HTML5 REGEX Form Validation: The Beginner’s Guide to Robust Client-Side Checks
Forms are the gateway to data on the web, and ensuring users provide valid information is crucial. While JavaScript is often used for validation, did you know that HTML5 offers a powerful, built-in solution using Regular Expressions (REGEX)?
This post will show you how to use the HTML5 pattern attribute with REGEX for robust, client-side validation right in your form markup, along with some simple CSS to make your form look great.
The HTML5 ‘pattern’ Attribute and REGEX
The secret weapon in HTML5 form validation is the pattern attribute, which can be applied to <input type="text">, <input type="tel">, <input type="email">, and other input fields.
The value of the pattern attribute must be a JavaScript-style regular expression. If the user’s input does not match the entire pattern, the browser will prevent form submission and display an error message.
Basic Form Structure
Let’s start with a simple form setup. We will include a <style> block for our CSS and a small <script> block for our future API connection.
HTML Code
<form id="dataForm">
<label for="username">Username (4-16 lowercase letters/numbers):</label>
<input
type="text"
id="username"
name="username"
required
pattern="^[a-z0-9]{4,16}$"
title="Username must be 4-16 characters and contain only lowercase letters and numbers."
/>
<label for="password">Password (Min 8 chars, incl. upper, lower, and number):</label>
<input
type="password"
id="password"
name="password"
required
pattern="(?=.*\d)(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z]).{8,}"
title="Must contain at least one number, one uppercase and one lowercase letter, and at least 8 or more characters."
/>
<button type="submit">Submit Data</button>
</form>
Optional JavaScript
// Only FETCH API for future use
const form = document.getElementById('dataForm');
form.addEventListener('submit', async (event) => {
event.preventDefault(); // Stop default form submission
if (form.checkValidity()) {
const formData = new FormData(form);
const data = Object.fromEntries(formData.entries());
// **THIS IS THE ONLY JAVASCRIPT: FETCH API for future endpoint**
try {
const response = await fetch('YOUR_FUTURE_API_ENDPOINT_URL', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify(data)
});
if (response.ok) {
console.log('Form data ready to be sent to a future endpoint.');
// Replace with actual success handling later
alert('Form validated! (Data logged to console for future API send.)');
form.reset();
} else {
throw new Error('Server error.');
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Submission failed:', error);
alert('Submission failed, check console.');
}
} else {
// This block is mostly for completeness, as HTML5 validation
// typically handles the invalid state before the submit event fires.
alert('Please correct the invalid fields.');
}
});
Common and Complicated REGEX Examples
Let’s implement REGEX patterns using the pattern attribute in the HTML for two inputs: a common one and a more complicated one.
1. Common REGEX: Simple Username
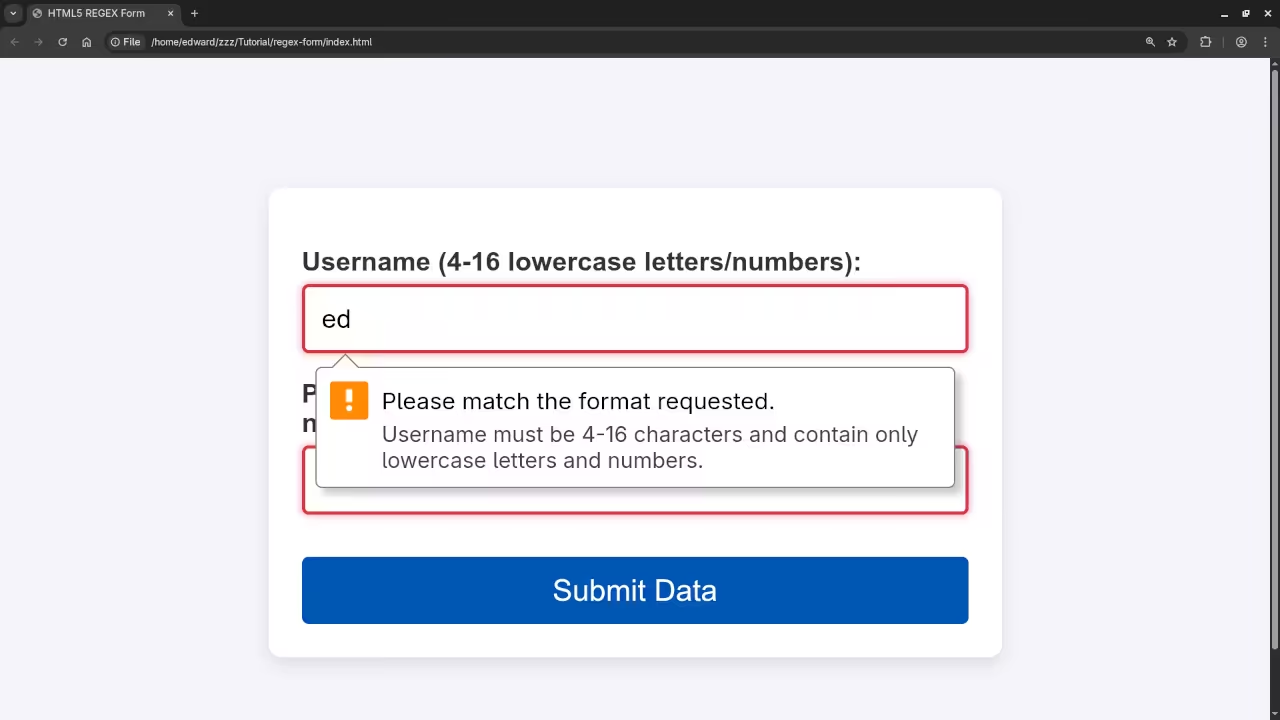
A common requirement is a username that only contains lowercase letters and numbers, and must be between 4 and 16 characters long.
- REGEX:
^[a-z0-9]{4,16}$ - Explanation:
^: Matches the beginning of the input.[a-z0-9]: Matches any lowercase letter (a-z) or any digit (0-9).{4,16}: Repeats the preceding set (the character class) between 4 and 16 times.$: Matches the end of the input. Crucial to ensure the entire string matches!
2. Complicated REGEX: Strong Password
A more complicated pattern is often a strong password policy requiring a mix of character types.
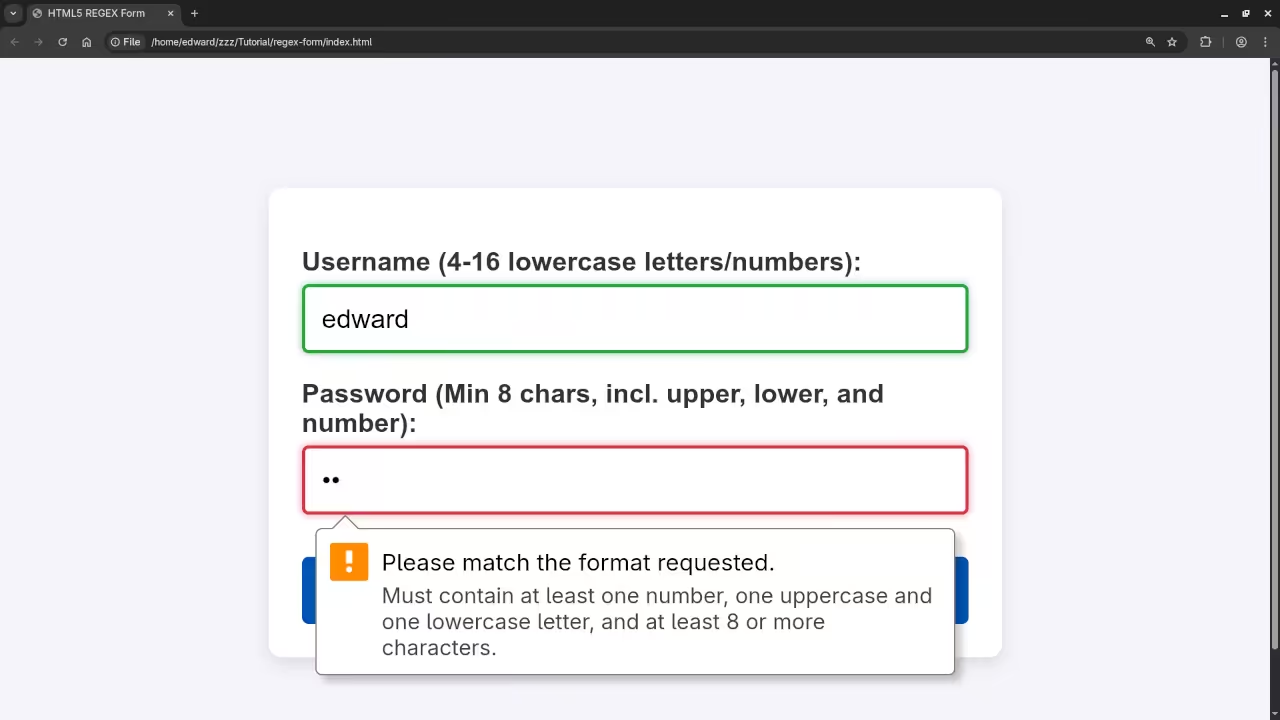
- Policy: At least 8 characters, and must contain at least one uppercase letter, one lowercase letter, and one number.
- REGEX:
(?=.*\d)(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z]).{8,} - Explanation: This uses Lookaheads
(?=...)which check for a condition without consuming characters, allowing us to enforce multiple rules simultaneously.(?=.*\d): Positive lookahead to ensure there is at least one digit (\d).(?=.*[a-z]): Positive lookahead to ensure there is at least one lowercase letter.(?=.*[A-Z]): Positive lookahead to ensure there is at least one uppercase letter..{8,}: Matches any character (.) repeated 8 or more times.
Styling to Make the Form Beautiful
HTML5 validation works best when paired with good CSS. By default, browsers use the pseudo-classes :valid and :invalid to apply styles to form elements based on their validation state.
Add the following CSS inside the <style> tags of your HTML file to create a clean, modern look and visually highlight validation status.
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f4f4f9;
padding: 20px;
}
form {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 50px auto;
padding: 20px;
background: #fff;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
label {
display: block;
margin-top: 15px;
margin-bottom: 5px;
font-weight: bold;
color: #333;
}
input[type="text"], input[type="password"] {
width: 100%;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: 16px;
transition: border-color 0.3s, box-shadow 0.3s;
}
/* 1. Base style for focus */
input:focus {
border-color: #007bff;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(0, 123, 255, 0.3);
outline: none;
}
/* 2. Styling for valid input */
input:not(:placeholder-shown):valid {
border: 2px solid #28a745; /* Green border for valid */
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(40, 167, 69, 0.5);
}
/* 3. Styling for invalid input */
input:not(:placeholder-shown):invalid {
border: 2px solid #dc3545; /* Red border for invalid */
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(220, 53, 69, 0.5);
}
button[type="submit"] {
display: block;
width: 100%;
padding: 10px;
margin-top: 25px;
background-color: #007bff;
color: white;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 18px;
transition: background-color 0.3s;
}
button[type="submit"]:hover {
background-color: #0056b3;
}
Here’s a preview of what you’ll create — an HTML5 Regex Form:
Screenshots and Screencast
Level Up Your JavaScript Skills
Mastering front-end development, from basic forms to complex API integrations, requires a strong foundation in JavaScript.
- My Book: For a comprehensive guide from a beginner’s perspective, check out my book, “Learning JavaScript” on Amazon: Learning JavaScript: Programming for the Beginner Guide.
- My Course: Dive even deeper with my structured online course, “Learning JavaScript”, available here: Learning JavaScript Course.
- One-on-One Tutorials: If you’re looking for personalized guidance on JavaScript, REGEX, or any other programming topic, I’m available for one-on-one programming tutorials. Feel free to reach out to me: Contact for Programming Tutorials.
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.