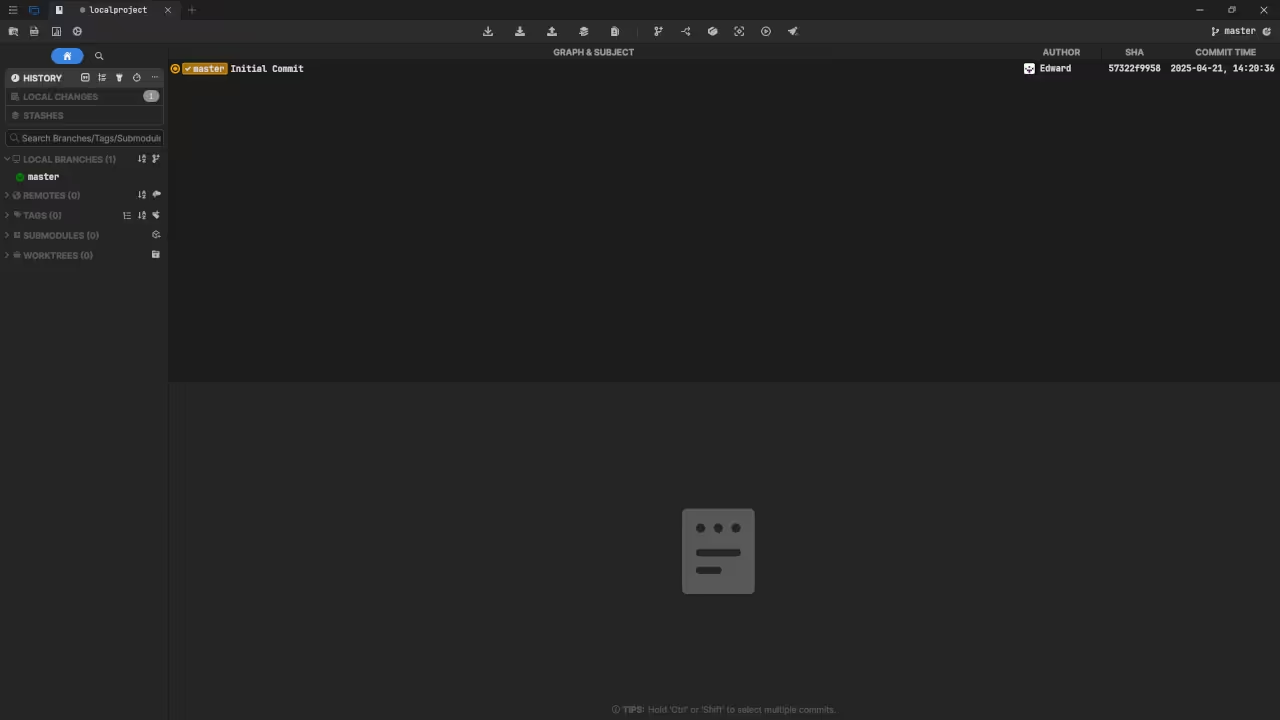
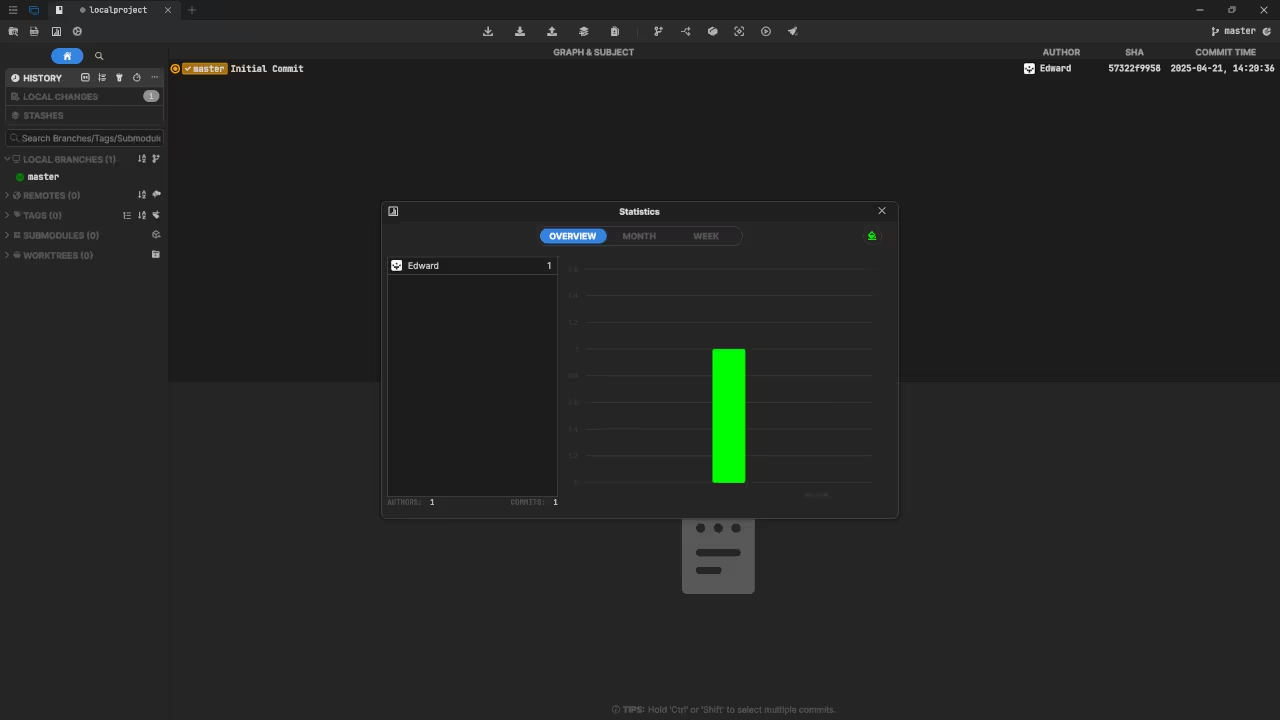
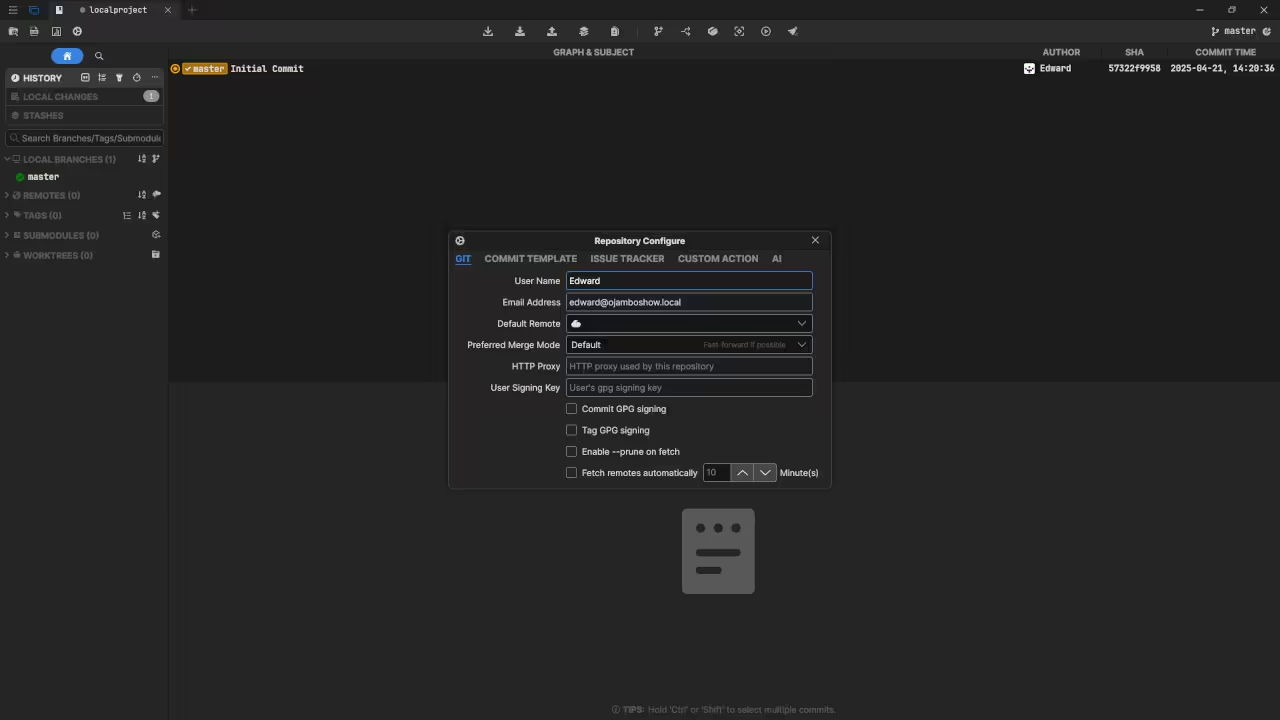
Usage
You can use any IDE or text editor and the command-line or a web browser (if applicable) to run Git commands. For this tutorial, Git was used for source code management. Git is cross-platform compatible (Unix, Linux, MacOS and Windows). Git can be downloaded from git-scm.com.
SourceGit is cross-platform compatible (Unix, Linux, MacOS and Windows). SourceGit can be downloaded from SourceGit
Open Source
Git is licensed under the GNU General Public License Version 2.0. The copyleft license comes with strict rules and requirements to ensure the software remains free and open-source. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
SourceGit is licensed under the MIT License. The permissive license requires the preservation of the copyright notice and disclaimer. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
Conclusion:
Git is a popular source code management system. Git is a distributed revision control system because every “working directory” contains the complete history and therefore revision tracking capabilities.
Git can work on remote servers or local machines to push committed changes and clone. SourceGit allows a user to manage Git via a GUI.
If you enjoy this article, consider supporting me by purchasing one of my WordPress Ojambo.com Plugins or programming OjamboShop.com Online Courses or publications at Edward Ojambo Programming Books or become a donor here Ojambo.com Donate
References:
- Customer Sets Price Plugin for WooCommerce on Ojambo.com
- Learning JavaScript Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning Python Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning PHP Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning JavaScript Paperback on Amazon
- Learning JavaScript Ebook on Amazon
- Learning Python Ebook on Amazon
- Learning PHP Ebook on Amazon
- OjamboServices.com For Custom Websites, Applications & Tutorials
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.