Getting Started with Leaf PHP 4.2 MVC: A Simple App with MariaDB Integration
If you’re learning PHP and want to dive into modern frameworks without the heavy lifting of Laravel, then Leaf PHP 4.2 is an amazing choice. It’s a lightweight, expressive PHP framework that supports MVC, Blade templates, and integrates easily with databases — perfect for new developers and PHP veterans alike.
In this beginner-friendly post, I’ll walk you through how to set up a simple Leaf PHP app that connects to a MariaDB database and displays records from a people table in HTML using Blade.
Why Leaf PHP?
Leaf PHP is designed to be simple and fast. It offers:
- MVC structure (Models, Views, Controllers)
- Blade templating out-of-the-box
- Easy integration with Eloquent ORM
- Composer-based project setup
Whether you’re migrating from raw PHP or learning to build structured apps, Leaf gives you power without the bloat.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have:
- PHP 8.1 or later
- Composer installed
- MariaDB running locally (or remotely)
- A database table called
peoplewith at least some sample data
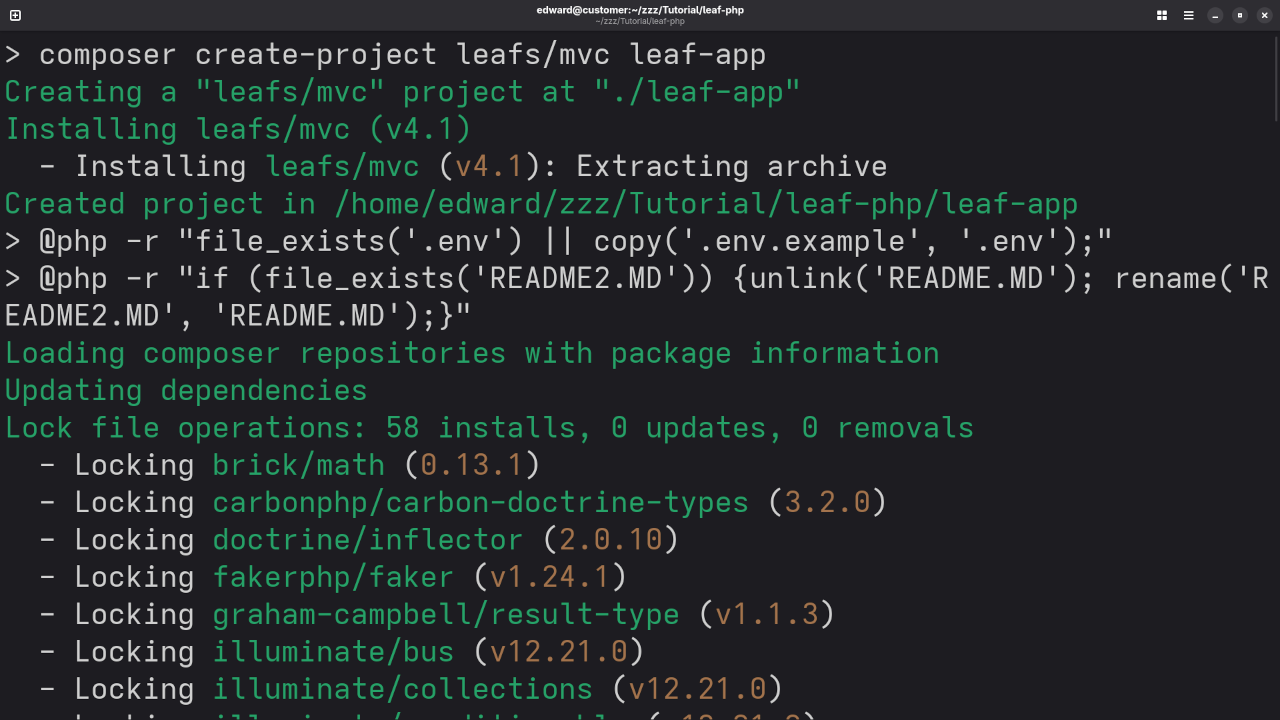
Step 1: Install Leaf MVC
Let’s create a new Leaf MVC project using Composer:
composer create-project leafs/mvc leaf-app
cd leaf-app
This gives you a ready-to-go folder structure with MVC support, Blade templating, routing, and more.
Step 2: Configure the Database
Open the .env file and set your database credentials:
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_NAME=your_database_name
DB_USER=your_db_user
DB_PASS=your_db_password
Then, open public/index.php and ensure the database is initialized:
\Leaf\Database::initDb();
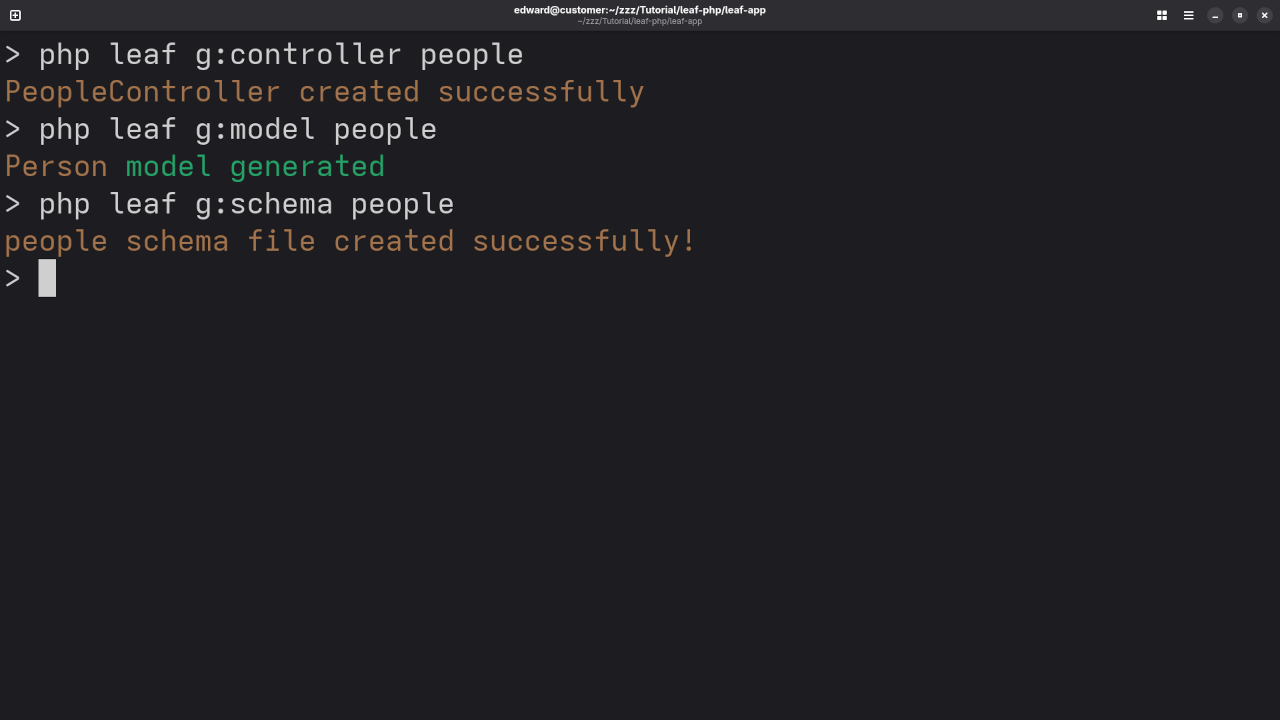
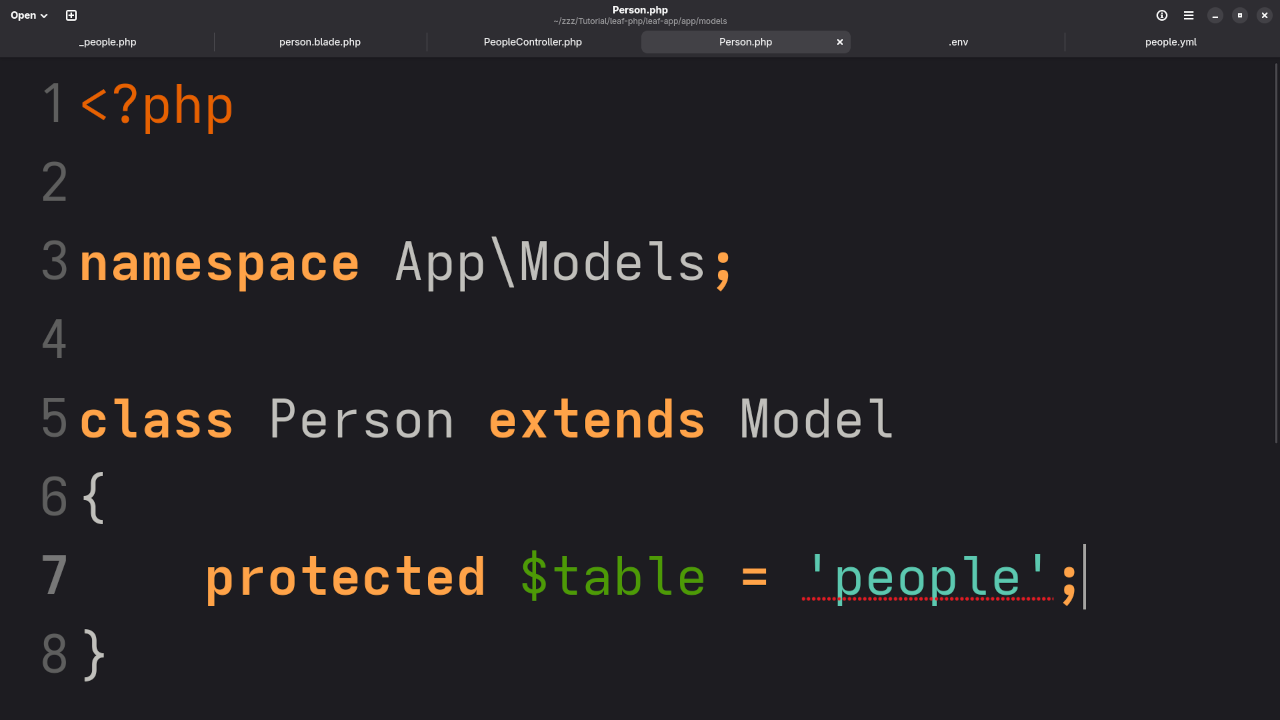
Step 3: Create the Model
Let’s define a model for our people table.
File: app/Models/Person.php
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Leaf\Model;
class Person extends Model
{
protected $table = 'people'; // Set the correct table name
}
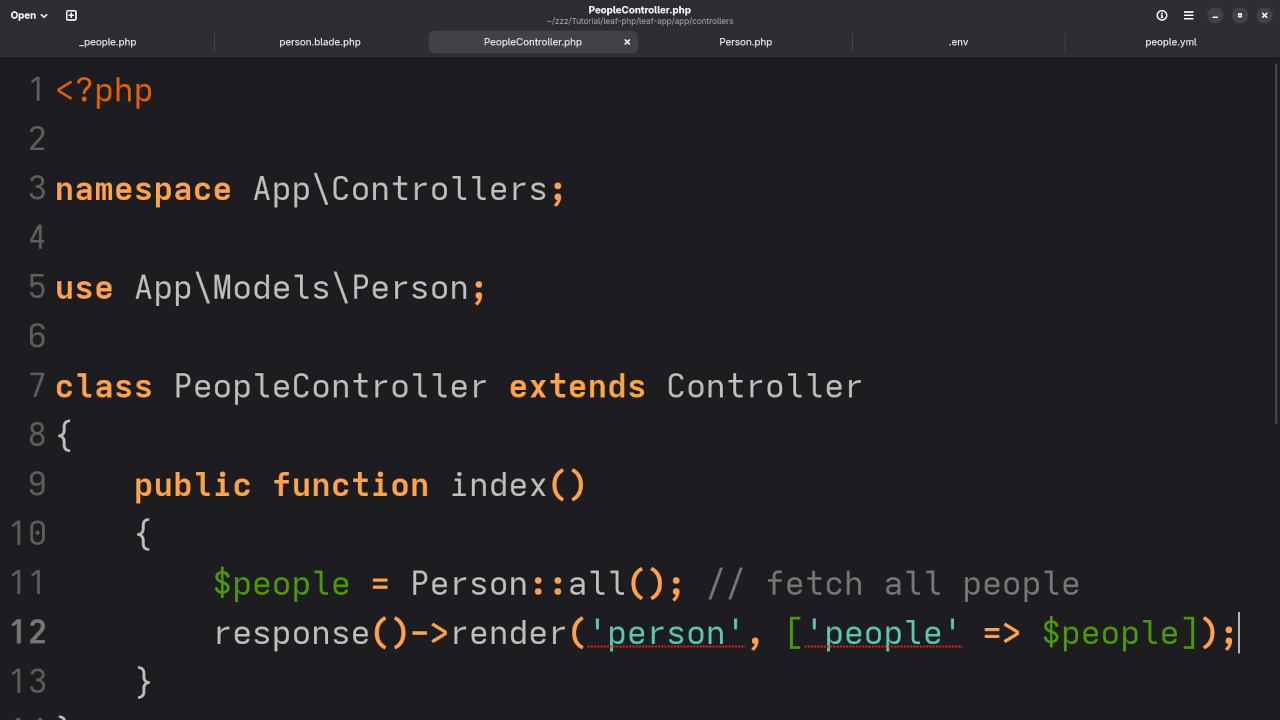
Step 4: Create the Controller
Generate a controller:
php leaf g:controller PeopleThen edit it to fetch all rows from the people table and pass them to the Blade view.
File: app/Controllers/PeopleController.php
<?php
namespace App\Controllers;
use App\Models\Person;
class PeopleController extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
$people = Person::all();
response()->render('people', [
'people' => $people
]);
}
}
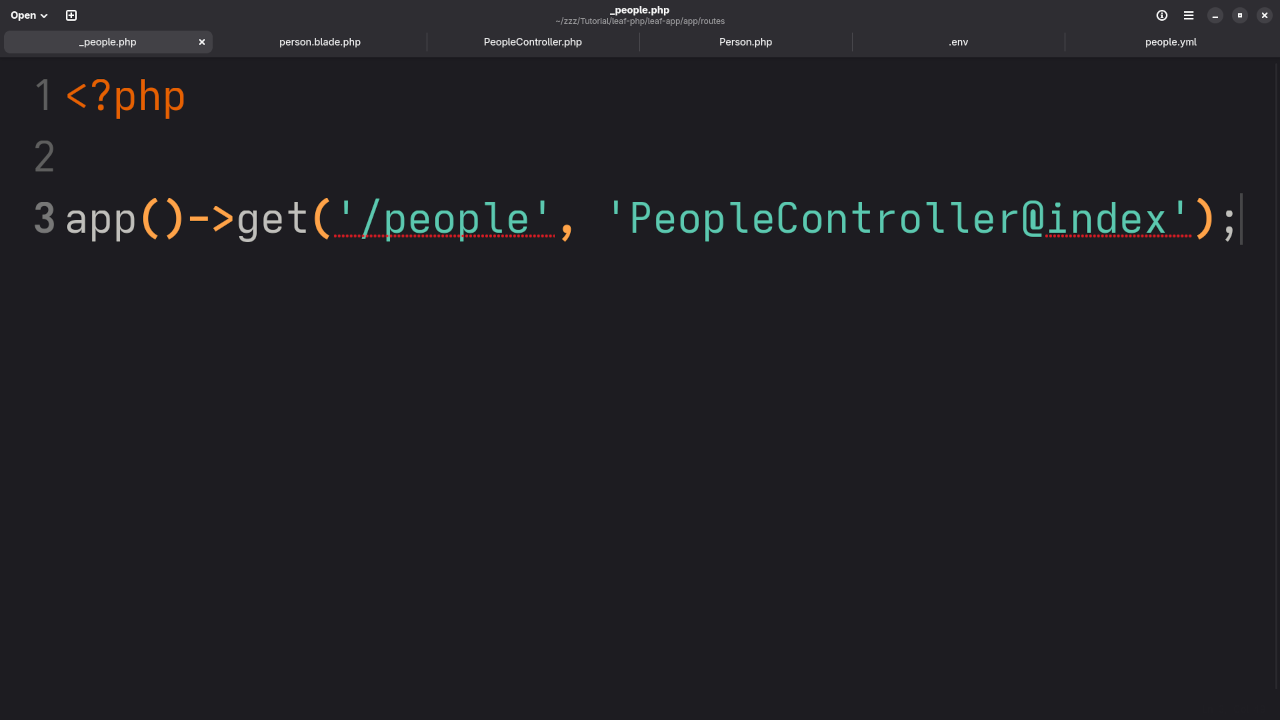
Step 5: Add the Route
File: app/routes/web.php
app()->get('/people', 'PeopleController@index');Step 6: Create the Blade View
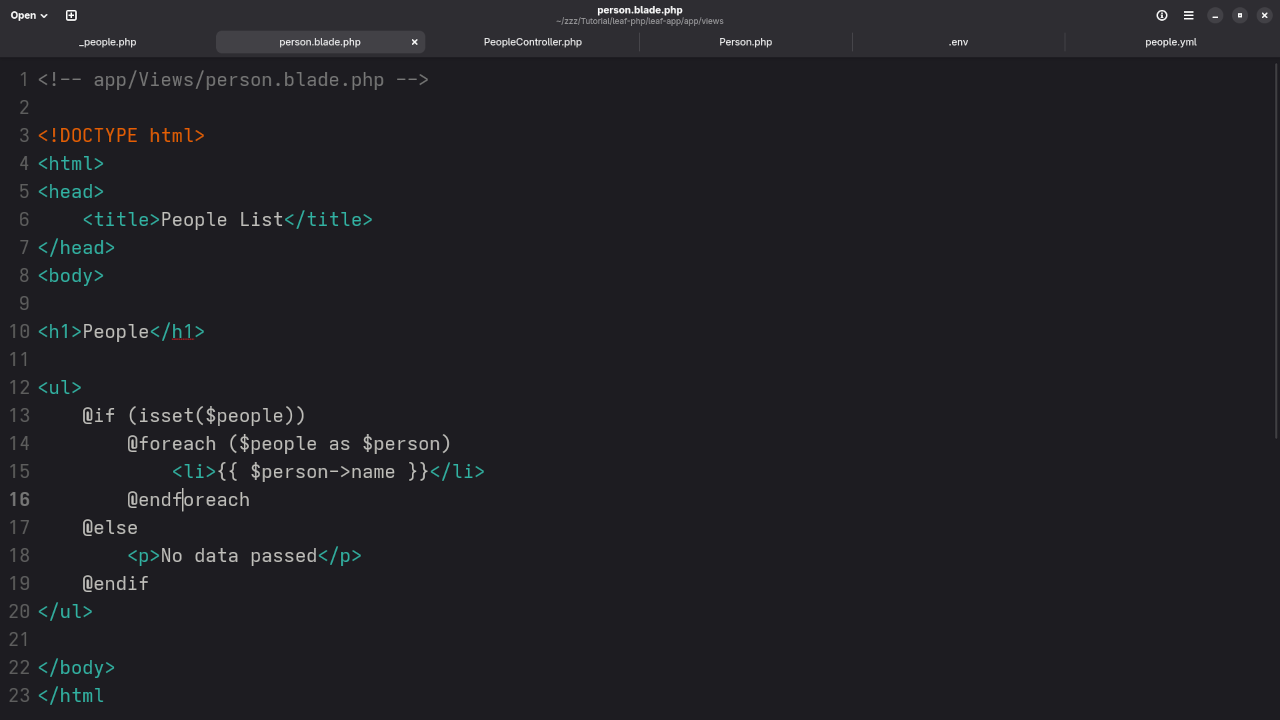
File: app/Views/people.blade.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>People List</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>List of People</h1>
@if (isset($people) && count($people) > 0)
<ul>
@foreach ($people as $person)
<li>{{ $person->name }} - {{ $person->email }}</li>
@endforeach
</ul>
@else
<p>No records found.</p>
@endif
</body>
</html>
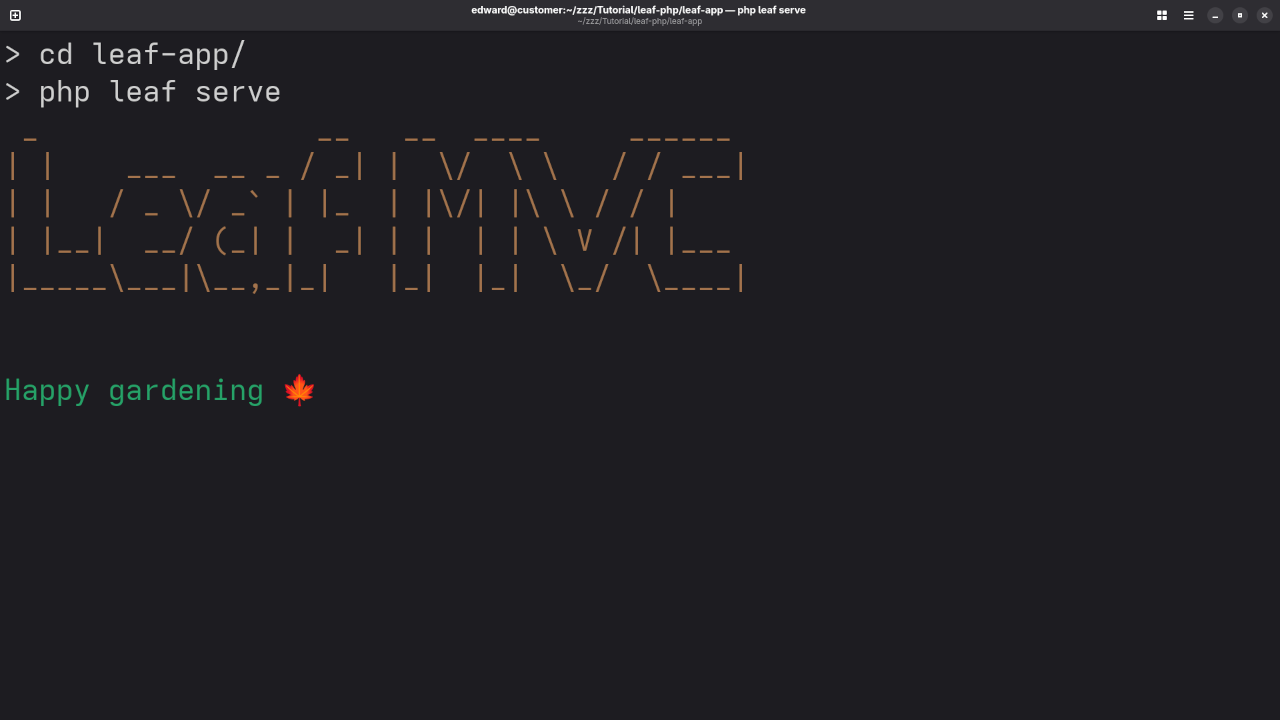
Screenshots & Screencast
Learn More: My PHP Book & Course
This post is a great introduction, but if you’re serious about mastering PHP, I recommend:
-
Learning PHP (eBook)
A complete beginner-to-advanced guide in PHP programming. -
Learning PHP (Course)
A full video course designed to build real-world PHP apps.
Need Help? Work with Me 1-on-1
I offer one-on-one PHP tutorials, Leaf PHP project upgrades, and custom migrations. If you’d like personalized help or to work on your own Leaf PHP app:
Conclusion
Leaf PHP makes MVC development simple and clean. In just a few steps, you connected to a MariaDB database and displayed results with Blade — without needing to learn a huge framework.
Whether you’re just getting started or migrating from vanilla PHP, Leaf 4.2 is a lightweight but powerful option.
Happy coding! 😄
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.