Git is an essential tool for version control, enabling developers to track changes, collaborate effectively, and manage code repositories. However, sometimes you may want to undo changes, whether it’s to revert a mistaken commit or just to roll back to an earlier state of your project. This post will guide you through three important Git commands to undo changes: git checkout, git reset, and git revert.
Since Git is open-source software, it’s freely available and widely used by developers around the world. Understanding these commands is crucial for managing your codebase effectively and avoiding unnecessary headaches. Let’s dive into these three commands and how to use them.
1. git checkout: Discard Changes in Your Working Directory
What It Does:
git checkout is typically used to switch between branches, but it can also be used to discard changes in your working directory. This command allows you to revert files to their last committed state.
How to Use It:
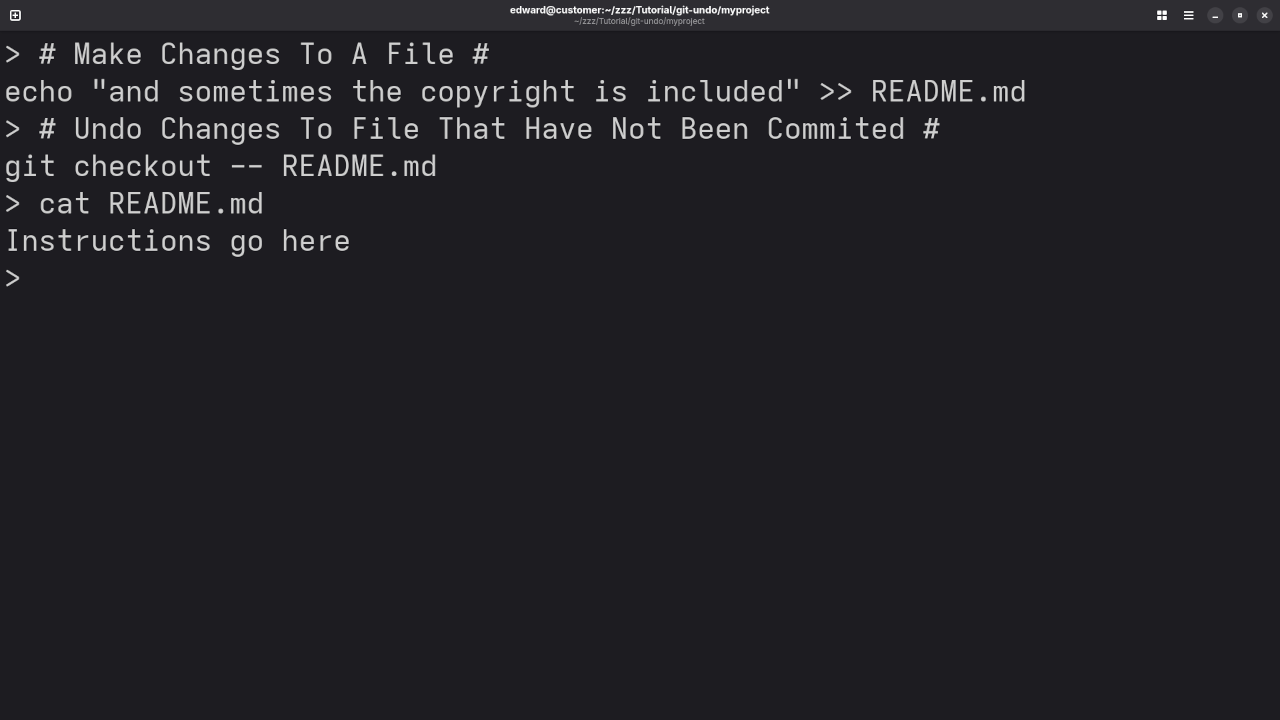
If you’ve made some changes to a file but haven’t committed them, and you want to undo those changes, you can use git checkout followed by the file name.
git checkout -- filenameExample:
Let’s say you’ve made some unwanted changes in the index.html file. You can use:
git checkout -- index.htmlThis will discard all the changes you’ve made to index.html and return it to the last committed version.
2. git reset: Remove Commits from the History
What It Does:
git reset is used to undo commits by resetting your branch to a previous commit. There are different types of resets:
- Soft Reset: Keeps your changes in the working directory.
- Mixed Reset: Keeps changes in the working directory, but unstages them.
- Hard Reset: Discards all changes in both the working directory and staging area.
How to Use It:
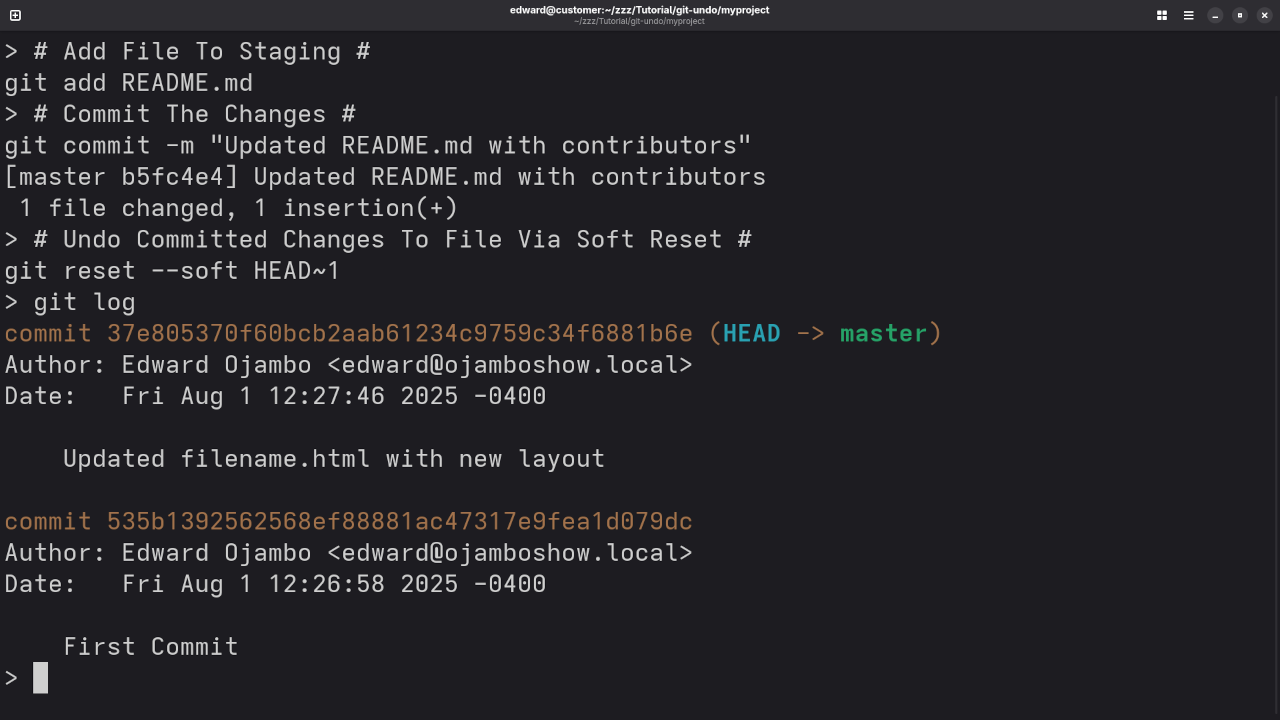
- Soft Reset: Keeps your changes but removes the commit from history.
git reset --soft HEAD~1 - Mixed Reset: Removes the commit and unstages changes.
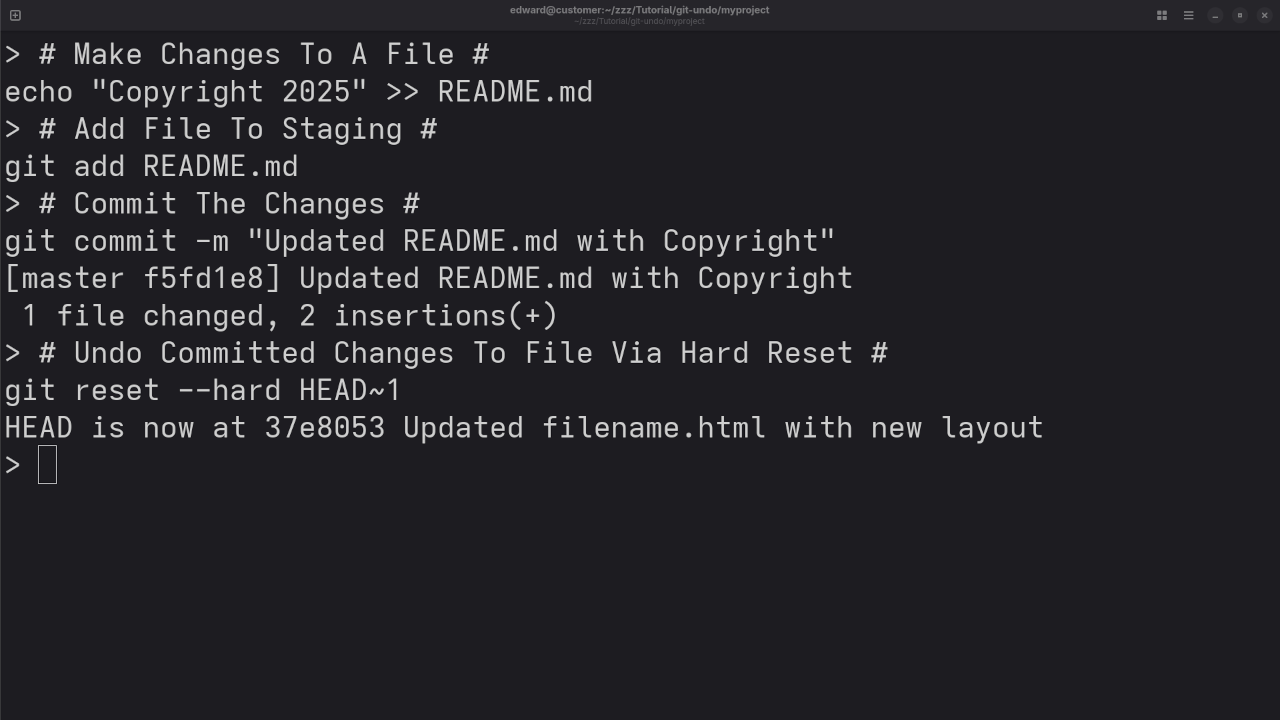
git reset HEAD~1 - Hard Reset: Removes the commit and any uncommitted changes.
git reset --hard HEAD~1
Example:
To undo your last commit but keep your changes in the working directory, use:
git reset --soft HEAD~1This will remove the most recent commit but leave your files unchanged.
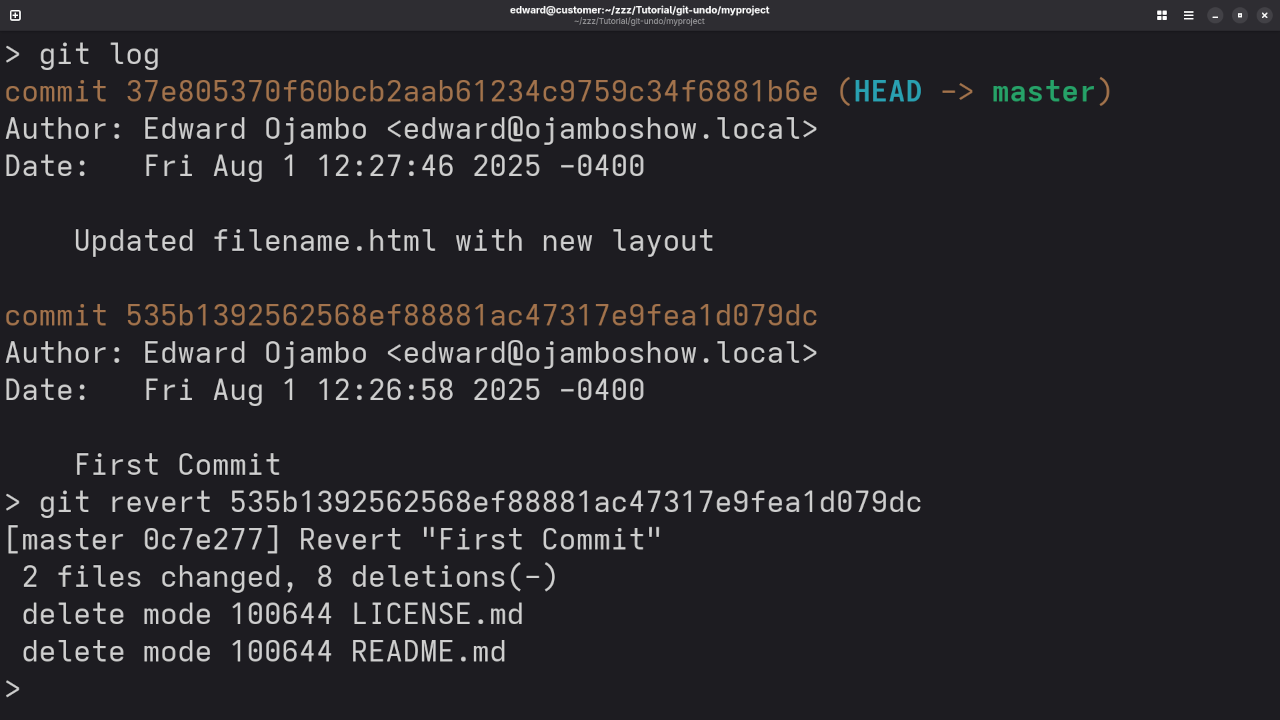
3. git revert: Create a New Commit to Undo Changes
What It Does:
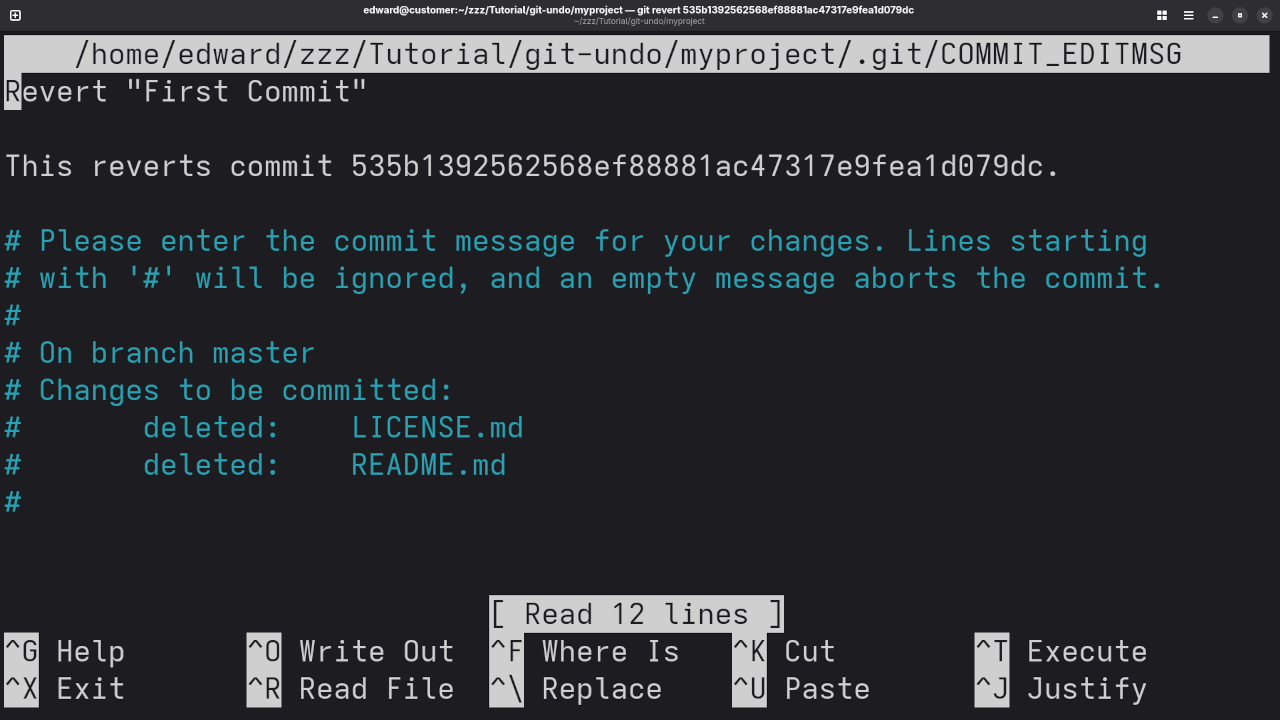
Unlike git reset, git revert doesn’t remove commits from history. Instead, it creates a new commit that undoes the changes introduced by a previous commit.
How to Use It:
To revert a specific commit, use the following command:
git revert <commit-hash>Example:
If you want to undo the changes from commit abc123, you can run:
git revert abc123This will create a new commit that undoes the changes from the commit abc123.
Visuals & Video Tutorial
Additional Resources
For more programming tutorials, tips, and tricks, feel free to explore my other resources:
- Programming Books: Check out my programming books on Amazon.
- Online Programming Courses: Browse through my collection of courses on Ojambo Shop.
- One-on-One Programming Tutorials: If you need personalized help, you can schedule a one-on-one programming tutorial with me here.
- Git Installation and Repository Migration: Need help with Git? I can install Git or migrate your repositories here.
Conclusion
Undoing changes in Git is a powerful skill that every developer should master. Whether you need to discard uncommitted changes, remove a commit from history, or create a new commit to revert changes, these Git commands will help you manage your codebase effectively.
Feel free to reach out if you have any questions or need additional assistance with Git or other programming topics. Happy coding!
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.
