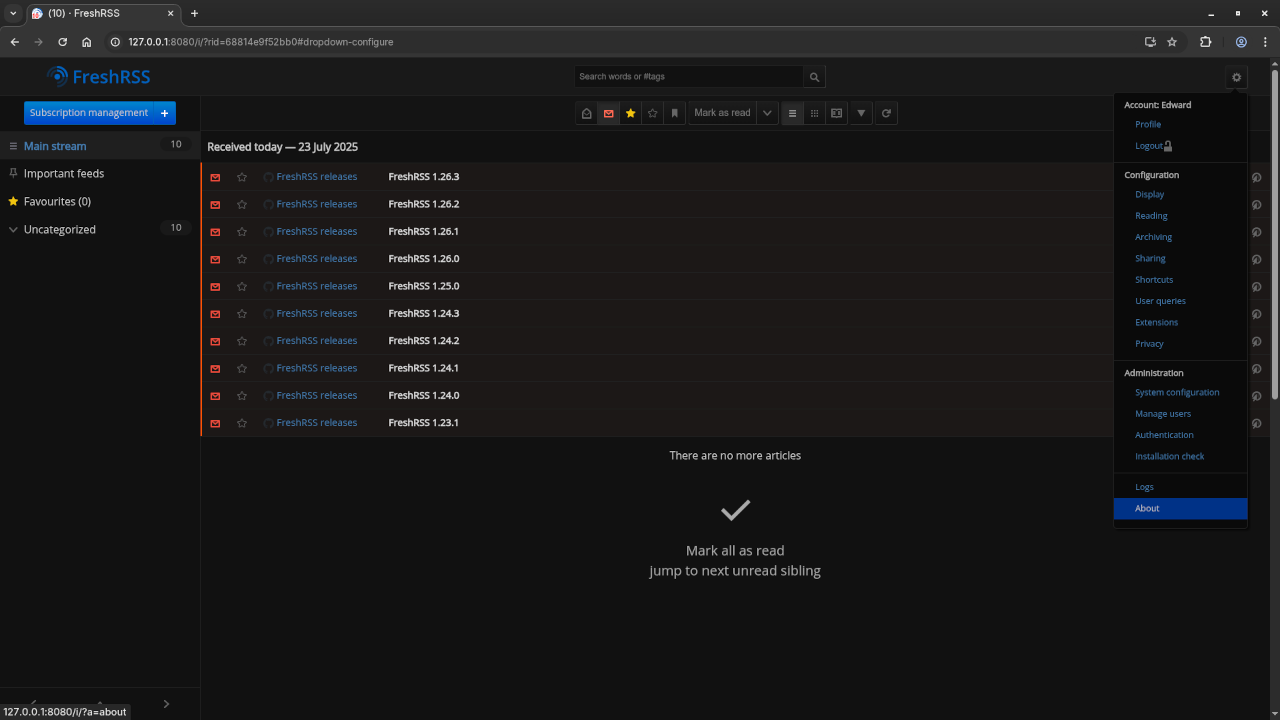
FreshRSS is an open-source, self-hosted RSS feed reader that you can use to stay up-to-date with your favorite blogs, news, and podcasts in one place. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, FreshRSS offers a simple and flexible way to manage all your RSS feeds.
In this blog post, we’ll walk through installing FreshRSS using Podman (a containerization tool), connecting it to a MariaDB database, and setting up your own self-hosted RSS solution.
Why Use FreshRSS?
- Open Source: FreshRSS is completely free and open-source, meaning you have full control over your data and can modify the software to suit your needs.
- Lightweight: FreshRSS is lightweight and easy to deploy on most servers.
- Customization: With an active community and several add-ons, FreshRSS can be customized to suit your preferences.
- Privacy: Since it’s self-hosted, all your RSS feeds remain private.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have the following:
- Podman installed on your server. If you don’t have it, you can install it by following the Podman Installation Guide.
- MariaDB for the database. We’ll be connecting FreshRSS to a MariaDB instance.
- A basic understanding of Docker and containerization (Podman works similarly to Docker).
Step 1: Create a Podman Compose File
We’ll use Podman Compose, which allows us to manage multi-container setups with a simple configuration file similar to Docker Compose.
mkdir ~/freshrss
cd ~/freshrssNow, create a file named podman-compose.yml:
version: '3.7'
services:
mariadb:
image: mariadb:latest
container_name: mariadb_freshrss
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: rootpassword
MYSQL_DATABASE: freshrss
MYSQL_USER: freshrss_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: userpassword
ports:
- "3306:3306"
volumes:
- mariadb_data:/var/lib/mysql
restart: unless-stopped
freshrss:
image: freshrss/freshrss:latest
container_name: freshrss
environment:
- FRESHRSS_DB_HOST=mariadb_freshrss
- FRESHRSS_DB_NAME=freshrss
- FRESHRSS_DB_USER=freshrss_user
- FRESHRSS_DB_PASSWORD=userpassword
ports:
- "80:80"
depends_on:
- mariadb
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
mariadb_data:Step 2: Start the Services
With the podman-compose.yml file in place, start both the MariaDB and FreshRSS services:
podman-compose up -dVerify everything is running smoothly:
podman psThis should show two containers running: one for MariaDB and another for FreshRSS.
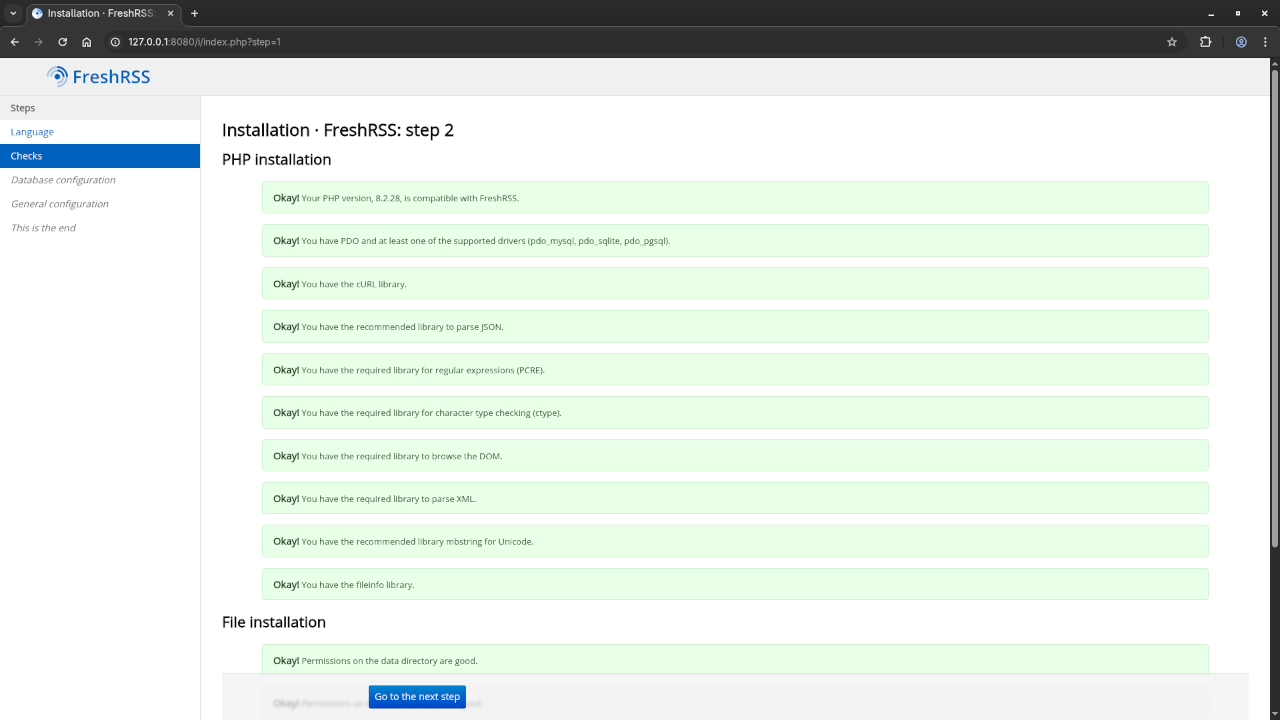
Step 3: Configure FreshRSS
Once running, open your browser and go to http://your-server-ip to begin the FreshRSS setup.
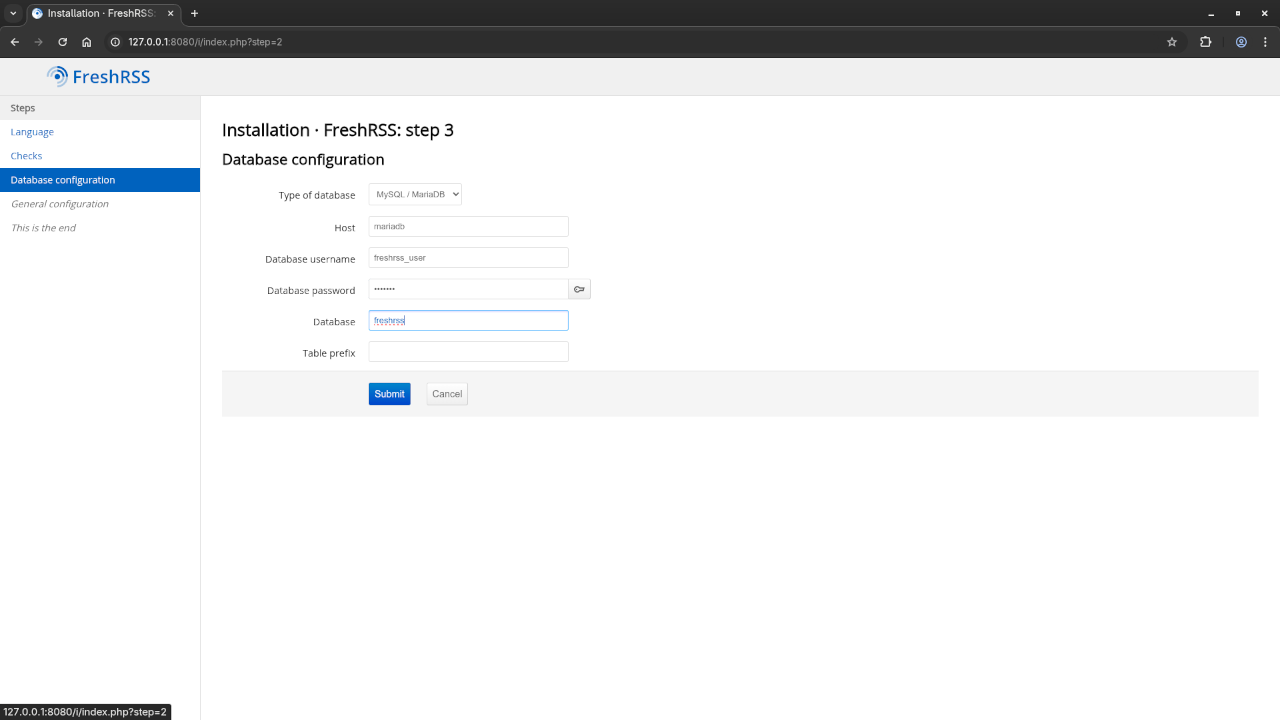
Database Configuration:
- Database Type: MariaDB
- Host: mariadb_freshrss
- Database Name: freshrss
- Database User: freshrss_user
- Database Password: userpassword
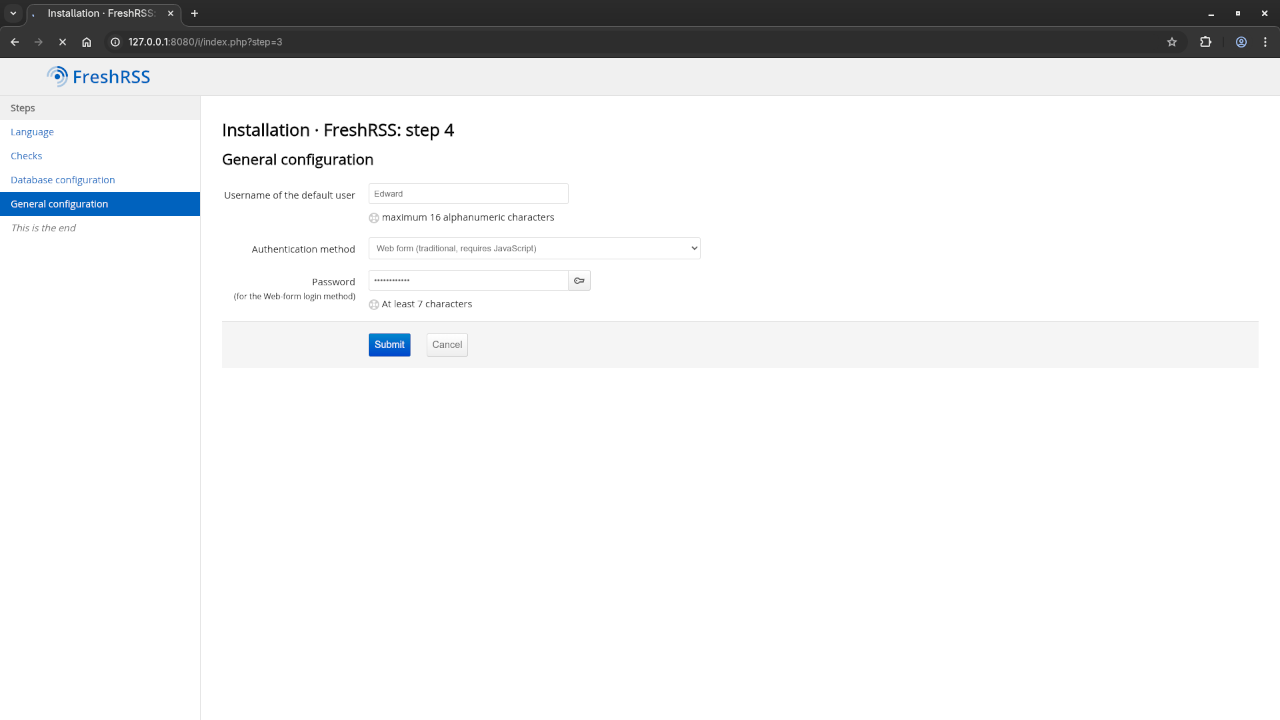
Then, set up your admin username and password and click “Install” to complete the process.
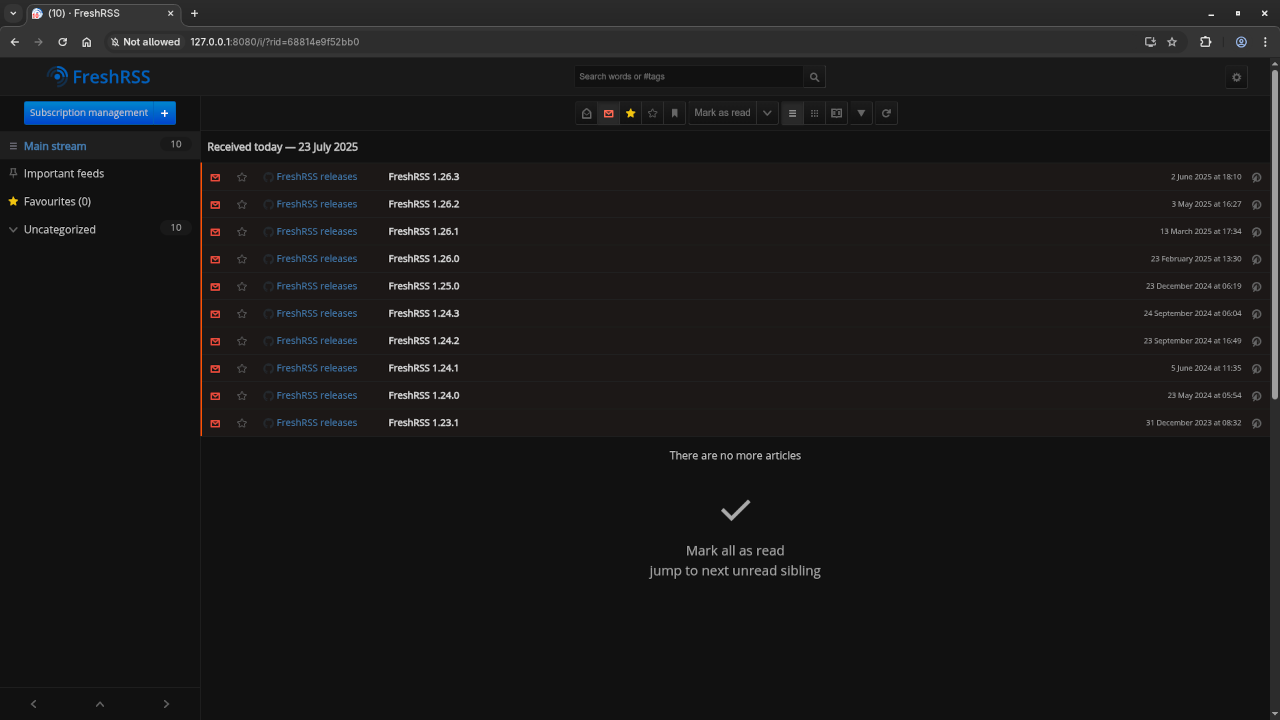
Step 4: Accessing FreshRSS
Visit your server IP or domain name in a browser. You’ll now have access to FreshRSS and can begin adding your feeds!
Screenshots
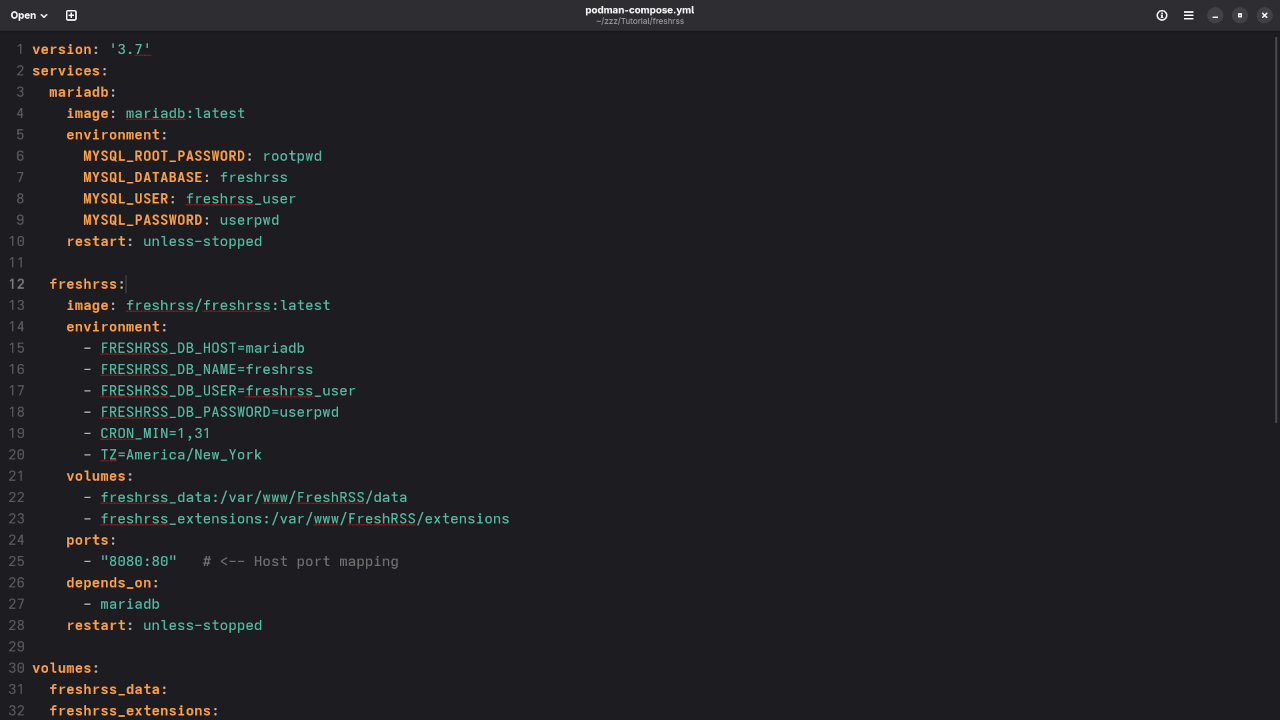
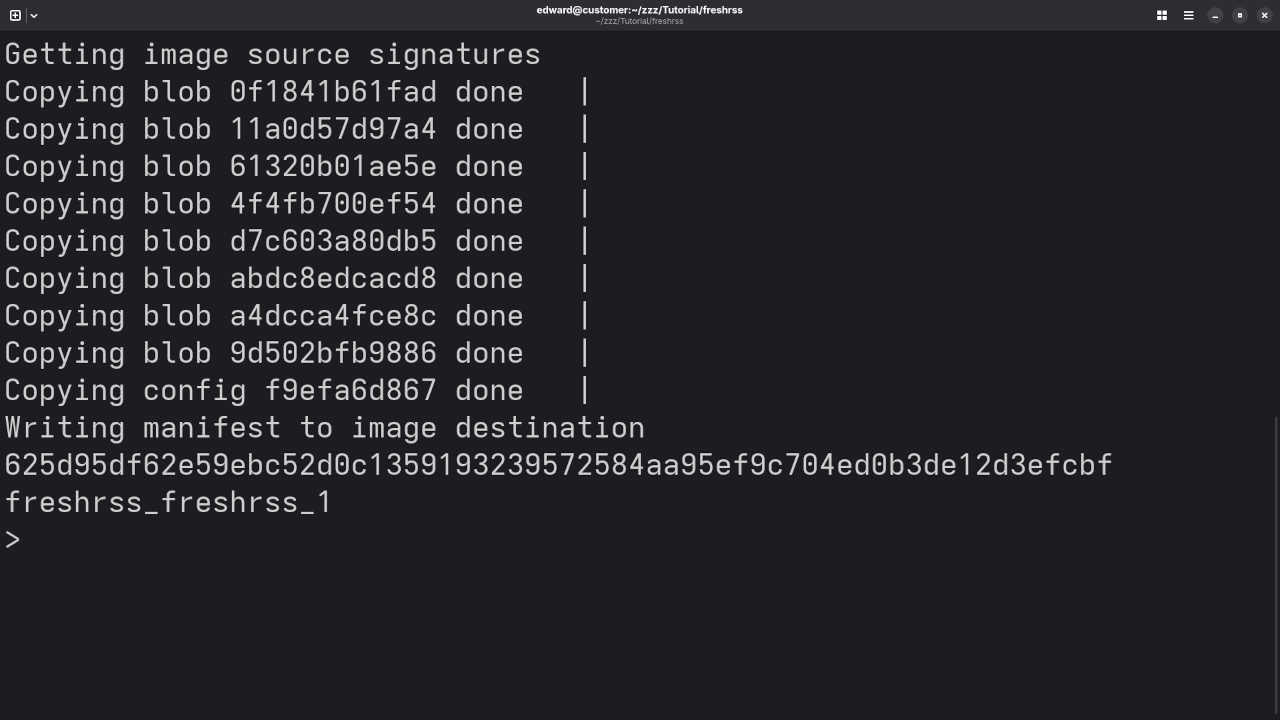
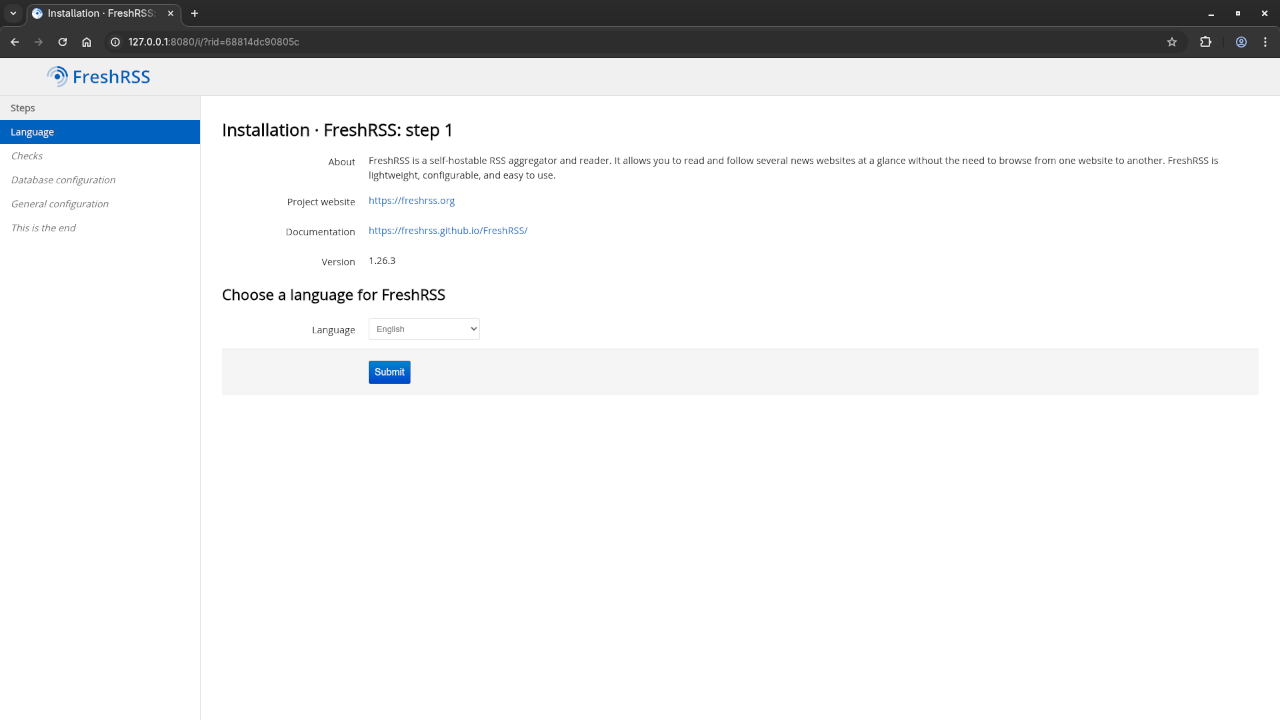
Embedded Screencast
Conclusion
By following these steps, you now have a self-hosted FreshRSS installation running with Podman and connected to a MariaDB database. You can enjoy all the benefits of an open-source RSS feed reader without sacrificing privacy or control over your data.
Resources
- Learning PHP Book on Amazon
- Learning PHP Course
- Contact for Programming Tutorials & FreshRSS Support
Final Thoughts
FreshRSS is a fantastic way to manage your RSS feeds while maintaining full control over your data. With the ease of installation via Podman and the ability to use MariaDB as the backend, it’s a perfect solution for anyone looking for a self-hosted RSS reader. Enjoy!
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral (affiliate) links. I may earn a commission if you purchase through them - at no extra cost to you.