Build GUI For Desktop Applications Using Python And Tkinter
Python is a programming language and Tkinter is a lightweight GUI framework.
Tkinter comes bundled with Python version 3 on Linux, macOS and Windows. It is the Python interface to the Tk GUI toolkit.
Tkinter needs to be imported as a module to create a GUI application main window.
Tkinter will be used for a future desktop only version of Learning PHP eBook.
This tutorial will create a simple multiplatform GUI application that can be used as a starting template.
For this example, I will assume that Python 3 is installed with the default Tkinter module. You do not need to know Python programming, as it is easy to grasp the basic tasks and follow along.
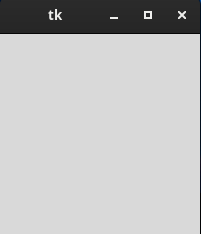
GUI Window
# Import Tkinter Module import tkinter # Create Instance Of Tkinter's Tk Class window = tkinter.Tk() # Run Tkinter Event Loop window.mainloop()
Build And Run
python3 gui.py
View
You will see a window open that resembles other desktop applications.
Other GUI Widgets
| Name | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Button | Displays buttons | b = Button ( master, option=value, … ) |
| Checkbutton | Displays options and multiple select | cb = Checkbutton ( master, option, … ) |
| Entry | Displays one line text field | e = Entry( master, option, … ) |
| Frame | Organize other widgets | f = Frame (master, option, … ) |
| Label | One line caption | l = Label ( master, option, … ) |
| LabelFrame | Spatial container with label similar to HTML fieldset and legend | lf = LabelFrame( master, option, … ) |
| Menubutton | Displays menus | mb = Menubutton ( master, option, … ) |
| PanedWindow | Container arranged vertically or horizontally | pw = PanedWindow( master, option, … ) |
| Radiobutton | Display options as radio buttons | rb = Radiobutton ( master, option, … ) |
| Scale | Provides slider | s = Scale ( master, option, … ) |
| Scrollbar | Adds scrolling capability | sb = Scrollbar ( master, option, … ) |
| Spinbox | Built-in Up and Down buttons | sp = Spinbox( master, option, … ) |
| Combobox | Combined Listbox and Entry field | co = Combobox( master, option, … ) |
| Notebook | Manages a collection of windows and displays one at a time | nb = Notebook( master, option, … ) |
| Progressbar | Displays status of long-running operation | pb = Progressbar( master, option, … ) |
| Separator | Partition widgets | sp = Separator( master, option, … ) |
| Sizegrip | Allows user to resize toplevel window | sg = Sizegrip( master, option, … ) |
| Treeview | Displays a hierarchical collection of items | tv = Treeview( master, option, … ) |
| master | Represents parent window | |
| options | can be comma-separated key-value pairs | |
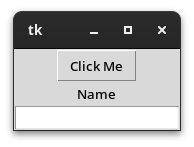
# Import Tkinter Module import tkinter # Create Instance Of Tkinter's Tk Class window = tkinter.Tk() # Create Button b = tkinter.Button ( window, text="Click Me" ) b.pack() # Create Label l = tkinter.Label( window, text="Name" ) l.pack() # Create Entry e = tkinter.Entry( window, Width=20 ) e.pack() # Run Tkinter Event Loop window.mainloop()
You will see a window open that resembles other desktop applications.
Screenshots:
Conclusion:
In summary, Python Tkinter can be used to create cross platform GUI applications. Python with Tkinter can be used for the GUI portion and the rest of the application can use another platform or programming language.
References:
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.