Introduction
The Skewb is a unique corner turning twisty puzzle. Modern AI models can help solve these complex rotations.
The Skewb differs from a standard Rubik cube mechanism. Its axes of rotation pass directly through the corners.
This deep cut design affects all six faces simultaneously. Solving it requires mastering a new form of reasoning.
Setting Up Llama Server On Fedora Linux
We use llama.cpp to run the Qwen3 model locally. Fedora Linux provides a stable environment for these computations.
Open your terminal and prepare the model file path. Execute the llama-server command with the provided GPU flags.
The command uses nine hundred ninety nine layers for offloading. This ensures your graphics card handles the heavy math.
Set the context length to twenty four thousand tokens. High context allows the AI to track long sequences.
Choosing The Right AI Model Architecture
I am using an instruct model instead of base. Base models only predict the next word in patterns.
Instruct models follow specific commands for puzzle solving logic. They provide direct answers instead of just more questions.
GGUF Format And Model Quantization
The GGUF format is essential for local Linux hosting. This format allows for fast loading and easy sharing.
We utilize quantization to fit large models on GPUs. The Q5_K_XL version uses five bits per weight.
Quantization reduces the memory footprint of the thirty billion model. It allows high performance on consumer grade hardware cards.
Optimal Sampling Parameters For Logic
The Qwen3 model suggests specific movements for the Skewb. Use a temperature of zero point seven for accuracy.
A top p value of zero point eight works. These parameters prevent the model from repeating illogical steps.
The output length should reach sixteen thousand tokens. This length is enough for complex step by step guides.
Adjust the presence penalty to stop endless repetitive loops. Be careful as high values might mix different languages.
Running The Local AI Server
Beginner programmers can easily host this server on Fedora. Use the provided port to send your puzzle queries.
The model used is the Qwen3 30B Instruct version. It features high performance for logical and spatial reasoning.
Use the jinja flag to enable proper chat templates. This helps the model understand your puzzle solving prompts.
The port eight thousand eighty one serves the API. Connect your local scripts to this specific network address.
Point the model flag to your local GGUF file. Ensure the file path matches your external mount points.
Server Configuration Summary
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Model Path | Location of GGUF file | /mnt/AI/models |
| Context Size | Total tokens available | 24576 |
| Server Port | Local network access | 8081 |
| GPU Layers | Offloading to hardware | 999 |
| Chat Template | Template engine enabled | jinja |
| Parameter | Description | Value |
Setting the top k to twenty improves output quality. This limits the AI to the most likely next moves.
A min p value of zero allows full sampling. This gives the model flexibility for creative puzzle solutions.
Presence penalty helps keep the instructions very clear. Use a value between zero and two for results.
Fedora Linux handles the server process with high efficiency. Monitor your VRAM usage while the llama server runs.
Testing AI logic on physical puzzles is very rewarding. These local models run without needing an internet connection.
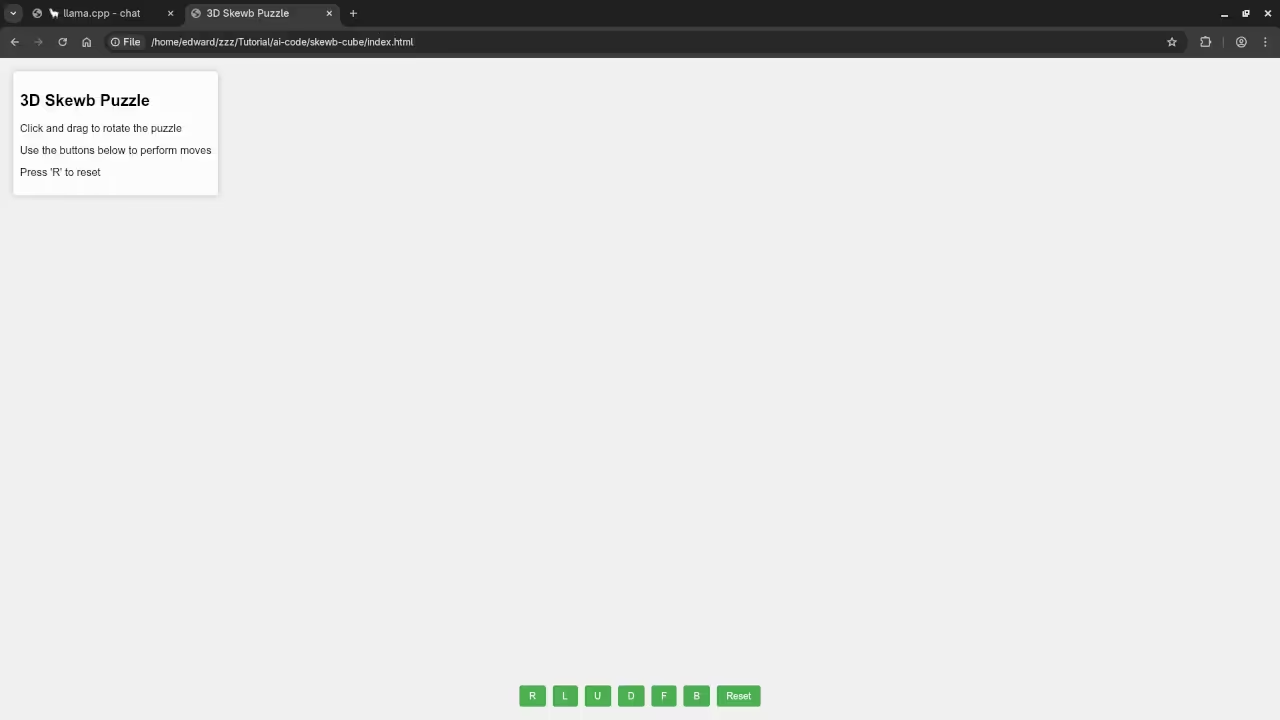
Consolidated Demo
Screenshot
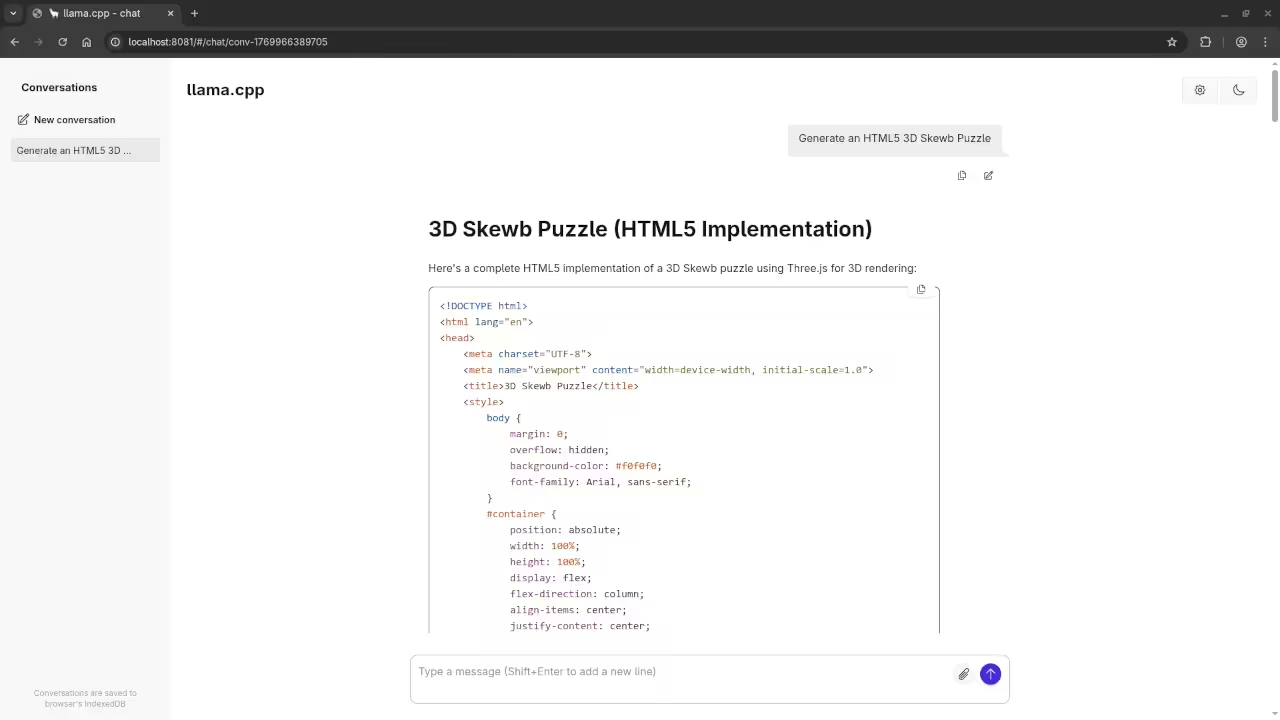

Live Screencast
Take Your Skills Further
- Books: https://www.amazon.com/stores/Edward-Ojambo/author/B0D94QM76N
- Courses: https://ojamboshop.com/product-category/course
- Tutorials: https://ojambo.com/contact
- Consultations: https://ojamboservices.com/contact
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.
Leave a Reply