Reinstalling ComfyUI on Linux with ROCm 6.4 and Unsupported AMD Instinct MI60 32GB HBM2
If you’re looking to get ComfyUI running on a Linux system with the AMD Instinct MI60 GPU, specifically under ROCm 6.4, you’ve come to the right place. In this guide, I’ll walk you through the process of reinstalling ComfyUI while dealing with the limitations of using an unsupported GPU, as well as how to make the most out of your hardware even when it’s not officially supported.
Let’s get started!
System Requirements
Before diving into the steps, let’s make sure your system is ready for this setup. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Linux Distribution: Fedora 42 or 43 (Fedora 43 ships with ROCm 6.4, but it doesn’t support the AMD Instinct MI60 GPU).
- ROCm Version: ROCm 6.3 (supports the MI60) or ROCm 6.4 (not officially supported for the MI60).
- Hardware:
- AMD Instinct MI60 32GB HBM2 (unsupported with ROCm 6.4).
- Compatible CPU (recommended: AMD Ryzen, Intel Core i5/i7).
- At least 16GB of system RAM.
- SSD with at least 50GB of free space for installation and model storage.
Important: Fedora 42 comes with ROCm 6.3, which was the last supported version for the MI60 GPU. If you’re using Fedora 43, ROCm 6.4 is installed by default, but this version does not support the AMD Instinct MI60.
Installation Steps
Step 1: Install ROCm 6.4 (If You’re on Fedora 43)
If you’re using Fedora 43 or another system with ROCm 6.4, you’ll need to manually adjust the environment to ensure compatibility with the MI60 GPU.
- Install Dependencies:
Open your terminal and run the following commands to install necessary dependencies:sudo dnf install kernel-core kernel-devel rocm-dkms sudo dnf install rocm-dev rocm-utils sudo dnf install miopen-hip - Install ComfyUI:
Now let’s get ComfyUI set up. Start by cloning the repository and setting up a Python virtual environment. Here are the steps:# Install dependencies sudo dnf install python3-pip python3-virtualenv # Clone the ComfyUI repository git clone https://github.com/comfyui/comfyui.git cd comfyui # Create a virtual environment python3 -m venv comfyui_env source comfyui_env/bin/activate # Install the required Python packages pip install -r requirements.txt
Step 2: Modify .bashrc for Compatibility
Since ROCm 6.4 doesn’t support the AMD Instinct MI60 GPU out-of-the-box, you’ll need to adjust some environment variables to force it to work.
Open your .bashrc file with a text editor:
nano ~/.bashrcAdd the following lines at the end of the file:
export HSA_OVERRIDE_GFX_VERSION=9.0.6
export HIP_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
export MIOPEN_DEBUG_CONV_WINOGRAD=0
export MIOPEN_FIND_ENFORCE=4
export MIOPEN_USER_DB_PATH=/mnt/AI/models/miopenAfter saving the file, refresh your shell:
source ~/.bashrcStep 3: Verify GPU Compatibility
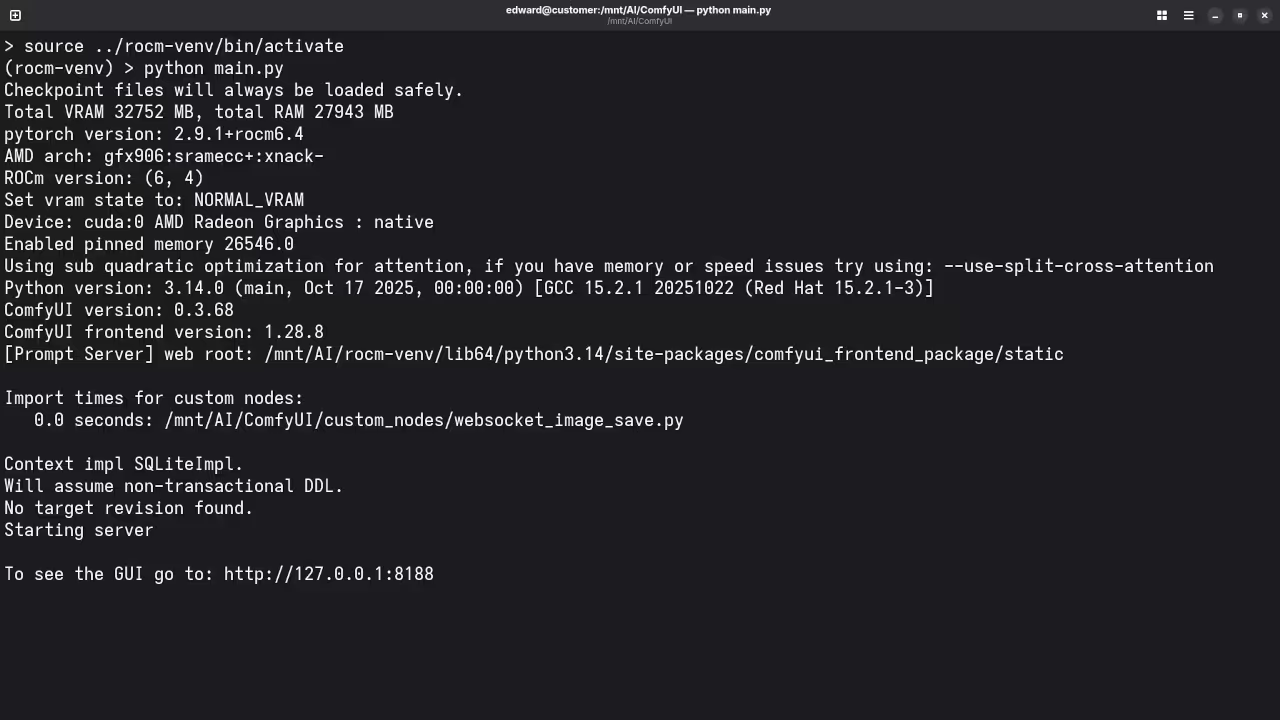
Once the setup is done, it’s important to verify whether your GPU is detected and functional. To check, run:
rocminfoThis will display details about your hardware, including whether your AMD Instinct MI60 is recognized. If you encounter any issues, double-check your .bashrc settings or try reinstalling any missing dependencies.
Step 4: Launch ComfyUI
Now that everything is set up, you can start ComfyUI! From the ComfyUI directory, simply run:
python comfyui.pyThis should launch the user interface in your web browser, and you can begin using ComfyUI for your AI/ML projects.
Why Are the Environment Variables Needed?
When using the AMD Instinct MI60 GPU with ROCm 6.4, which doesn’t officially support the MI60, certain environment variables must be set to enable compatibility. Below is an explanation of each of the necessary variables and why they are needed:
1. export HSA_OVERRIDE_GFX_VERSION=9.0.6
This variable is crucial because ROCm 6.4 doesn’t officially support the MI60 GPU. The HSA (Heterogeneous System Architecture) defines which GPU architectures ROCm is compatible with. By overriding this version with 9.0.6, you’re forcing ROCm to treat your MI60 GPU like a supported GPU, such as those based on the Vega architecture. Without this, ROCm may not recognize your GPU or fail to load certain libraries needed for computation.
2. export HIP_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
The HIP (Heterogeneous-compute Interface for Portability) runtime controls which GPUs are used for computations. Setting this variable ensures that the system uses the MI60 as the device for workloads. If you have multiple GPUs in your system, you can modify this variable to select a different GPU (e.g., HIP_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 for the second GPU). Without this, the system may fail to recognize or utilize your GPU for computations.
3. export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
This variable is similar to HIP_VISIBLE_DEVICES but for CUDA programs, which typically expect to use NVIDIA GPUs. However, in some cases, programs or libraries may still reference CUDA, so by setting this variable, you’re ensuring that your MI60 GPU is used even when CUDA is involved. Without it, the system might try to use an unsupported NVIDIA GPU or default to the CPU.
4. export MIOPEN_DEBUG_CONV_WINOGRAD=0
This environment variable disables debugging for the Winograd algorithm, which is used in deep learning convolution operations. By setting this variable to 0, you’re preventing any debug output or errors related to this optimization. This can improve stability during training or inference, especially when using the MI60 with a version of ROCm that doesn’t fully support it.
5. export MIOPEN_FIND_ENFORCE=4
This variable controls how MIOpen, the AMD deep learning library, searches for the best convolution algorithms. Setting it to 4 forces MIOpen to always search for and apply the best algorithms, even when ROCm versions change or the system doesn’t officially support the hardware. This ensures that you get the best performance and stability, even on unsupported hardware like the MI60.
6. export MIOPEN_USER_DB_PATH=/mnt/AI/models/miopen
MIOpen uses a performance database to store optimizations for various neural network operations. By setting this variable, you tell MIOpen to store and load its optimizations from a custom location. This is useful if you want to separate MIOpen data from the rest of your system or store it on a faster disk, such as an SSD dedicated to AI/ML workloads.
Is ComfyUI Open Source?
Yes, ComfyUI is an open-source project. It is licensed under the MIT License, meaning you are free to use, modify, and distribute the software as you see fit. You can explore the full source code on the ComfyUI GitHub repository.
Where to Place Your Models
| Model Type | Folder |
|---|---|
| Checkpoints (e.g. *.safetensors) | ComfyUI/models/checkpoints/ |
| LoRA models | ComfyUI/models/loras/ |
| VAEs | ComfyUI/models/vae/ |
| ControlNet | ComfyUI/models/controlnet/ |
Just drop your files into the appropriate folder and rerun stable-diffusion.cpp.
Test Tools
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CPU | AMD Ryzen 5 5600GT (6C/12T, 3.6GHz). |
| Memory | 32GB DDR4. |
| GPU | AMD Instinct MI60 (32GB HBM2). |
| Operating System | Fedora Linux Workstation 43. |
| Desktop Environment | Gnome 49. |
| Name | Description |
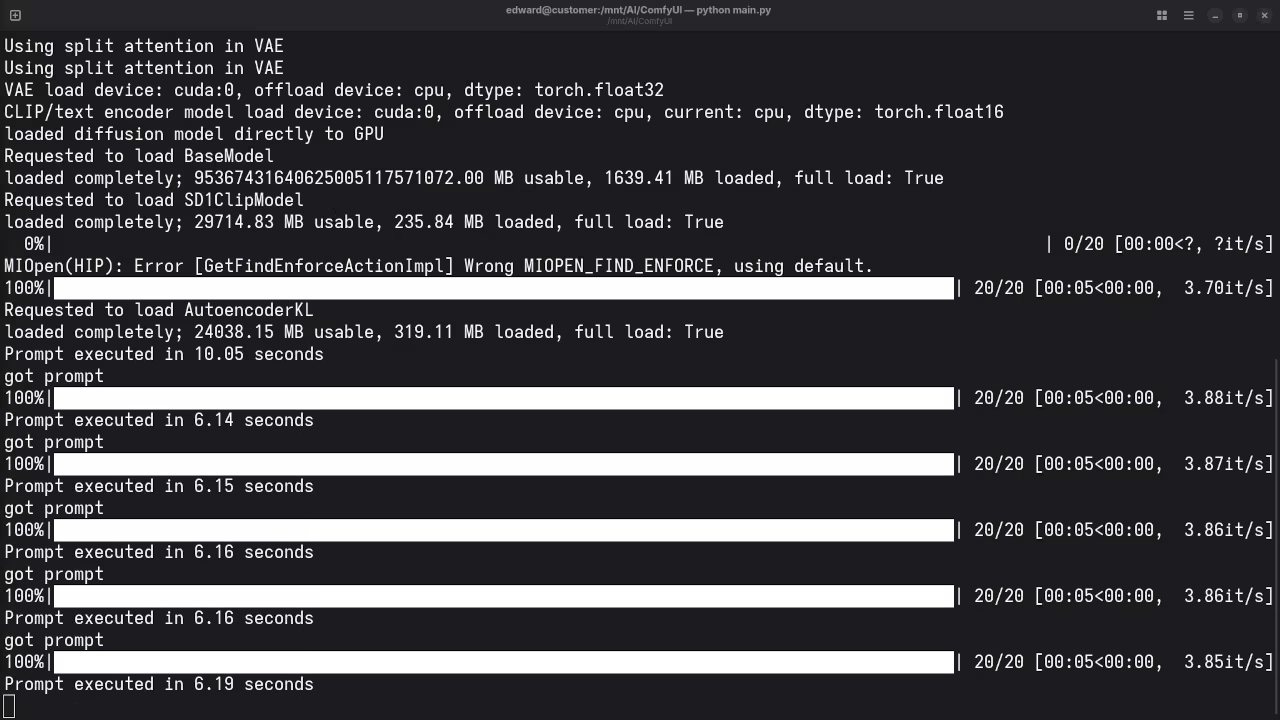
Screenshots and Screencast
Here’s where you’ll find a visual walkthrough of setting up v1-5-pruned-emaonly-fp16.safetensors using ComfyUI on your local system:
Results:
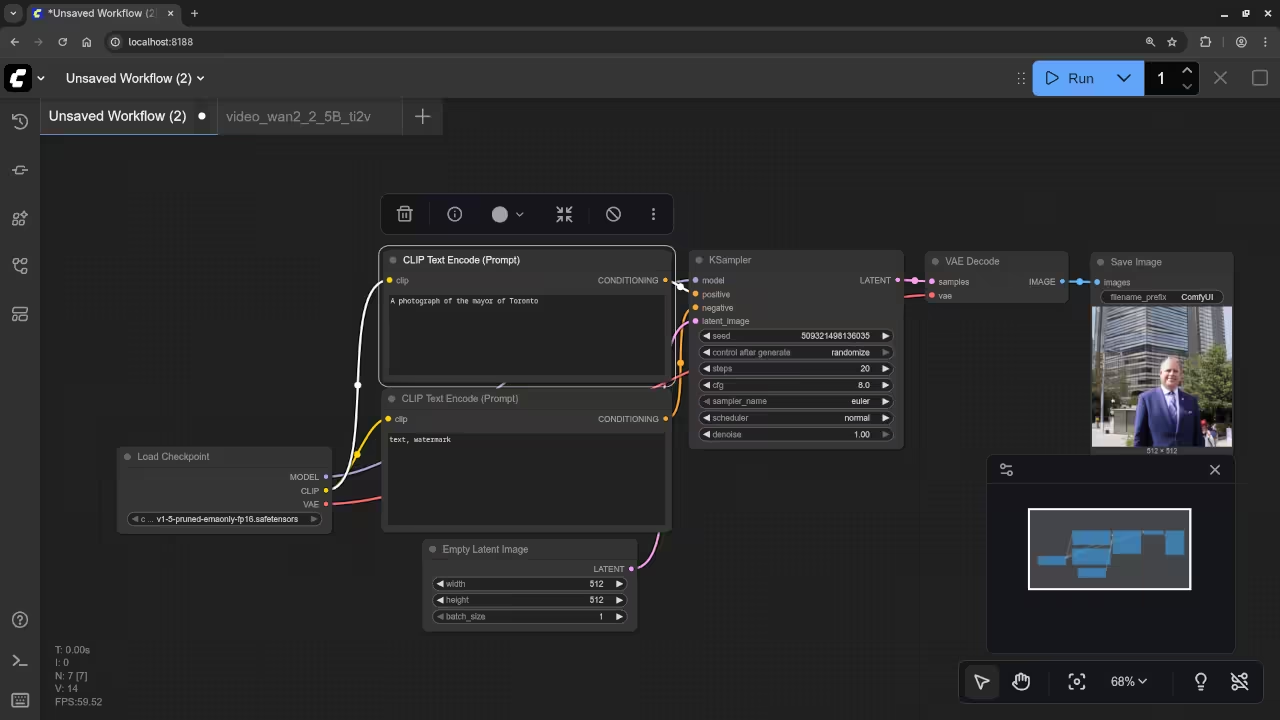
A photograph of the mayor of Toronto
Accurately drew a photograph mishmash of past mayors of Toronto.
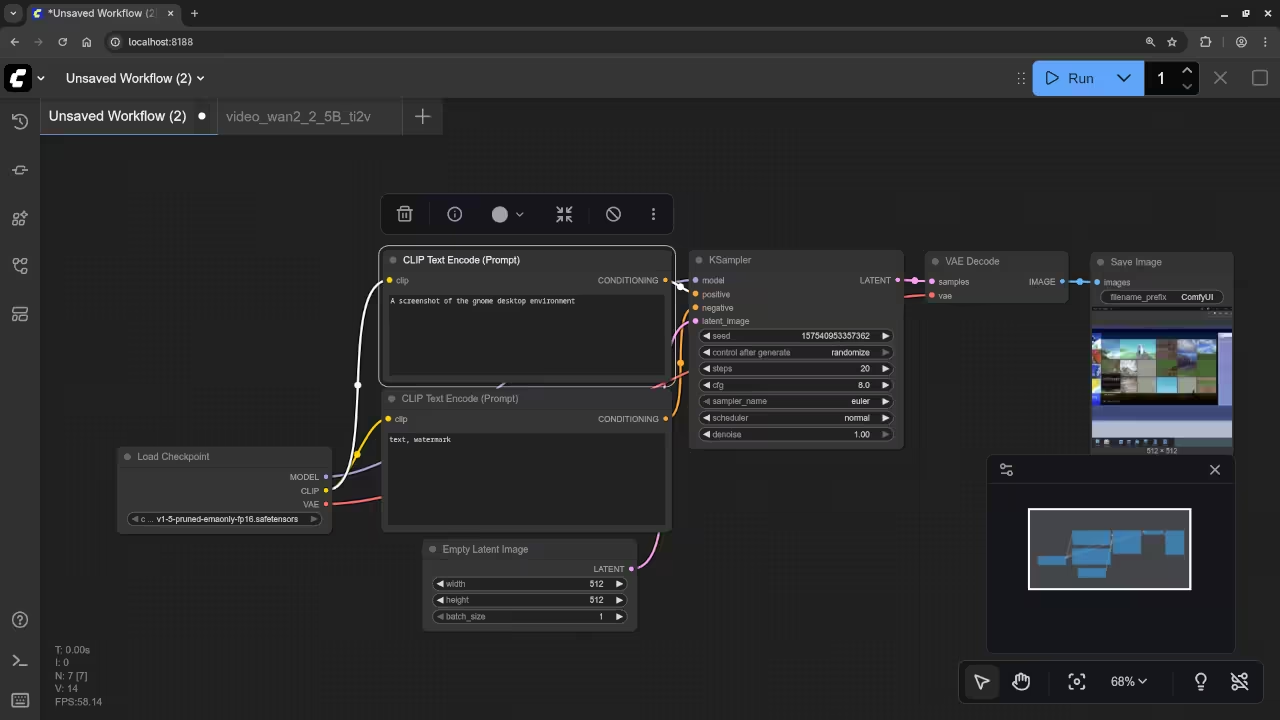
A screenshot of the gnome desktop environment.
Accurately drew a screenshot of an older version of the Gnome desktop environment.
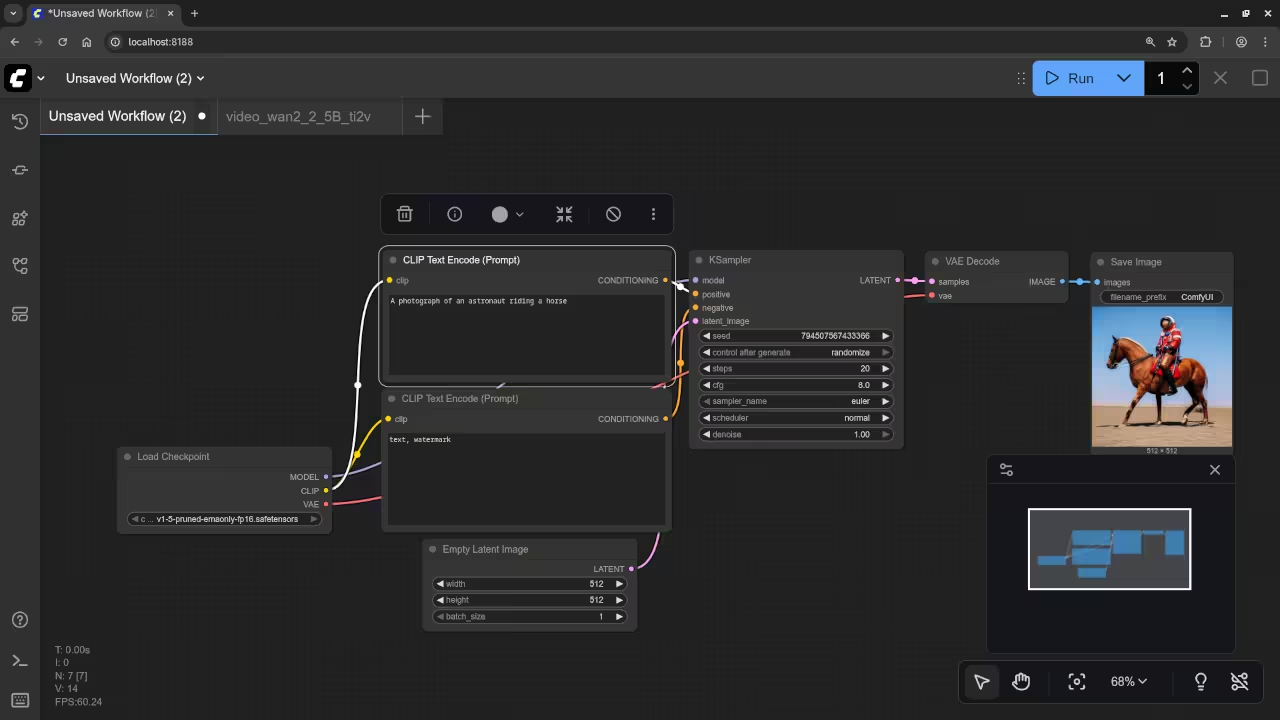
A photograph of an astronaut riding a horse.
Accurately drew a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse.
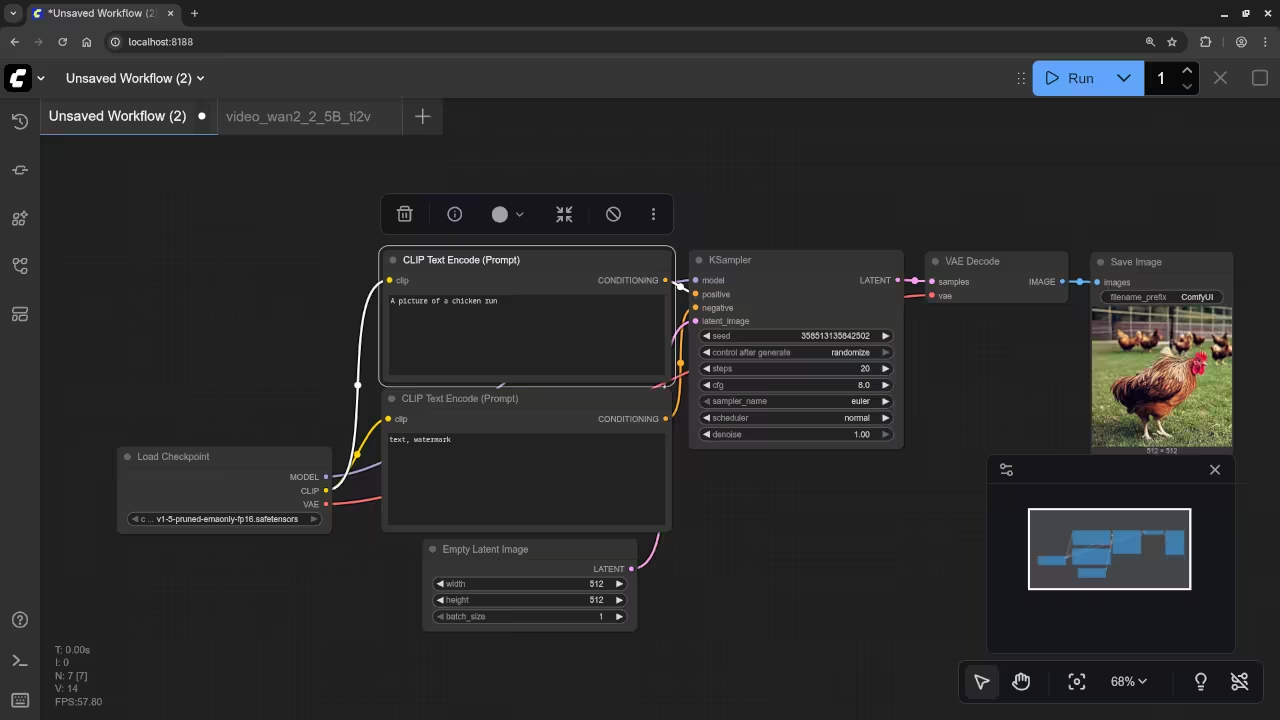
A picture of a chicken run.
Accurately drew a picture of a chicken run.
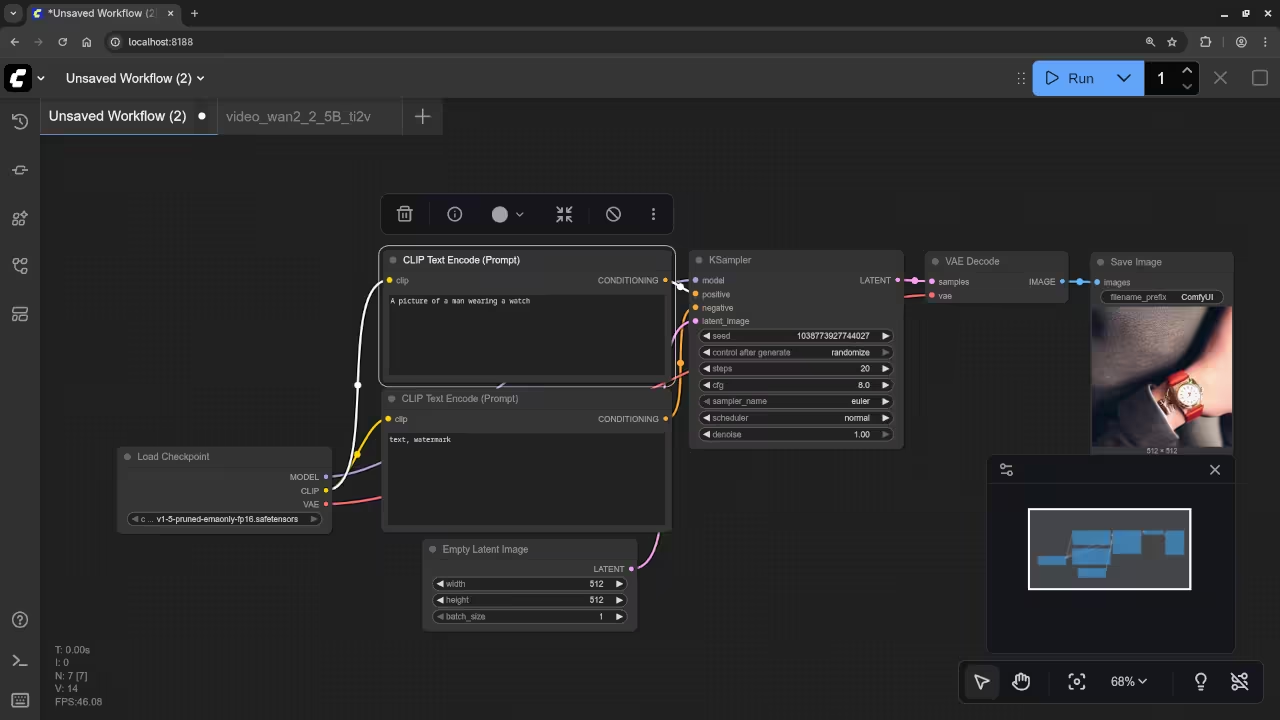
A picture of a man wearing a watch.
Accurately drew a picture of a man wearing a watch.
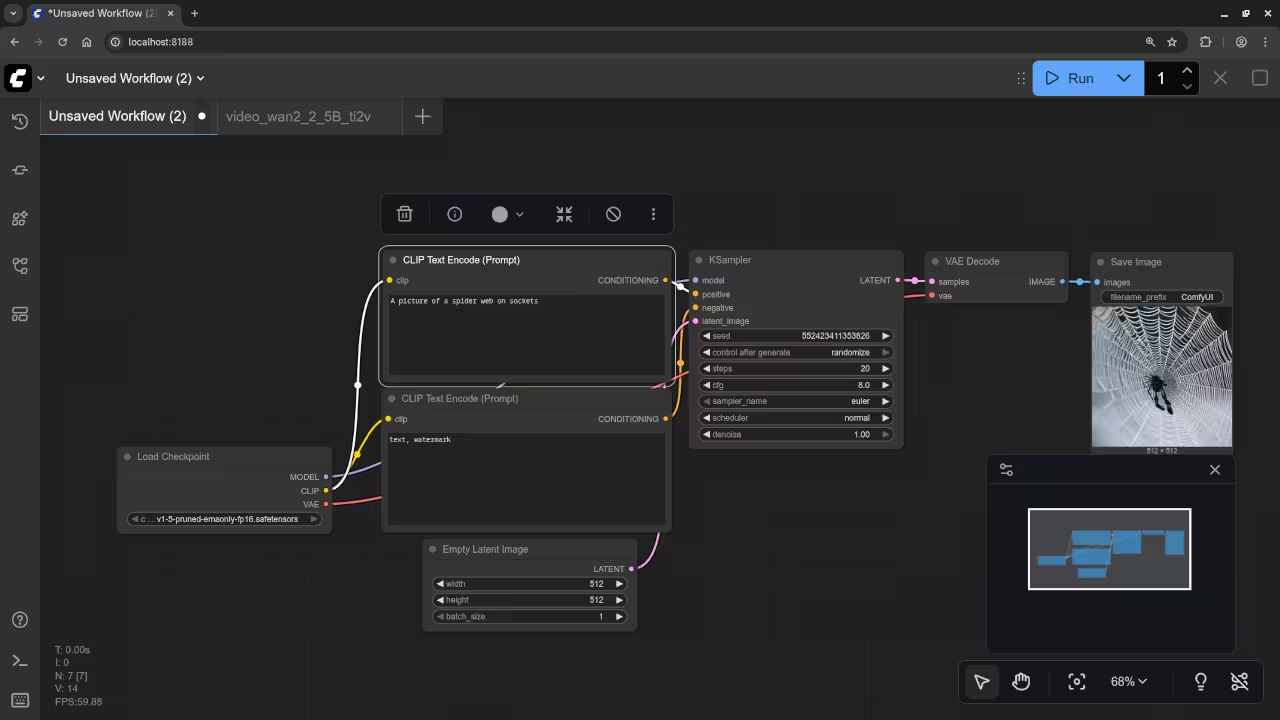
A picture of a spider web on sockets.
Accurately drew a picture of a spider web on sockets.
Additional Resources
If you’re looking to expand your programming skills, I also offer a couple of great resources:
- Book: Learning Python – A beginner-friendly guide to learning Python.
- Course: Learning Python – A detailed course that covers Python basics and intermediate topics.
- One-on-One Python Tutorials: If you need personalized help with Python programming, feel free to reach out for one-on-one online tutorials at ojambo.com/contact.
- If you need assistance with ROCm or want to migrate your setup, you can contact me at ojamboservices.com/contact.
I hope this guide helps you get your ComfyUI up and running on Linux with the AMD Instinct MI60. Let me know if you have any questions or run into any issues!
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.