Source Code Management Web Interface
The version control platform Gitlab and all its components will be installed inside a container using podman.
Podman allows a regular user to manage their pods (containers) without the need for root user privileges. Podman is free, open source and cross-platform (Mac, Windows and Linux) for use as a replacement for Docker.
By default, Podman stores containers in your home folder. This could be an issue if the home folder is on a smaller drive or partition (common for smaller faster SSD Drives). It is possible to move the container storage to another location.
Podman was originally used to compile PHP for the Learning PHP eBook.
This tutorial will create a container that uses the official Gitlab container to run a web-based platform that provides a comprehensive suite of tools for software development and DevOps.
For this example, I will assume that Podman is installed on your platform of choice. The latest version of Gitlab will be downloaded and setup. Podman can use any name for the reference. No Dockerfile or YAML is required so that Docker fans can follow along by replacing “podman” with “docker”.
Requirements For Gitlab Podman
Glossary:
Container
Software unit that packages code and all its dependencies for different computing environments.
Image
Container that is standalone and executable.
Docker
Platform that builds, shares and runs container applications.
Dockerfile
Text file without a file extension contains a script of instructions for building an image.
YAML
Text file extension defines how multi-container applications should be built, run, and managed.
Version Control
Allows teams to track changes to their code and collaborate effectively.
Project Planning
Manage project tasks, including issue tracking, merge requests, and milestone tracking.
CI/CD
Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery or Deployment automates the build, test, and deployment of code.
Code Review
Provide a dedicated interface for reviewing code changes, providing feedback, and ensuring code quality.
Issue Tracking
Allows teams to manage bugs, feature requests, and other issues related to their projects.
DevOps
Combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to improve the speed and quality of software delivery.
Open source
Freely available for possible modification and redistribution.
Test Tools
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel(R) i7 2600 @ 3.40GHz. |
| Memory | 16GB DDR3. |
| Storage | 400GB SSD. |
| Operating System | Fedora Linux Workstation 42. |
| Desktop Environment | Gnome 48. |
| Name | Description |
Generate Services Script
# Create Start Services File # cat > startservices.sh << 'EOF' #!/bin/sh nohup /usr/sbin/php-fpm -c /etc/php.ini -y /etc/php-fpm.conf & mysqld --datadir='/var/lib/mysql/' --user=mysql & EOF
Download GitLab Community Edition
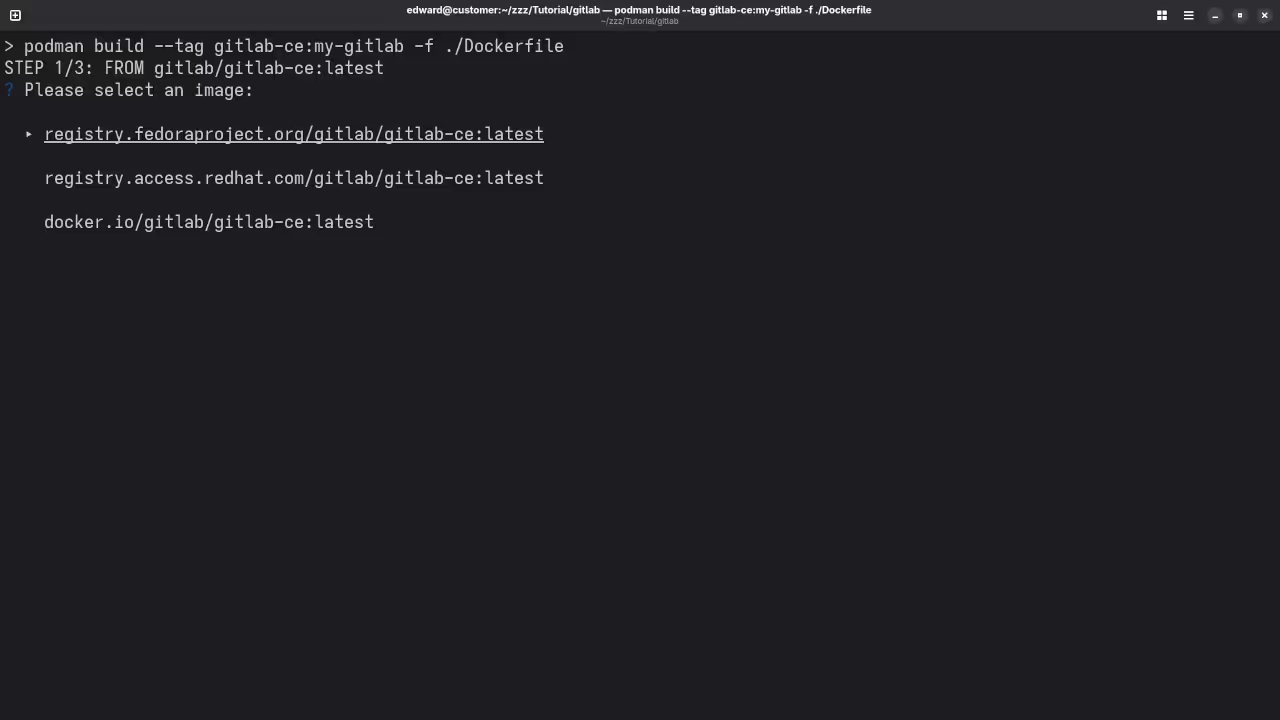
# Get Lastest GitLab Version # podman pull gitlab/gitlab-ce:latest
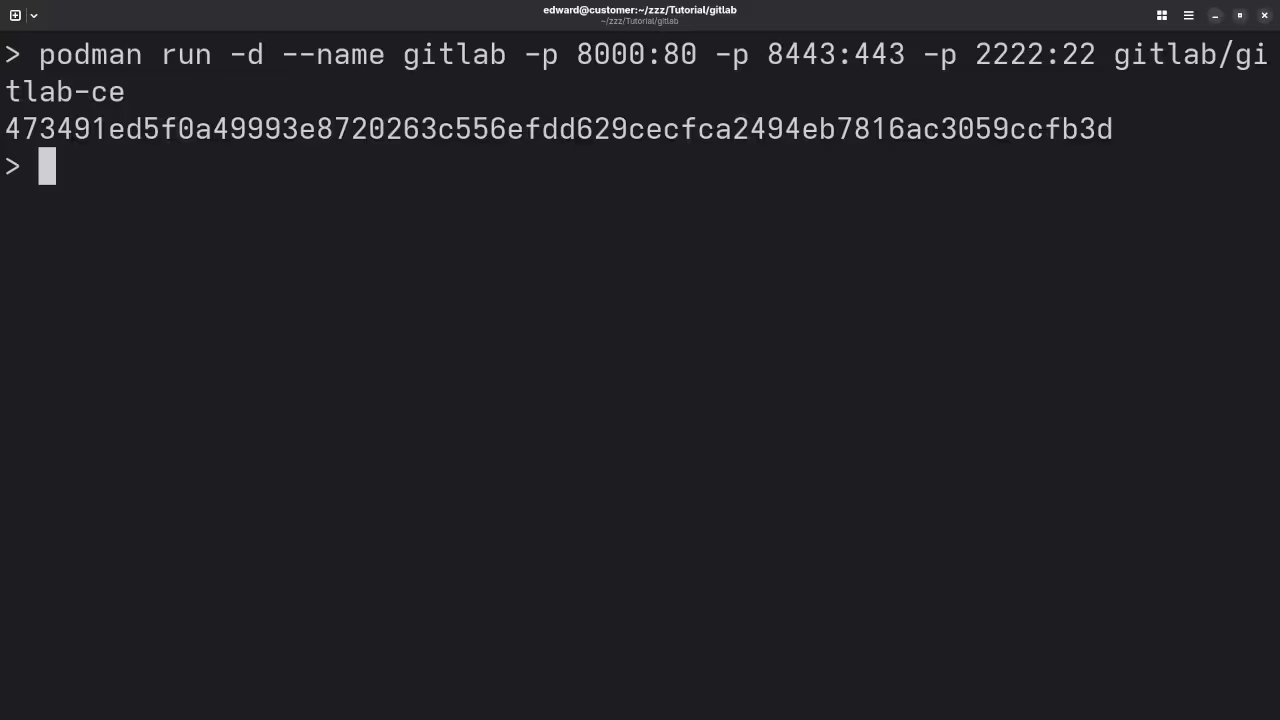
Run
podman run -d --name gitlab -p 8000:80 -p 8443:443 -p 2222:22 gitlab/gitlab-ce
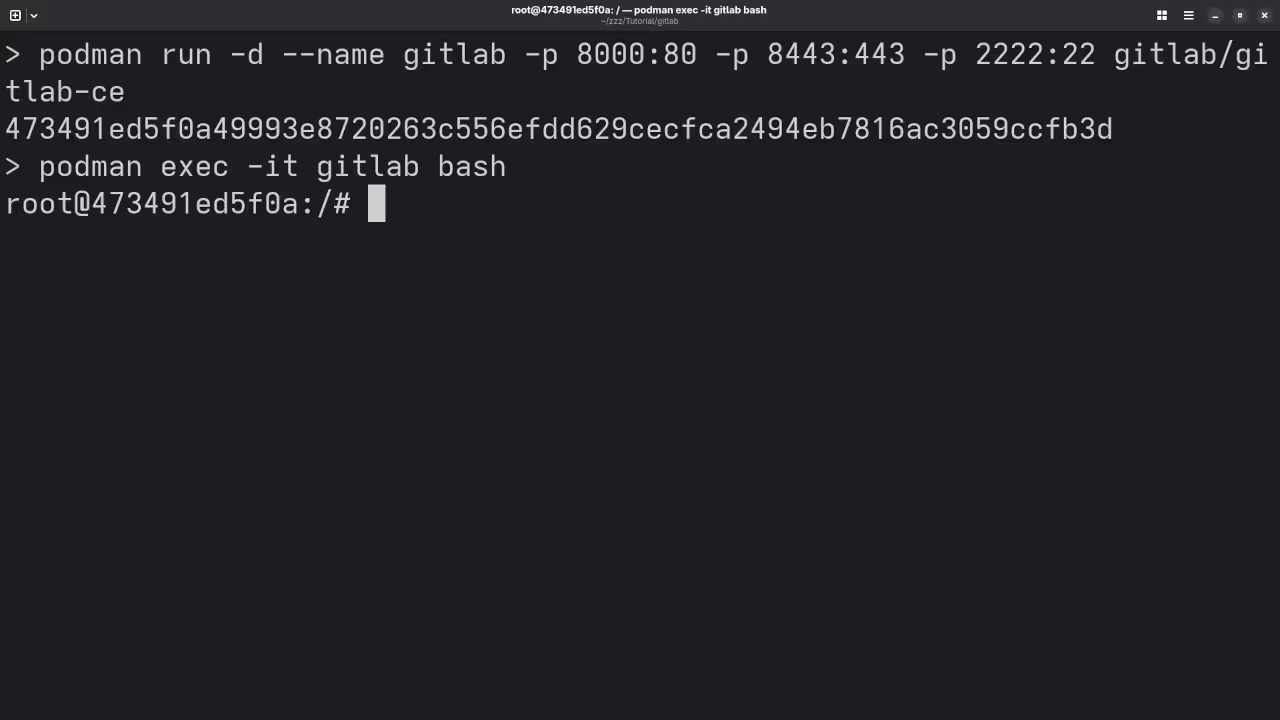
Enter Pod
podman exec -it gitlab /bin/bash # Obtain Initial Password # cat /etc/gitlab/initial_root_password
Start Or Stop Or Restart Container
# Start Container # podman start gitlab # Stop Container # podman stop gitlab # Restart Container # podman restart gitlab
View
Open your web browser and point it to http://localhost:8080 or the internal intranet IP address and then wait for the HTML page to load.
Explanation:
- Download latest Gitlab version.
- Optionally create a volume for persistent data.
- Use podman to run the specified container and make it accessible via a specific mapped port number.
- Enter the pod container to obtain or change the initial root password.
- Open your workstation web browser and navigate to the localhost and the assigned port number.
- For other devices such as phones and tablets, use the local workstation IP address and assigned port number in the web browser.
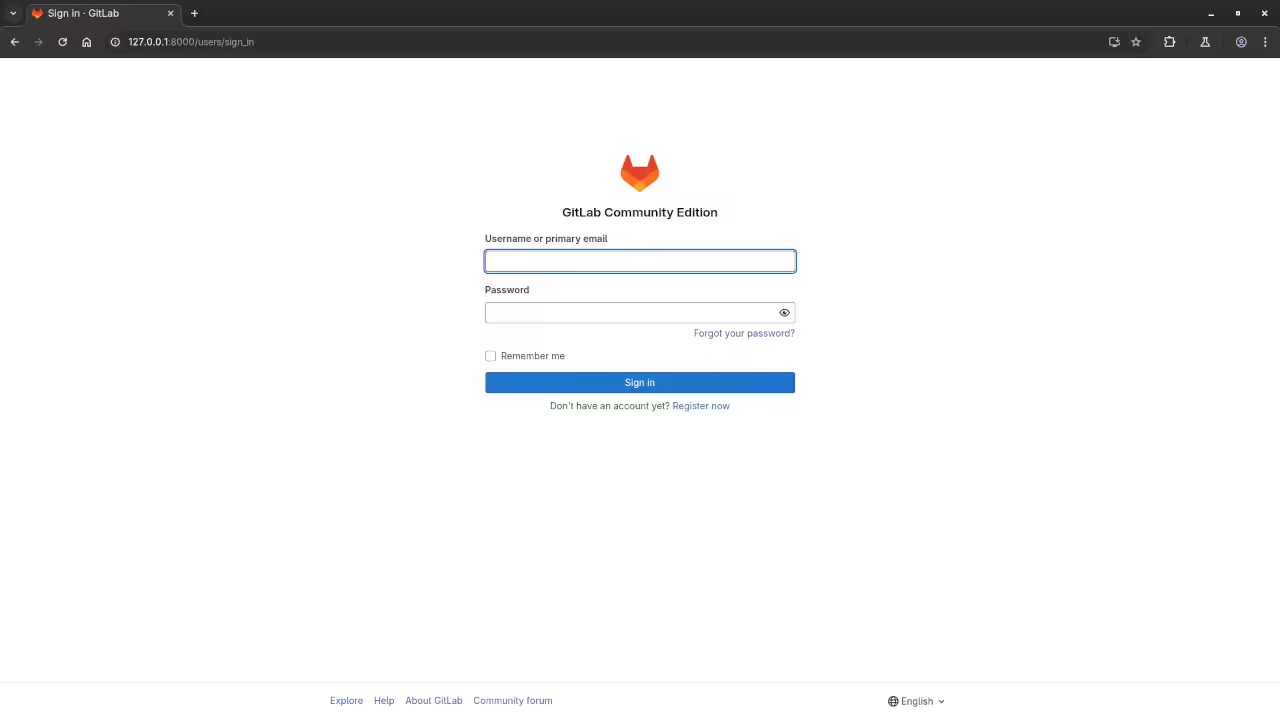
Usage
You can use any Docker command arguments with Podman. For this tutorial, a pre-built GitLab CE container was used. Podman can be downloaded from Podman.
GitLab is POSIX-compatible (Unix, Linux, MacOS). GitLab CE can be downloaded from Gitlab.
Open Source
Podman is licensed under the Apache License version 2.0. The permissive license requires the preservation of the copyright notice and disclaimer. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
GitLab Community Edition (CE) is licensed under the MIT License. The permissive license requires the preservation of the copyright notice and disclaimer. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
Conclusion:
Podman can be used a Docker alternative to run the GitLab CE container. Podman uses the same commands as Docker and is daemon-less, allowing a regular user to manage containers.
Podman can manage multiple containers as a single unit, providing a more flexible and powerful way to manage containerized applications. GitLab CE was completely managed from a single container.
If you enjoy this article, consider supporting me by purchasing one of my WordPress Ojambo.com Plugins or programming OjamboShop.com Online Courses or publications at Edward Ojambo Programming Books or become a donor here Ojambo.com Donate
References:
- Customer Sets Price Plugin for WooCommerce on Ojambo.com
- Learning JavaScript Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning Python Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning PHP Course on OjamboShop.com
- Master Blender Python API Paperback on Amazon
- Master Blender Python API Ebook on Amazon
- Learning JavaScript Paperback on Amazon
- Learning JavaScript Ebook on Amazon
- Learning Python Ebook on Amazon
- Learning PHP Ebook on Amazon
- OjamboServices.com For Custom Websites, Applications & Tutorials
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.