How to Upload Multiple Files in PHP (With MariaDB Integration)
Are you just starting out with PHP and want to learn how to build a multiple file upload system that saves filenames to a MariaDB database? You are in the right place.
In this post, you will learn:
- How to build a multiple file upload form using HTML
- How to handle file uploads securely with PHP (latest version)
- How to store file names in a MariaDB database
- How to manage uploads: insert, update, and delete records
- Best practices for secure and clean file handling
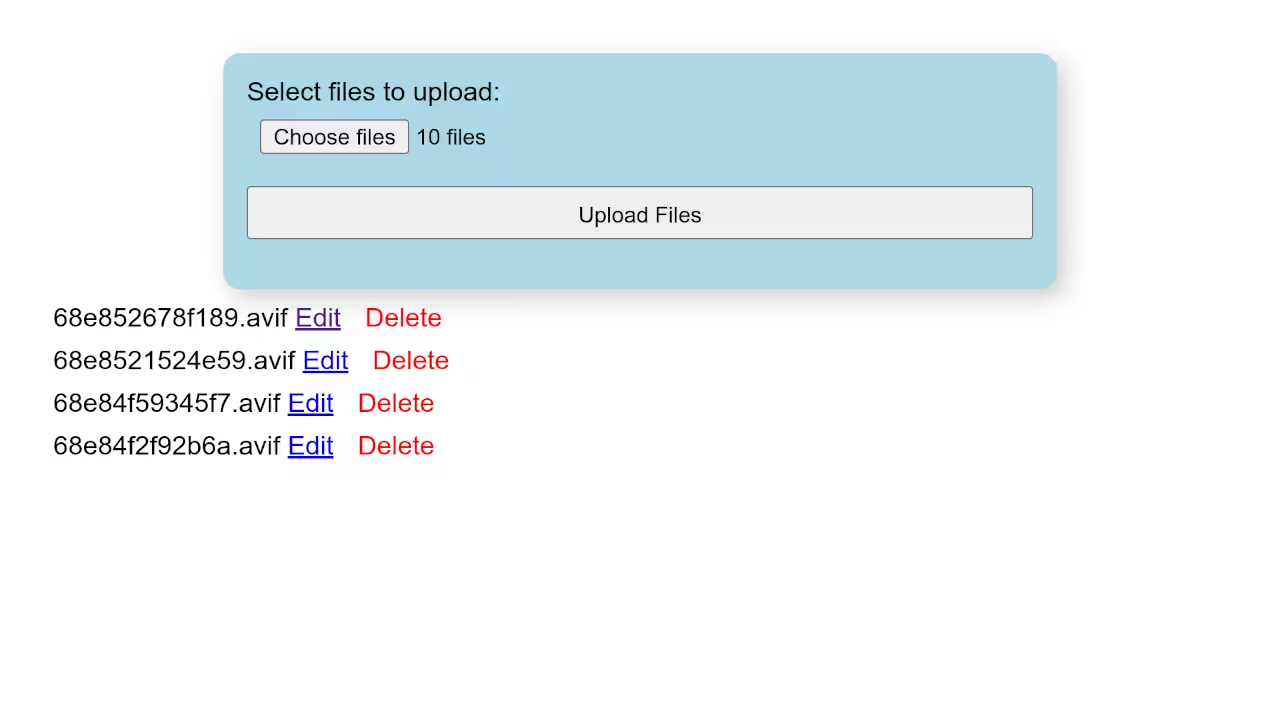
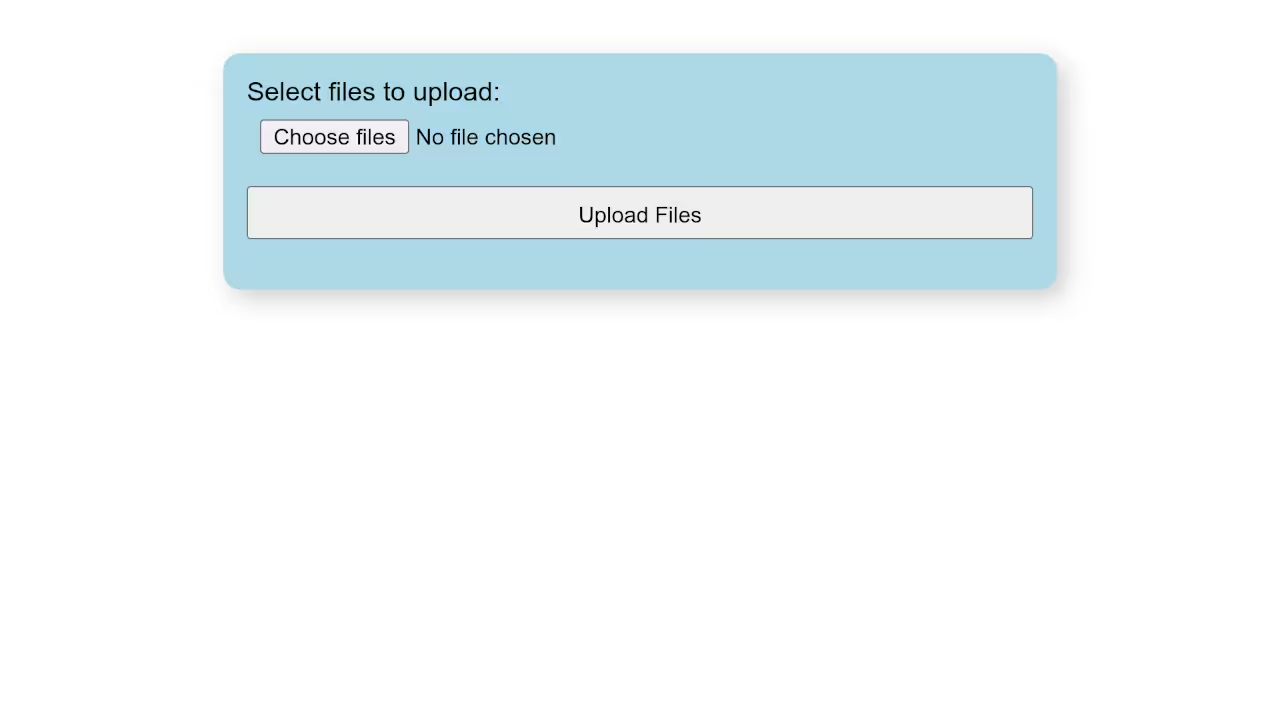
Step 1: Create the HTML Upload Form
<form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <label>Select files to upload:</label> <input type="file" name="files[]" multiple /> <input type="submit" name="submit" value="Upload Files"> </form>
Step 2: PHP Script to Handle Multiple File Uploads (upload.php)
$host = 'localhost';
$db = 'file_uploads';
$user = 'your_user';
$pass = 'your_password';
$conn = new mysqli($host, $user, $pass, $db);
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$uploadDir = "uploads/";
$allowedTypes = ['avif', 'jpg', 'jpeg', 'png', 'gif', 'pdf'];
if (isset($_POST['submit']) && !empty($_FILES['files']['name'][0])) {
foreach ($_FILES['files']['name'] as $key => $name) {
$tmpName = $_FILES['files']['tmp_name'][$key];
$error = $_FILES['files']['error'][$key];
$size = $_FILES['files']['size'][$key];
$ext = strtolower(pathinfo($name, PATHINFO_EXTENSION));
if ($error === 0 && in_array($ext, $allowedTypes)) {
$newName = uniqid() . '.' . $ext;
$uploadPath = $uploadDir . $newName;
if (move_uploaded_file($tmpName, $uploadPath)) {
$stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO uploads (filename) VALUES (?)");
$stmt->bind_param("s", $newName);
$stmt->execute();
$stmt->close();
//echo "$name uploaded successfully.<br>";
header("Location: " . $_SERVER['PHP_SELF']);
exit;
} else {
echo "Error uploading $name.<br>";
}
} else {
echo "$name is not a valid file type or has an error.<br>";
}
}
} else {
echo "No files selected.";
}
$conn->close();
Step 3: MariaDB Table Structure
CREATE TABLE uploads (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
filename VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
uploaded_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
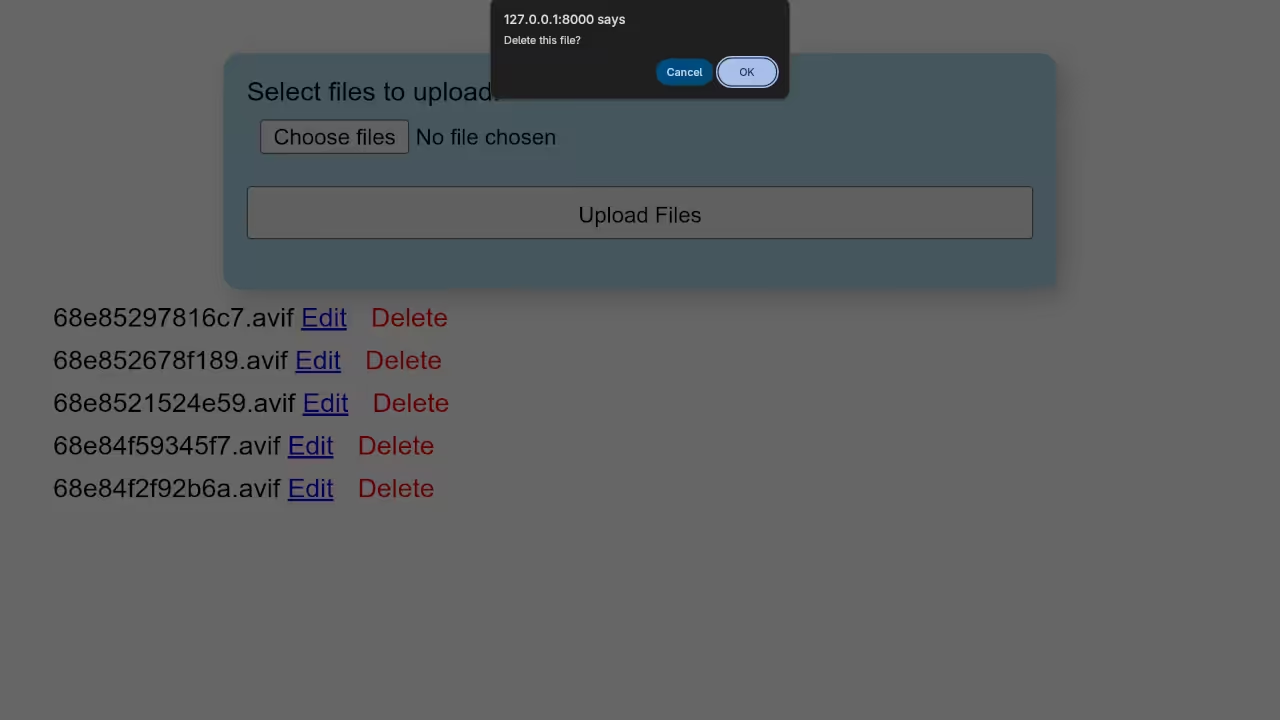
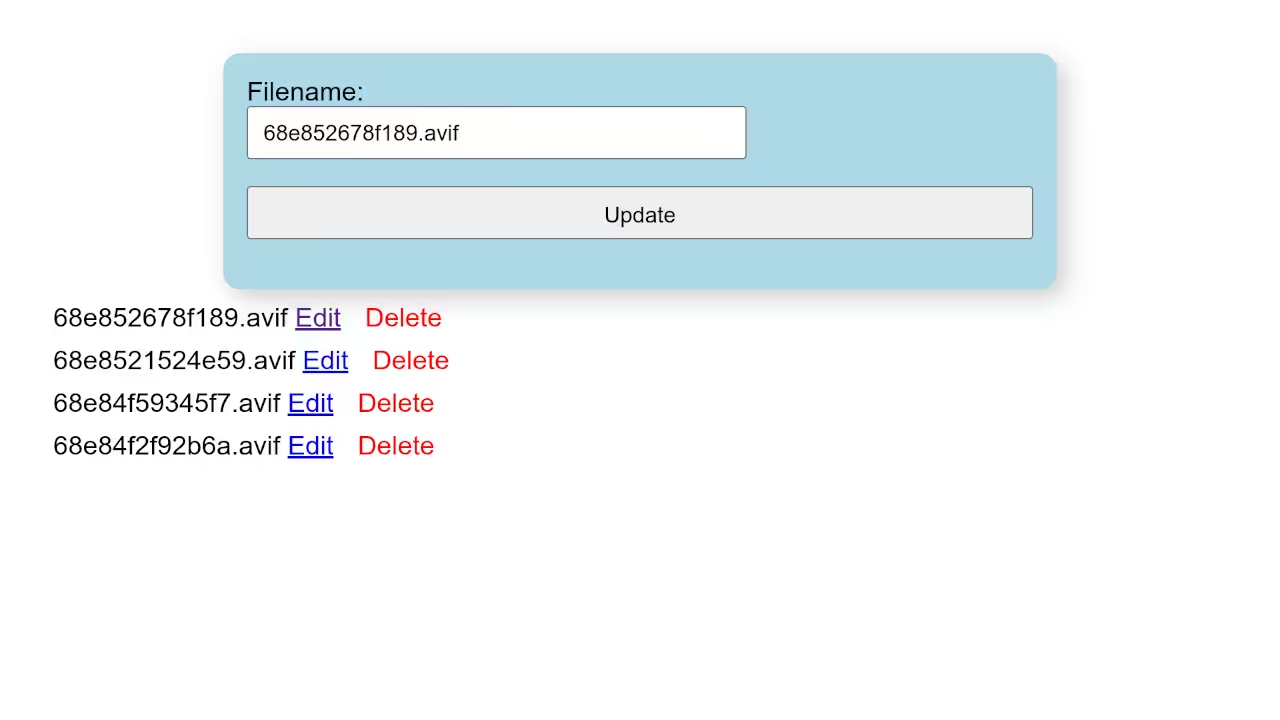
Bonus: Updating and Deleting Files
You can add update and delete features using simple SQL queries like:
Delete File
$stmt = $conn->prepare("DELETE FROM uploads WHERE id = ?");
$stmt->bind_param("i", $id);
$stmt->execute();
Update File Name
$stmt = $conn->prepare("UPDATE uploads SET filename = ? WHERE id = ?");
$stmt->bind_param("si", $newFilename, $id);
$stmt->execute();
Always remember to remove the file from the server using:
unlink('uploads/' . $filename);Best Practices
- Always validate file types to avoid malicious uploads
- Store files outside the web root if possible
- Rename files to avoid name collisions
- Use prepared statements to protect against SQL injection
- Limit file size and number of files uploaded at once
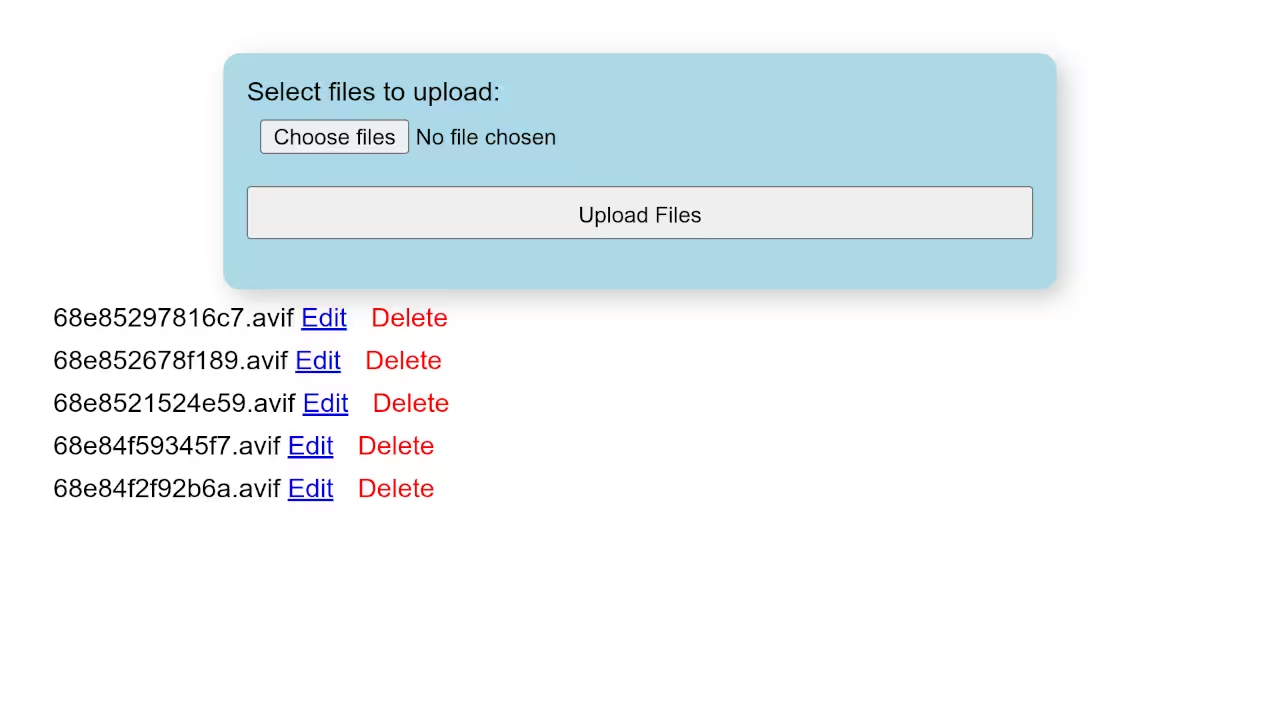
Screenshots and Screencast
Further Learning
Book: Learning PHP
If you want to go deeper into PHP, check out my book:
Learning PHP on Amazon
Course: Learning PHP
Prefer video and interactive examples? Enroll in the full course:
Learning PHP Course
Need Help with PHP?
I offer one-on-one programming tutorials, project migration services, and custom PHP development.
Got questions? Drop them in the comments or message me directly.
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.