Beginner’s Guide to Laravel Framework with a Simple MariaDB Example
Laravel is a modern, open-source PHP web application framework that is known for its elegant syntax and ease of use. If you are coming from a procedural PHP background, Laravel is an excellent way to write cleaner, more maintainable code using Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) concepts.
One of Laravel’s core strengths is that it supports the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern, which separates your application into three main components:
- Model: Handles data and business logic
- View: Handles the presentation layer (HTML/CSS)
- Controller: Handles user input and updates the model/view accordingly
Laravel is actively maintained, has strong community support, and can be installed easily using Composer.
Laravel Example Application (CRUD with MariaDB)
In this beginner example, we will create a Laravel application that connects to an existing MariaDB table called people with the following columns:
idusernamenameageverified
The application will perform full CRUD operations:
- Create (Insert)
- Read (Display)
- Update
- Delete
Step 1: Install Laravel Using Composer
composer create-project laravel/laravel laravel-mariadb-appStep 2: Configure the Database
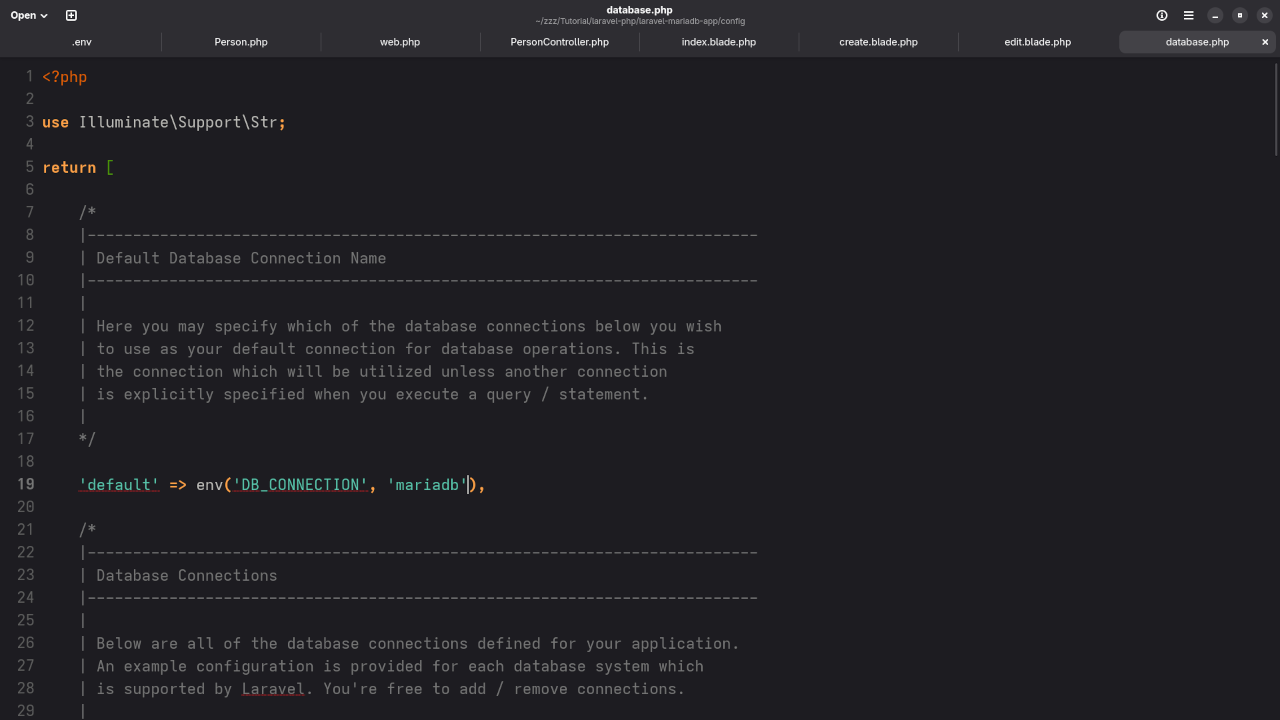
Update your .env file:
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=your_database
DB_USERNAME=your_username
DB_PASSWORD=your_passwordNote: Laravel supports MariaDB since it is a drop-in replacement for MySQL.
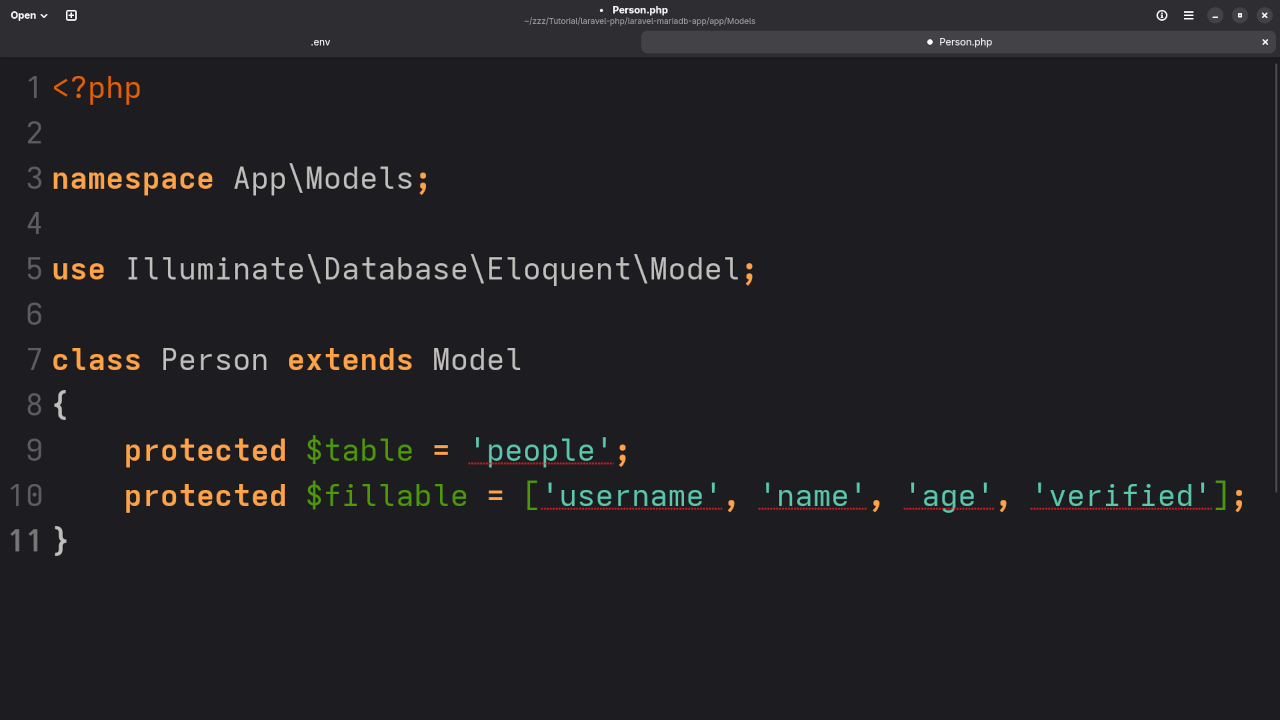
Step 3: Create the Model and Controller
php artisan make:model Person -mcrUpdate the model app/Models/Person.php:
protected $table = 'people';
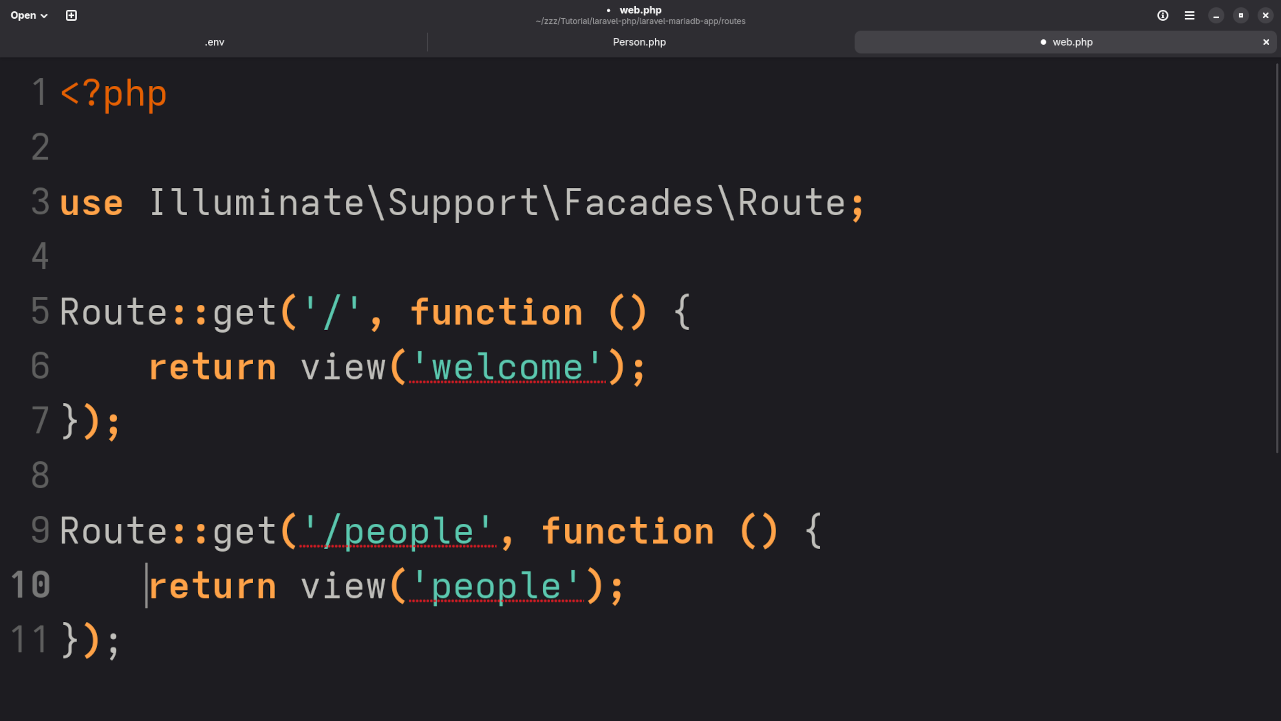
protected $fillable = ['username', 'name', 'age', 'verified'];Step 4: Set Up Routes in routes/web.php
>use App\Http\Controllers\PersonController;
Route::resource('people', PersonController::class);
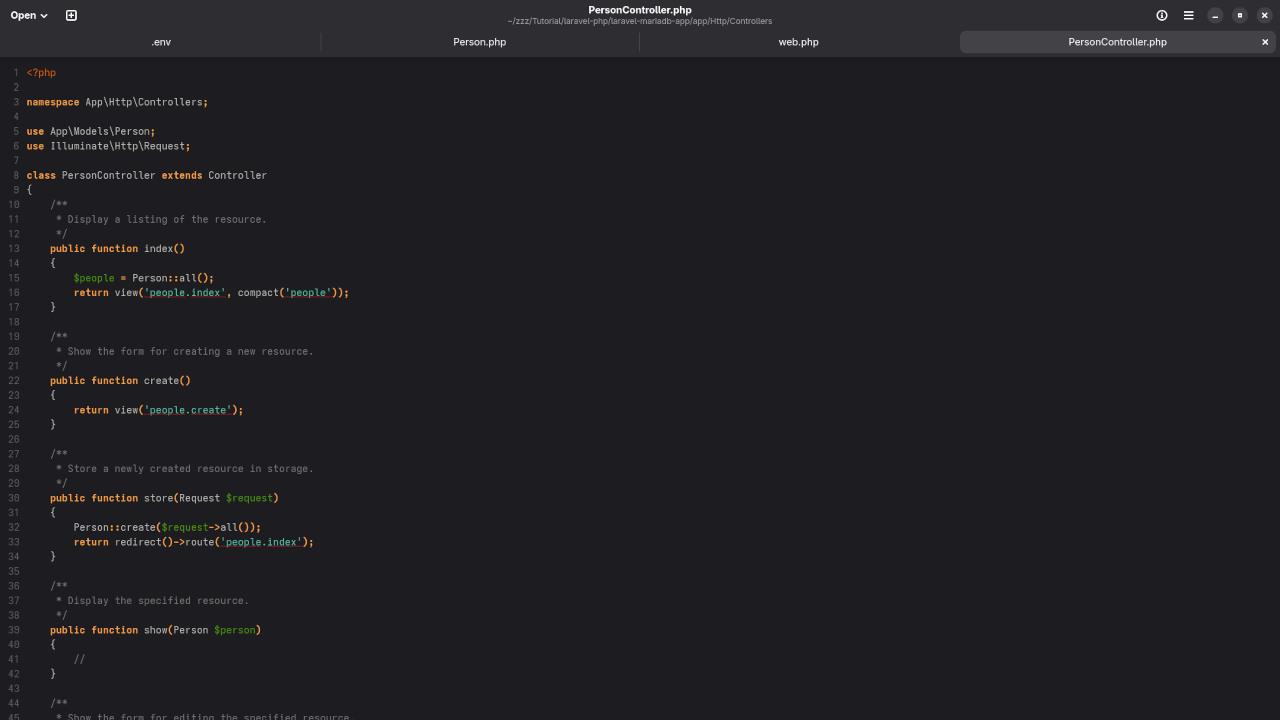
Step 5: Implement Controller Logic (PersonController.php)
use App\Models\Person;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class PersonController extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
$people = Person::all();
return view('people.index', compact('people'));
}
public function create()
{
return view('people.create');
}
public function store(Request $request)
{
Person::create($request->all());
return redirect()->route('people.index');
}
public function edit(Person $person)
{
return view('people.edit', compact('person'));
}
public function update(Request $request, Person $person)
{
$person->update($request->all());
return redirect()->route('people.index');
}
public function destroy(Person $person)
{
$person->delete();
return redirect()->route('people.index');
}
}
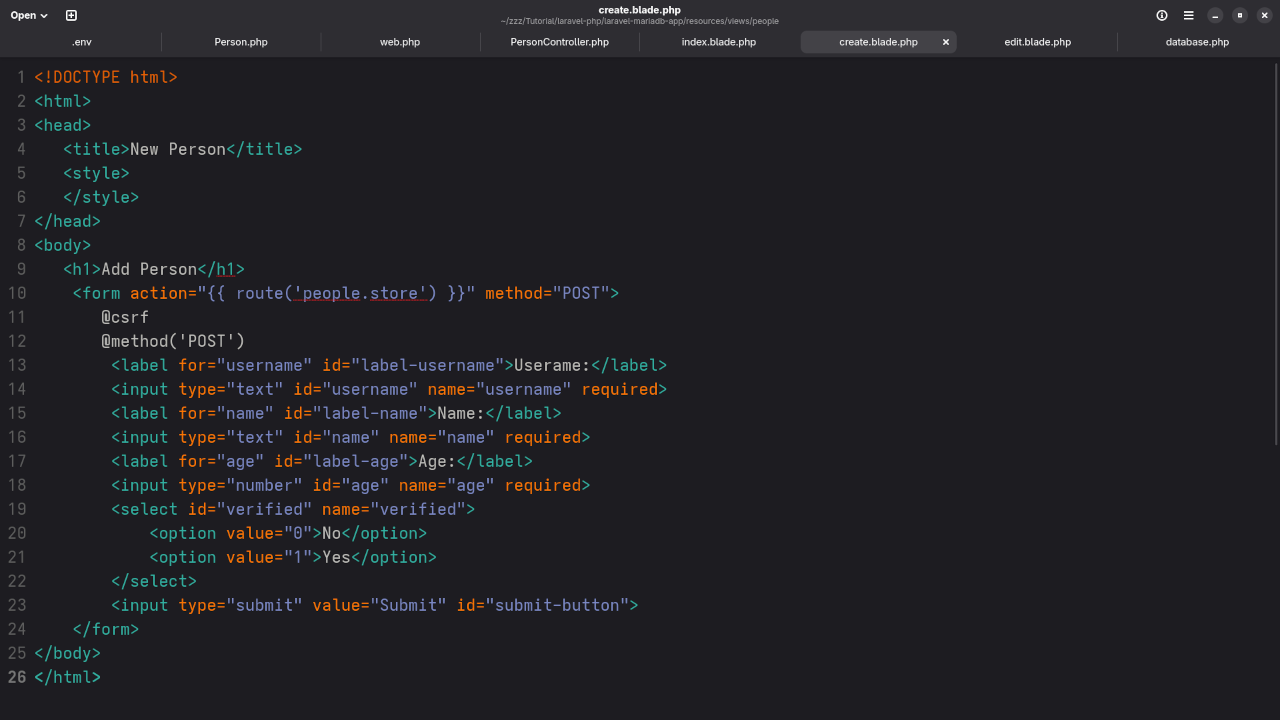
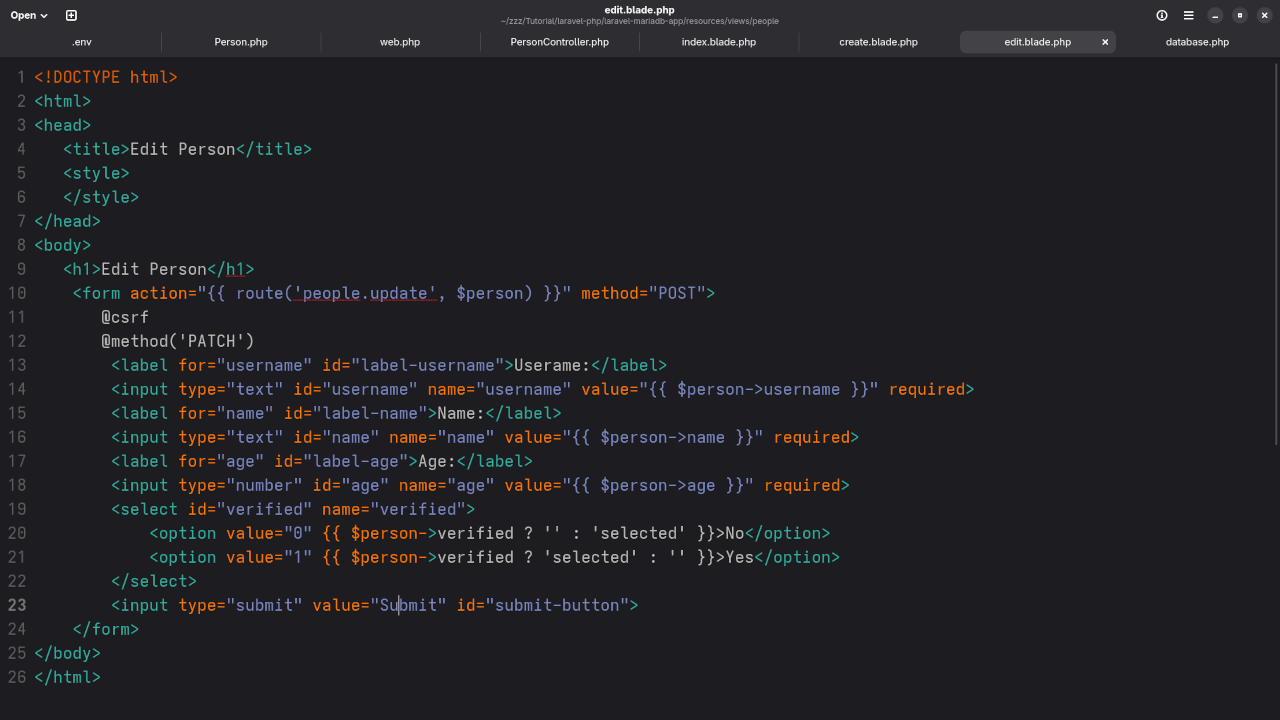
Step 6: Create Views (Blade Templates)
Inside resources/views/people folder, create the following files:
index.blade.phpto list all entriescreate.blade.phpfor adding entriesedit.blade.phpfor updating entries
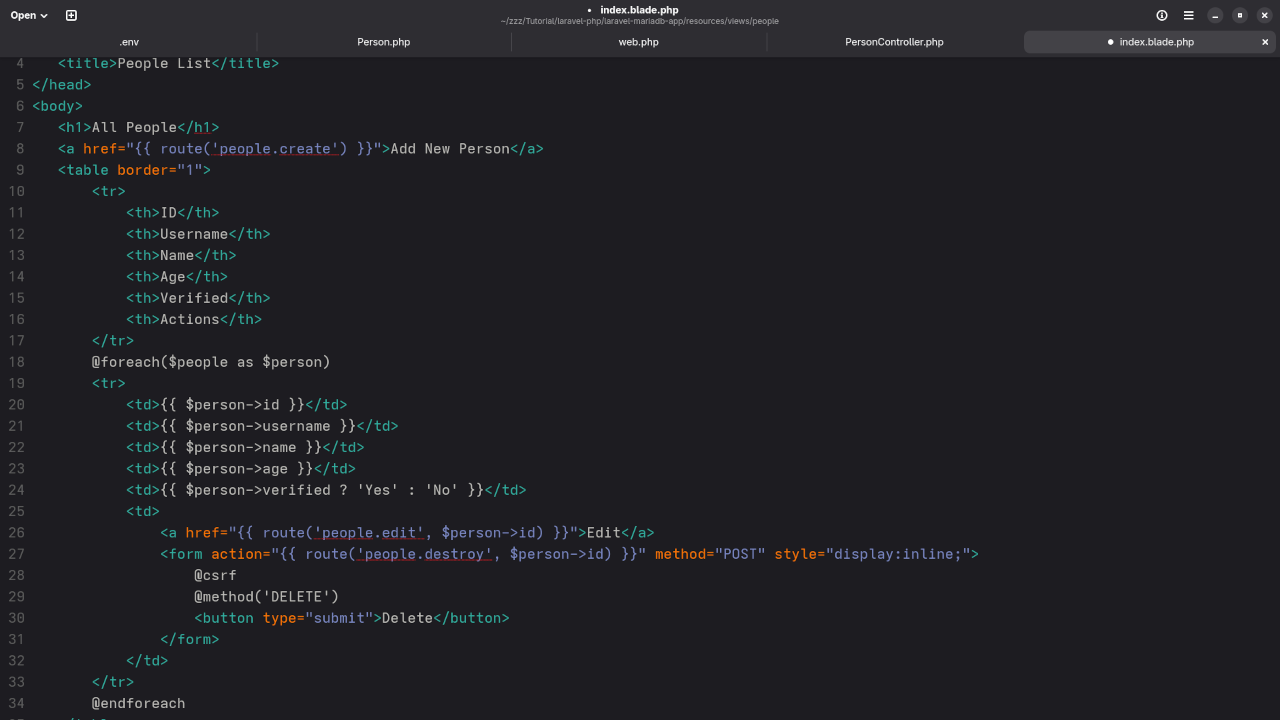
Example for index.blade.php:
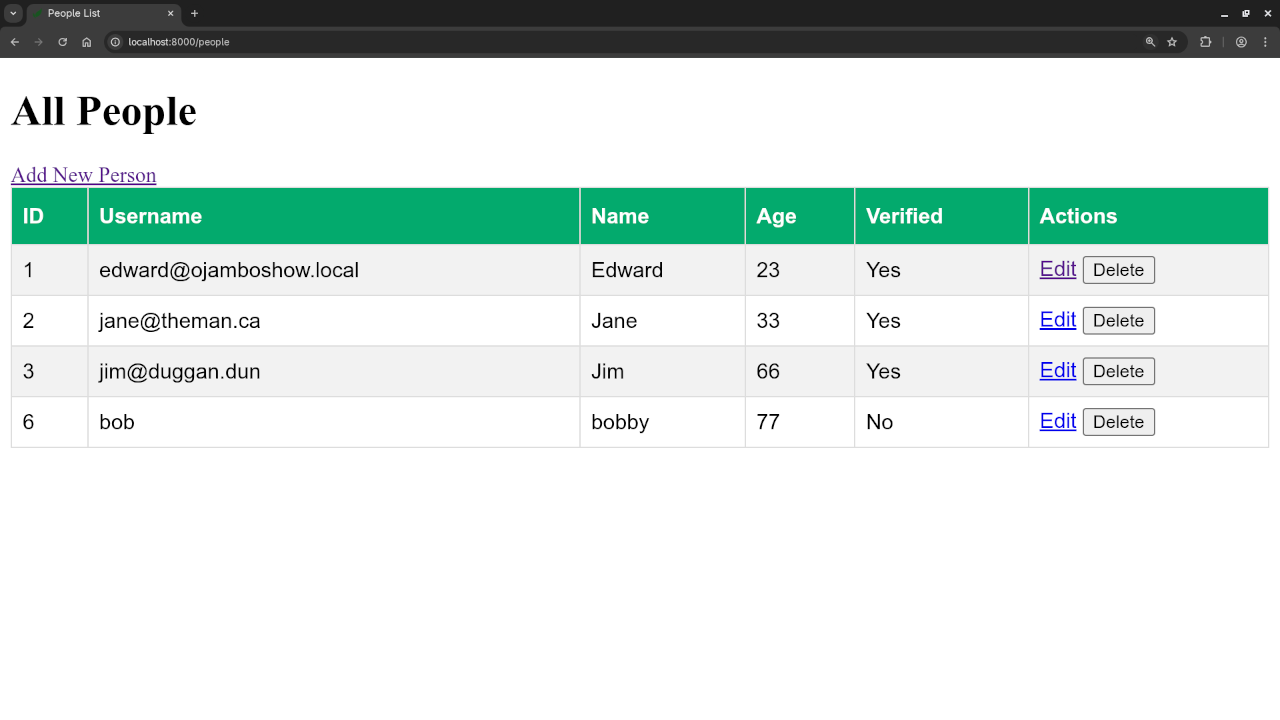
<h1>All People</h1>
<a href="{{ route('people.create') }}">Add New Person</a>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Username</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>Verified</th>
<th>Actions</th>
</tr>
@foreach($people as $person)
<tr>
<td>{{ $person->id }}</td>
<td>{{ $person->username }}</td>
<td>{{ $person->name }}</td>
<td>{{ $person->age }}</td>
<td>{{ $person->verified ? 'Yes' : 'No' }}</td>
<td>
<a href="{{ route('people.edit', $person->id) }}">Edit</a>
<form action="{{ route('people.destroy', $person->id) }}" method="POST" style="display:inline;">
@csrf
@method('DELETE')
<button type="submit">Delete</button>
</form>
</td>
</tr>
@endforeach
</table>
Screenshots And Screencast
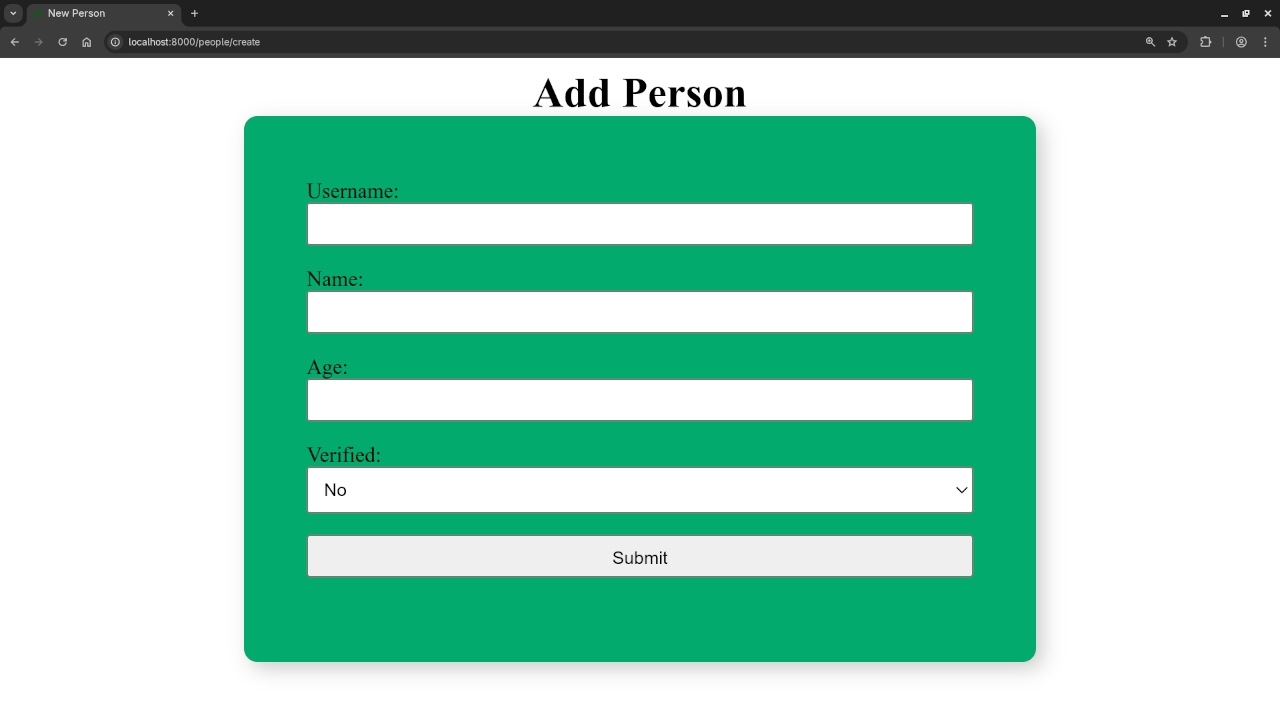
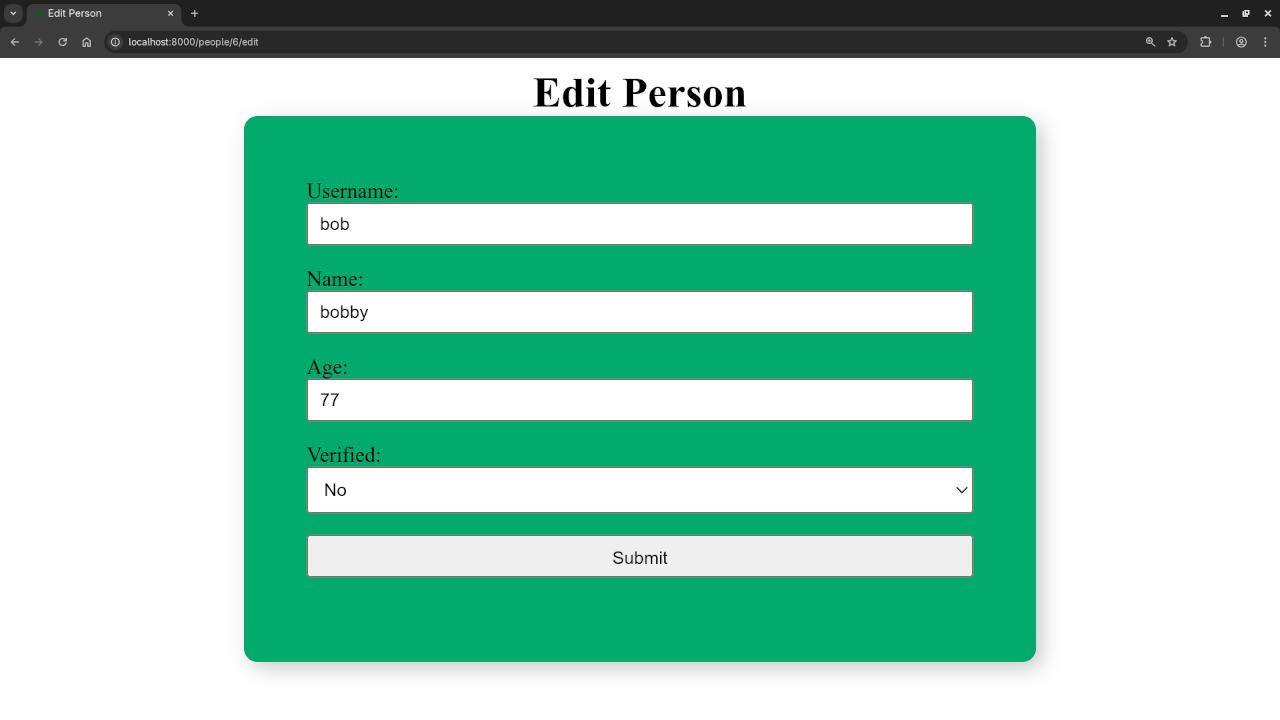
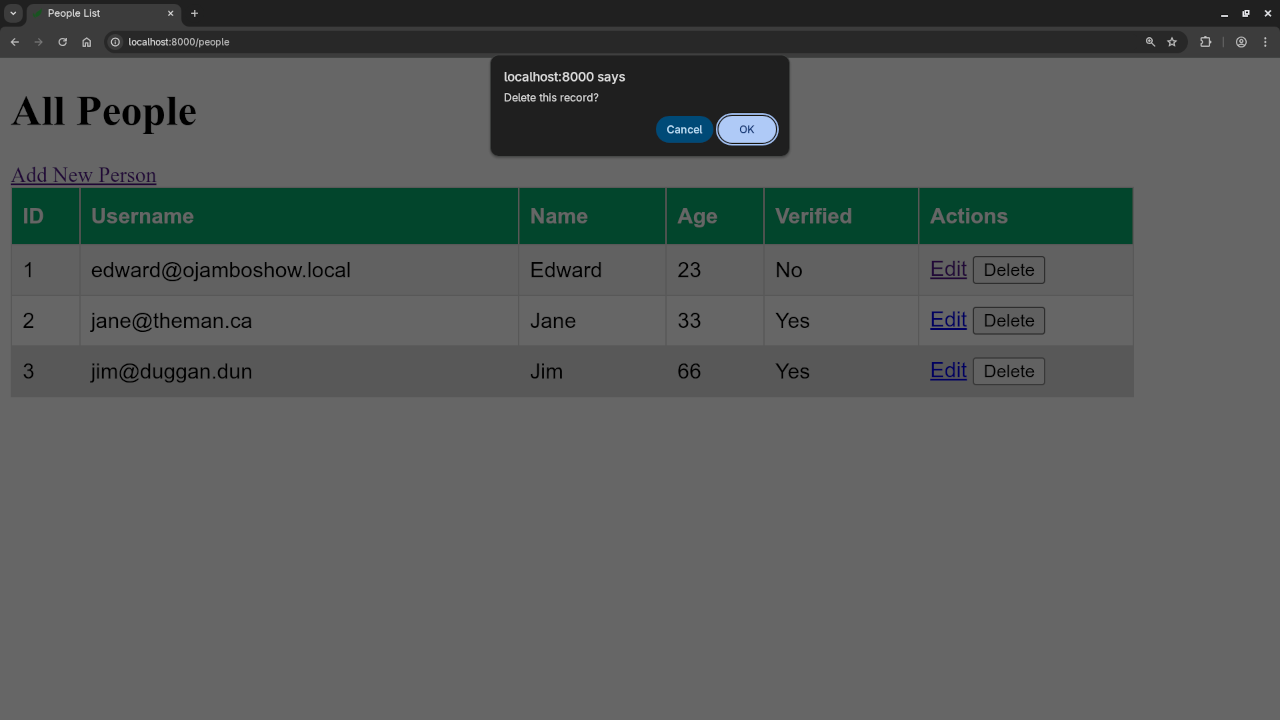
Want to Learn More?
If you are interested in mastering PHP and Laravel, check out my book and course:
- Book: Learning PHP on Amazon
- Course: Learning PHP on Ojambo Shop
Need Help?
I am available for:
- One-on-one programming tutorials
- Updating or migrating your Laravel or PHP applications
Let me know in the comments if you have any questions or want a follow-up tutorial.
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral (affiliate) links. I may earn a commission if you purchase through them - at no extra cost to you.
