Upload Photos Using Camera2 API
The Android Camera2 API was introduced in Android API level 21 corresponding to Android 5.0 Lollipop. Camera2 API introduced new features to control, capture and manipulate captured images.
Camera2 API offers developers more control over the camera hardware, allowing for fine-grained adjustments such as shutter speed (ISO), autofocus, and RAW capture. Camera2 API Reference provides detailed documentation.
For this tutorial, Camera2 API will be used to place the camera in a TextureView and save a photo and then upload the photo. This is part of the ongoing Chicken Webcam App series. Most of the samples found in the documentation did not work in Android Studio, instead trail and error was required to take a photo.
This is a native Kotlin Android application, and not the HTML5 application that runs in a web browser. Kotlin is a cross-platform, statically typed, general-purpose high-level programming language with type inference.
An SSL Certificate for requests will not be needed since the URL will contain localhost and a port number. The article Generate Android Self Signed Certificate With OpenSSL explains how to package certificates for local area networks.
Requirements For Native Android Application
Glossary:
IP
Internet Protocol address is a numerical label that is assigned to a device connected to a computer network.
Wi-Fi
Wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 standards for local area networks.
WLAN
Wireless LAN is a computer network that links 2 or more devices.
TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol is a framework for computer networking.
USB
Universal Serial Bus is a standard for digital data transmission and power delivery between electronics.
SSL
Secure Sockets Layer is an encryption security protocol.
TLS
Transport Layer Security is a cryptographic protocol for secure communication over a network.
HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
SSL Certificate
Digital certificate that authenticates a website’s identity and enables an encrypted connection between the web server and the browser.
CA
Certificate Authority or Certification Authority is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates.
ADB
Android Debug Bridge.
API
Application Programming Interface is a set of rules or protocols that enables software applications to communicate with each other to exchange data, features, and functionality.
UI
User Interface is the point of interaction between humans and machines, allowing effective operation and control of the machine from the human end.
TextureView
Android component used for rendering video and graphics into the Android UI hierarchy.
File
The named storage location on a computer that stores data, information, or instructions.
Android Devices
| Name | Description | Recording | Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sony Xperia XA1 Ultra | Updated to Android 8.0 and latest web browser. | Takes photos and videos on front and back cameras. | USB Type-C 2.0 10W charging |
| Samsung Galaxy S21 FE 5G | Updated to Android 14.0 and default camera application. | Takes photos and videos on front and back cameras. | USB Type-C 2.0 <25W charging |
| Medium PHone API 36 | Android Emulator. | Takes audio, photos and videos on front camera. | N/A |
| Name | Description | Example |
Take Photo
protected fun takePicture() {
if (null == cameraDevice) {
Log.e(TAG, "cameraDevice is null")
return
}
val manager = getSystemService(CAMERA_SERVICE) as CameraManager
try {
val characteristics = manager.getCameraCharacteristics(
cameraDevice!!.id
)
var jpegSizes: Array<Size>? = null
if (characteristics != null) {
jpegSizes =
characteristics.get(CameraCharacteristics.SCALER_STREAM_CONFIGURATION_MAP)!!
.getOutputSizes(ImageFormat.JPEG)
}
var width = 640
var height = 480
if (jpegSizes != null && 0 < jpegSizes.size) {
width = jpegSizes[0].width
height = jpegSizes[0].height
}
val reader = ImageReader.newInstance(width, height, ImageFormat.JPEG, 1)
val outputSurfaces: MutableList<Surface> = ArrayList(2)
outputSurfaces.add(reader.surface)
outputSurfaces.add(Surface(textureView!!.surfaceTexture))
val captureBuilder =
cameraDevice!!.createCaptureRequest(CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_STILL_CAPTURE)
captureBuilder.addTarget(reader.surface)
captureBuilder.set(CaptureRequest.CONTROL_MODE, CameraMetadata.CONTROL_MODE_AUTO)
// Orientation
val rotation = windowManager.defaultDisplay.rotation
captureBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.JPEG_ORIENTATION,
ORIENTATIONS[rotation]
)
val cw = ContextWrapper(applicationContext)
val directory = cw.getDir("imageDir", MODE_PRIVATE)
val file = File(directory, "pic" + ".jpg")
// final File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory()+"/pic.jpg");
val readerListener: OnImageAvailableListener = object : OnImageAvailableListener {
override fun onImageAvailable(reader: ImageReader) {
var image: Image? = null
try {
image = reader.acquireLatestImage()
val buffer = image.planes[0].buffer
val bytes = ByteArray(buffer.capacity())
buffer[bytes]
save(bytes)
//upload(bytes);
} catch (e: FileNotFoundException) {
e.printStackTrace()
} catch (e: IOException) {
e.printStackTrace()
} finally {
image?.close()
}
}
@Throws(IOException::class)
fun upload(bytes: ByteArray?) {
val url = URL("https://192.168.1.230:8443/save-jpeg.php")
val conn = url.openConnection() as HttpURLConnection
conn.doOutput = true
conn.requestMethod = "POST"
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream")
val outputStream = conn.outputStream
outputStream.write(bytes)
outputStream.close()
val responseCode = conn.responseCode
println("Response Code : $responseCode")
}
@Throws(IOException::class)
fun save(bytes: ByteArray?) {
var output: OutputStream? = null
try {
output = FileOutputStream(file)
output.write(bytes)
upload(bytes)
} finally {
output?.close()
}
}
}
reader.setOnImageAvailableListener(readerListener, mBackgroundHandler)
val captureListener: CaptureCallback = object : CaptureCallback() {
override fun onCaptureCompleted(
session: CameraCaptureSession,
request: CaptureRequest,
result: TotalCaptureResult
) {
super.onCaptureCompleted(session, request, result)
Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Saved:$file", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
createCameraPreview()
}
}
cameraDevice!!.createCaptureSession(
outputSurfaces,
object : CameraCaptureSession.StateCallback() {
override fun onConfigured(session: CameraCaptureSession) {
try {
session.capture(
captureBuilder.build(),
captureListener,
mBackgroundHandler
)
} catch (e: CameraAccessException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
}
override fun onConfigureFailed(session: CameraCaptureSession) {
}
},
mBackgroundHandler
)
} catch (e: CameraAccessException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
}
Download
The Android SDK tools can be downloaded from SDK Platform Tools and installed on your workstation.
The OpenSSL tools can be downloaded from OpenSSL Library and installed on your workstation.
Explanation
- Use the ADB tool to connect to your Android device if applicable.
- Generate a Certificate Authority.
- Generate a Certificate and sign it using the Certificate Authority.
- Convert the Certificate to PEM format if you are targeting older Android versions.
- Add the Certificate to the res/raw folder in the Android Project.
- Generate an Android Network Security Configuration XML file as app -> res/xml/network_security_config.xml.
- Generate an Android Layout XML file as app -> res/xml/activity_main.xml.
- Generate an Android Manifest Permissions of for Camera as app -> manifests/AndroidManifest.xml.
- Generate Android code snippet to show camera preview, take photo and upload button.
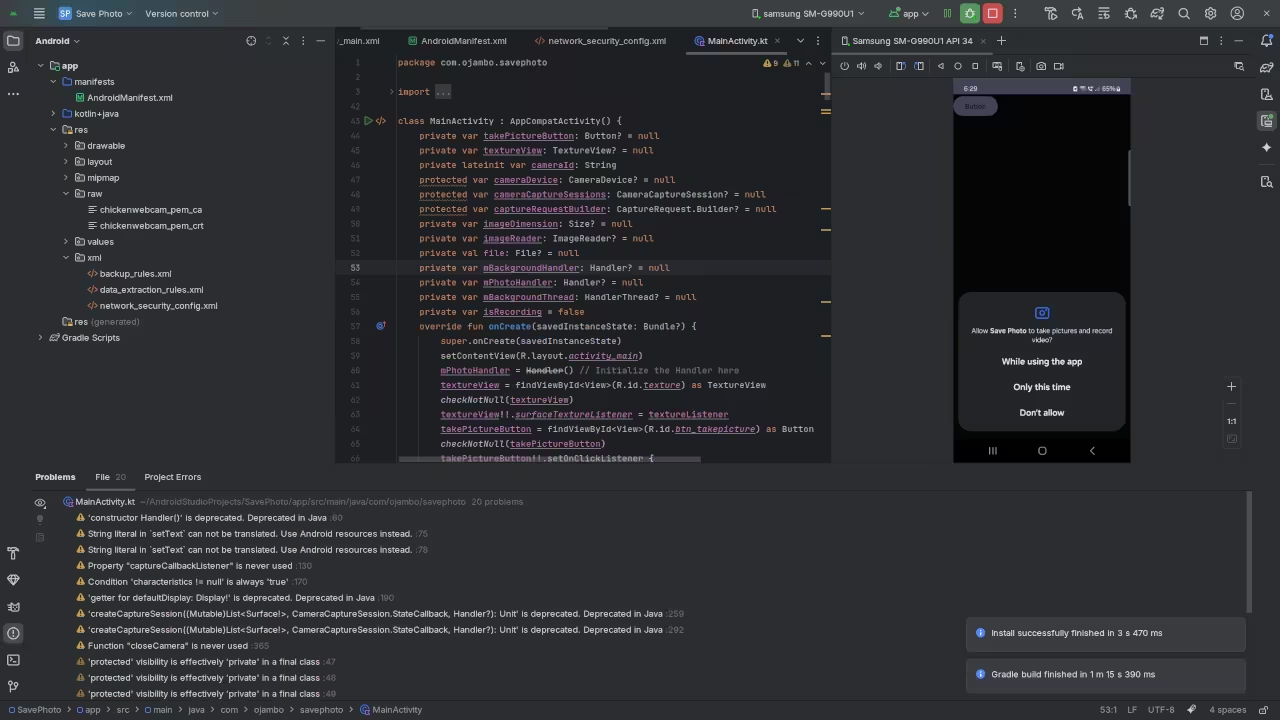

Usage
You can use any IDE or text editor to compile and execute Android code. For this tutorial, Android Studio IDE was used, but it was not needed for coding the camera preview.
Open Source
OpenSSL is licensed under the Apache License 2.0. The permissive license has conditions requiring preservation of copyright and license notices. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
Stunnel is licensed under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2 or later with OpenSSL exception. The copyleft license comes with strict rules and requirements to ensure the software remains free and open-source. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
The PHP License is an open-source under which the PHP scripting language is released. The permissive license has conditions requiring preservation of copyright and license notices. Redistribution is permitted in source or binary form with or without modifications, consult the license for more specific details.
Kotlin is licensed under the Apache License version 2.0. The permissive license requires the preservation of the copyright notice and disclaimer. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
OpenJDK is licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2. The copyleft license comes with strict rules and requirements to ensure the software remains free and open-source. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
Android is licensed under the Apache License version 2.0 for the userspace software and GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2 for the Linux kernel. The permissive license requires the preservation of the copyright notice and disclaimer, while the copyleft license comes with strict rules and requirements to ensure the software remains free and open-source. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
Conclusion:
An SSL Certificate is required when an Android application attempts to upload to a server. For a LAN application, a self-signed Certificate can be packaged and used in the Android application. OpenSSL can generate a Certificate Authority and the SSL Certificate signed by the CA.
The Android Camera2 API can be used by Kotlin to preview the camera, take photos and upload them to a server. The Camera 2 API is supported in Android versions starting from 5.0. A photo can be taken and saved on the Android device.
You can use an emulator to test the application but a real device is recommended via USB or WiFi connection for debugging.
If you enjoy this article, consider supporting me by purchasing one of my OjamboShop.com Online Programming Courses or publications at Edward Ojambo Programming Books or simply donate here Ojambo.com Donate
References:
- Customer Sets Price Plugin for WooCommerce on Ojambo.com
- Learning JavaScript Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning Python Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning PHP Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning JavaScript Paperback on Amazon
- Learning JavaScript Ebook on Amazon
- Learning Python Ebook on Amazon
- Learning PHP Ebook on Amazon
- OjamboServices.com For Custom Websites, Applications & Tutorials
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.
