Getting Started with the Tempest PHP Framework (v1.6.0): A Beginner’s Guide with MariaDB Integration
Why Try Tempest PHP Framework?
If you’re looking for a modern, lightweight, and fast PHP framework that supports MVC architecture, look no further than the Tempest PHP Framework. Recently updated to version 1.6.0, Tempest is perfect for both beginners and experienced developers who want a streamlined alternative to bloated frameworks.
In this beginner-friendly tutorial, we’ll:
- Install Tempest using Composer
- Build a simple app that connects to a MariaDB table called
people - Fetch all the records
- Output them as HTML using the MVC pattern
Step 1: Installing Tempest PHP (v1.6.0)
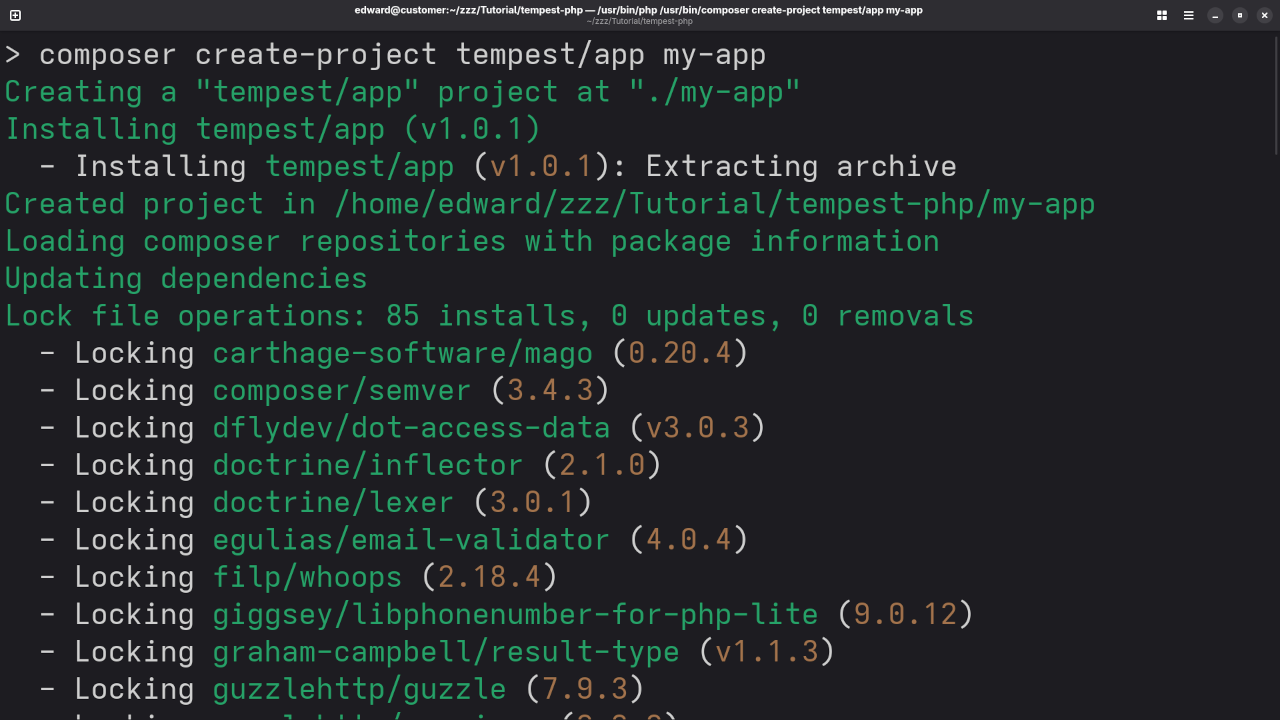
Make sure you have Composer installed on your system. Then, in your terminal or command prompt, run the following command:
composer create-project tempest/framework my-tempest-app 1.6.0This will set up a new Tempest project in the my-tempest-app folder using version 1.6.0.
Step 2: Starting the Web Server
Navigate into your new project directory:
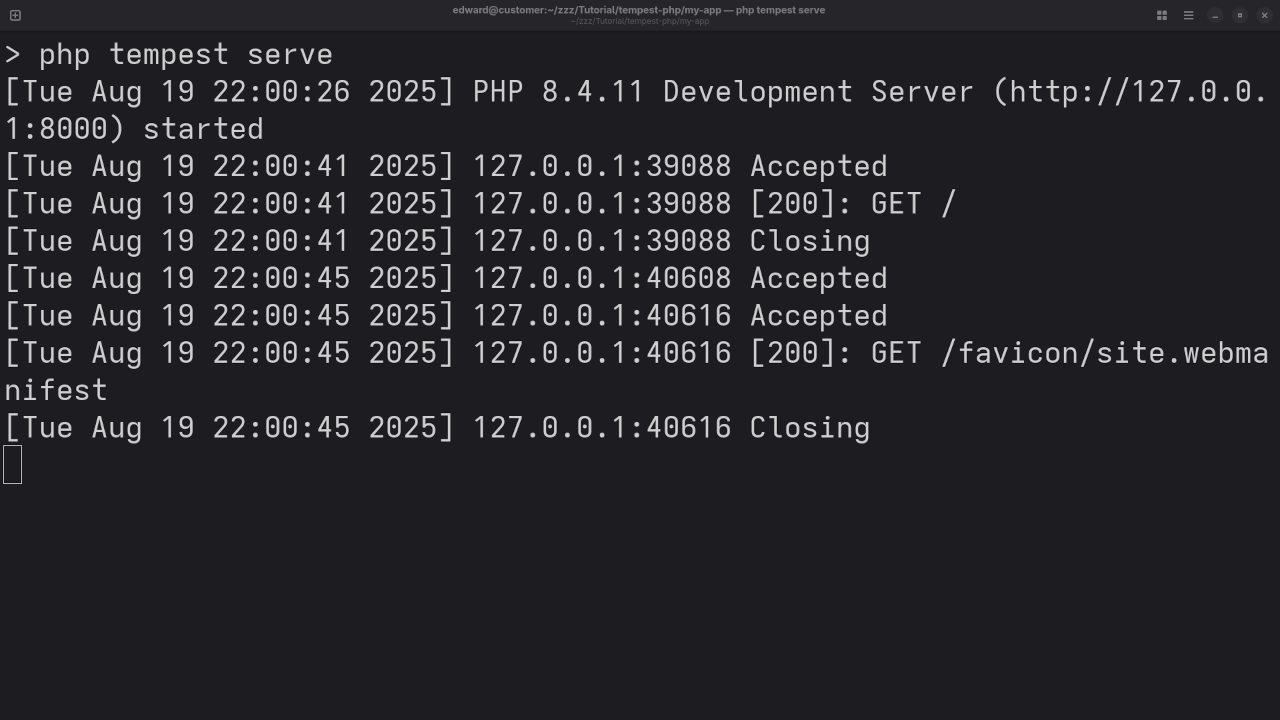
cd my-tempest-appThen run the following command to start the built-in development web server:
php tempest serveBy default, this will start a development server at:
http://localhost:8000Open your browser and go to http://localhost:8000/people to view the app once everything is set up (we’ll create that route below).
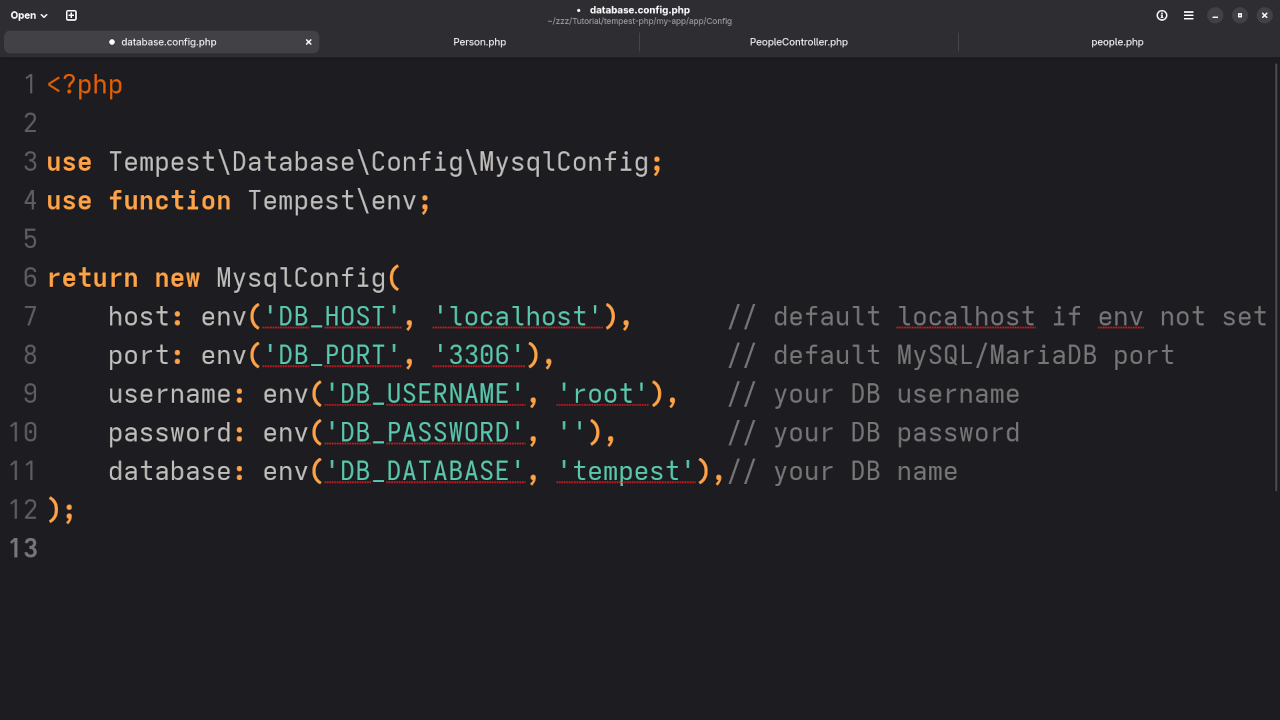
Step 3: Set Up Database Connection
Edit your .env file to include your MariaDB database credentials:
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=my_database
DB_USERNAME=my_user
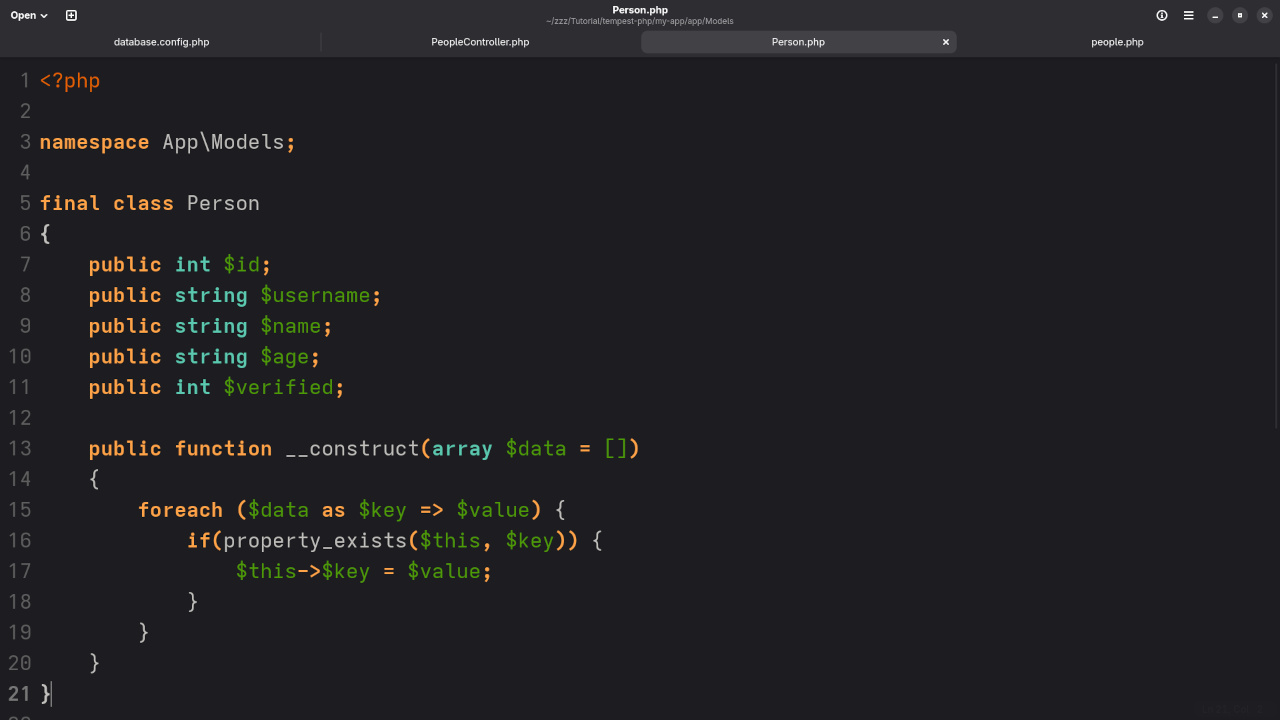
DB_PASSWORD=my_passwordStep 4: Create a Model for the "people" Table
Create the following model file: App/Models/Person.php
namespace App\Models;
final class Person
{
public int $id;
public string $username;
public string $name;
public string $age;
public int $verified;
public function __construct(array $data = [])
{
foreach ($data as $key => $value) {
if(property_exists($this, $key)) {
$this->$key = $value;
}
}
}
}
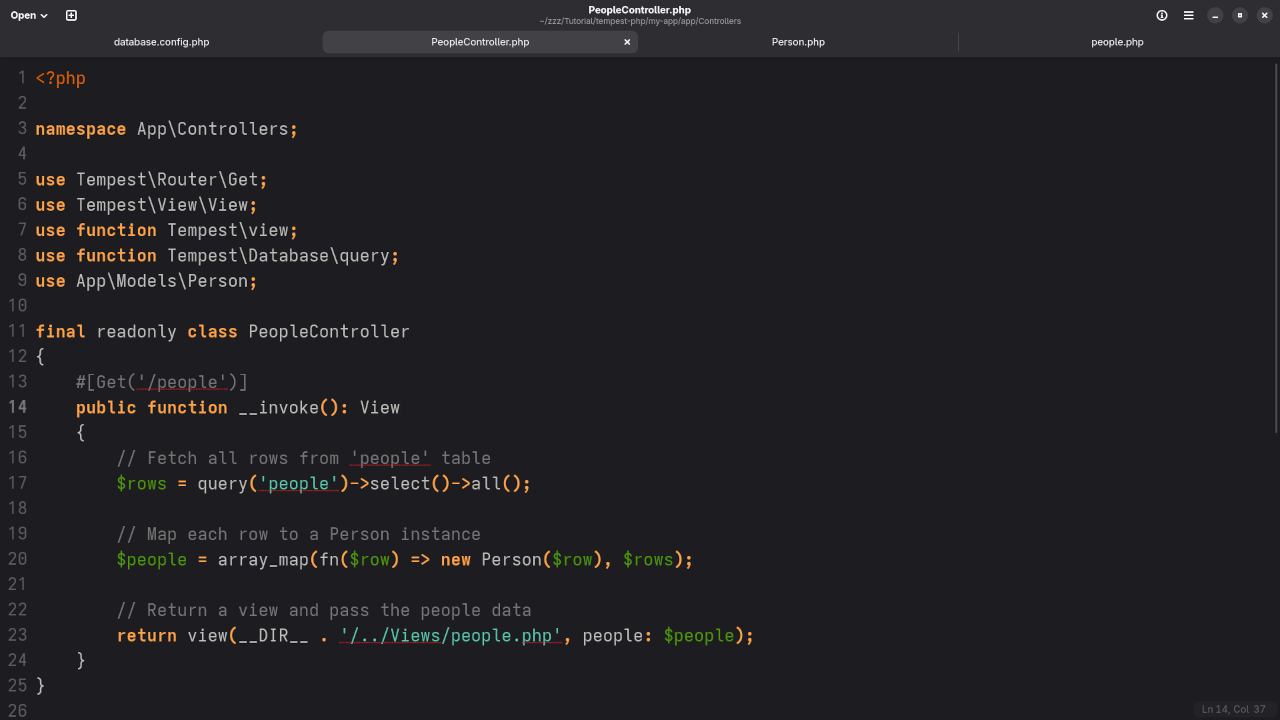
Step 5: Create a Controller
Create a controller at: App/Controllers/PeopleController.php
namespace App\Controllers;
use Tempest\Router\Get;
use Tempest\View\View;
use function Tempest\view;
use function Tempest\Database\query;
use App\Models\Person;
final readonly class PeopleController
{
#[Get('/people')]
public function __invoke(): View
{
// Fetch all rows from 'people' table
$rows = query('people')->select()->all();
// Map each row to a Person instance
$people = array_map(fn($row) => new Person($row), $rows);
// Return a view and pass the people data
return view(__DIR__ . '/../Views/people.php', people: $people);
}
}
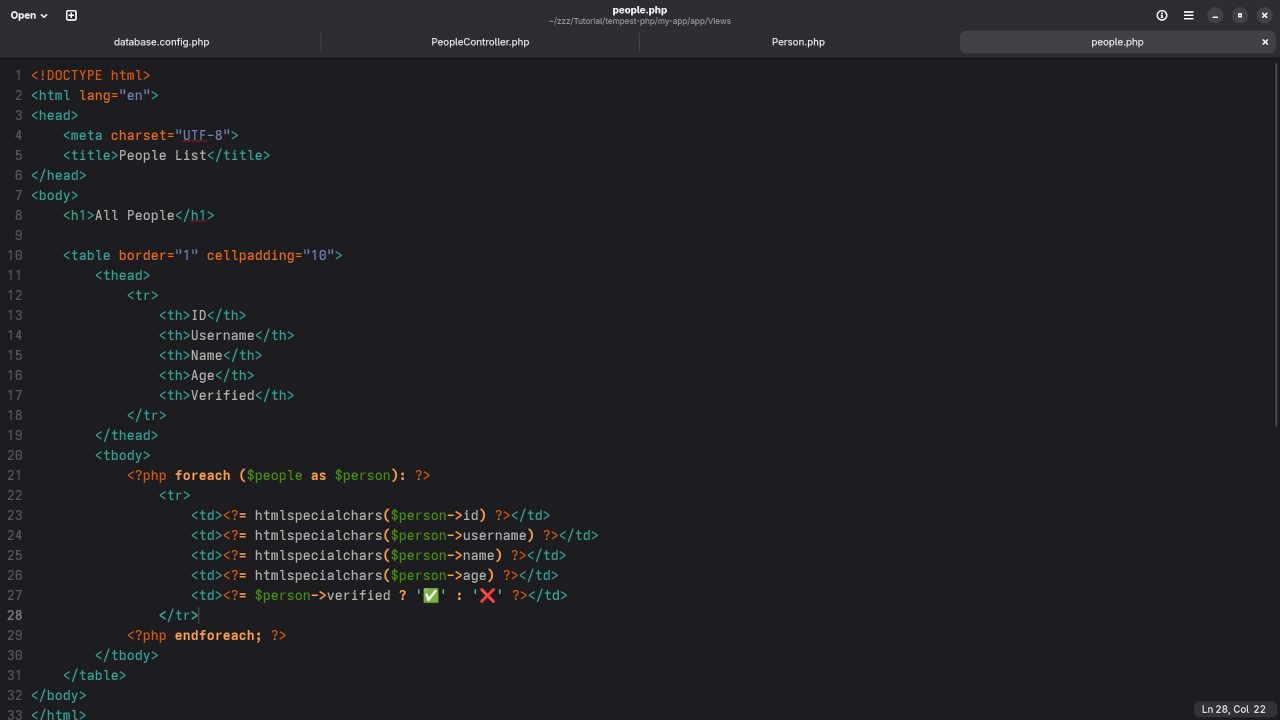
Step 6: Define a View
Register a route in App/Views/people.php:
<?php foreach ($people as $person): ?>
<tr>
<td><?= htmlspecialchars($person->id) ?></td>
<td><?= htmlspecialchars($person->username) ?></td>
<td><?= htmlspecialchars($person->name) ?></td>
<td><?= htmlspecialchars($person->age) ?></td>
<td><?= $person->verified ? '✅' : '❌' ?></td>
</tr>
<?php endforeach; ?>
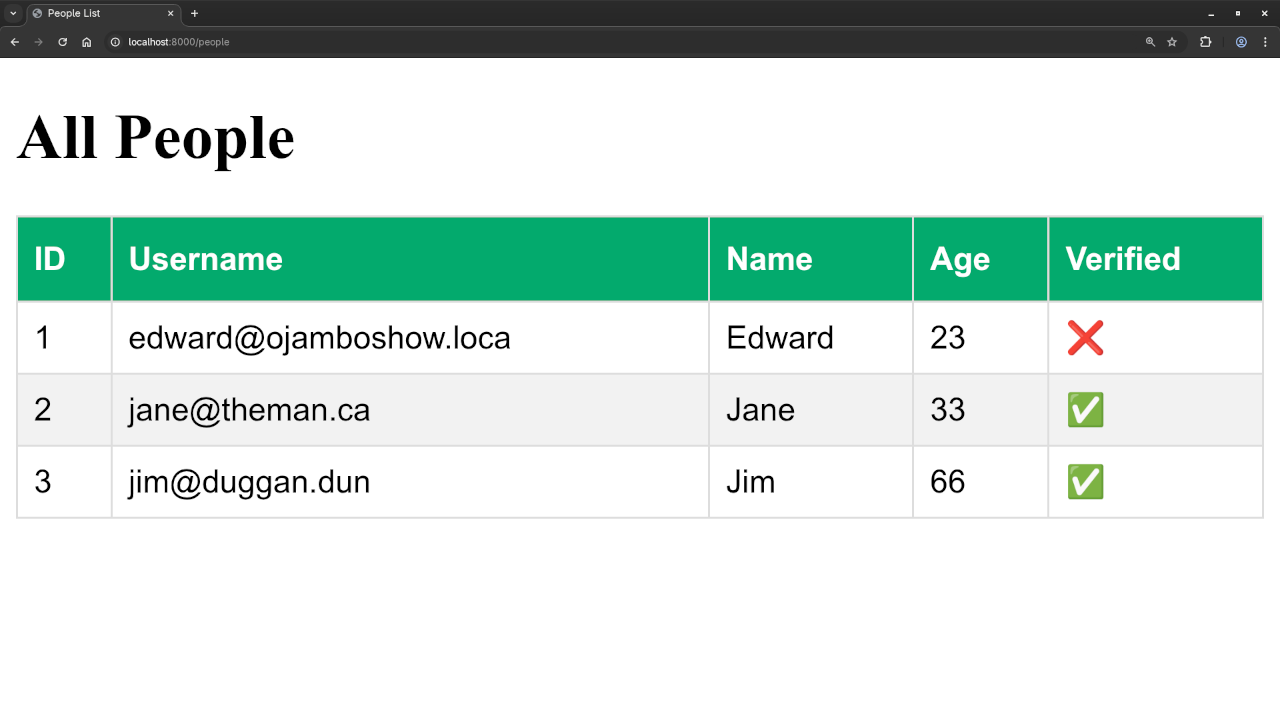
Now when you visit /people on your local Tempest server, it will display the data from your people table in a clean HTML list.
Screenshots And Screencast
Further Learning
If you’re new to PHP or want to deepen your skills, I’ve written a book just for you:
📚 Learning PHP – By Edward Ojambo
Also, check out my online course:
🎓 Learning PHP (Online Course)
Need Help?
I’m available for:
- One-on-one programming tutorials
- Upgrading to Tempest v1.6.0
- Migration from older PHP frameworks to Tempest
Final Thoughts
The Tempest PHP framework is fresh, simple, and effective—perfect for those who want power without complexity. With MVC support, modern tooling, and beginner-friendly structure, it’s a great choice for launching your next PHP project.
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.
