Getting Started with the Prado PHP Framework: A Beginner’s Guide to MVC and MariaDB Integration
Prado PHP is an open-source, event-driven web application framework that simplifies the development of complex web applications. In this beginner-level tutorial, we’ll explore the fundamentals of Prado PHP, focusing on its support for the MVC (Model-View-Controller) design pattern. You’ll also learn how to connect Prado to a MariaDB database, query data from a table, and display it as HTML.
In this post, we will use Prado PHP version 4.3.1, and we’ll install it using Composer, the popular PHP dependency manager.
Before we dive into the code, if you’re interested in learning more about PHP, I highly recommend checking out my book, Learning PHP, and my course, Learning PHP, where I go deeper into the fundamentals and best practices.
What is Prado PHP?
Prado is a full-stack web application framework that supports rapid development of web applications. It is based on the MVC architecture, which helps in organizing your code for better maintainability and scalability.
- Model: Represents the data and business logic of the application.
- View: Represents the presentation layer (HTML, CSS, JavaScript).
- Controller: Handles the user requests and interacts with the model to prepare data for the view.
Setting Up Prado PHP 4.3.1 with Composer
To begin, you need to install Prado PHP using Composer. Here’s how:
- Install Composer (if you haven’t already):
Download Composer from https://getcomposer.org/ and follow the installation instructions for your operating system.
- Install Prado Framework:
Open your terminal and run the following command to install Prado PHP 4.3.1 via Composer:
composer create-project pradosoft/prado myproject - Create Your Application:
After the installation is complete, you can begin building your Prado application. Here’s the directory structure:
your-project-folder/protected │-- Common/ │ └-- PeopleRecord.php │-- Pages/ │ └-- People.page │ └-- People.php │ └-- PeopleRenderer.php │ └-- PeopleRenderer.tpl └-- application.xml - Set Up Your Web Server:
Make sure your web server is set up to point to the
protecteddirectory as the public root. If you’re using Apache, you can configure it with a virtual host.
Connect to MariaDB and Retrieve Data
Now that your Prado PHP framework is ready, let’s create a simple application that connects to a MariaDB database, queries a table, and displays the results as HTML.
1. Database Setup
First, make sure you have a MariaDB database with a table for this example. Below is a sample SQL script to create a table and insert some sample data.
CREATE DATABASE prado_example;
USE prado_example;
CREATE TABLE users (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES ('John Doe', 'john@example.com');
INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES ('Jane Smith', 'jane@example.com');
2. Create the Prado Model
Next, create a model that will interact with the database.
In the /protected/Common directory, create a new file User.php:
<?php
class User extends TActiveRecord
{
const TABLE = 'users';
public $id;
public $name;
public $email;
public function tableName()
{
return self::TABLE;
}
public function findAllUsers()
{
return User::finder()->findAll();
}
}
?>
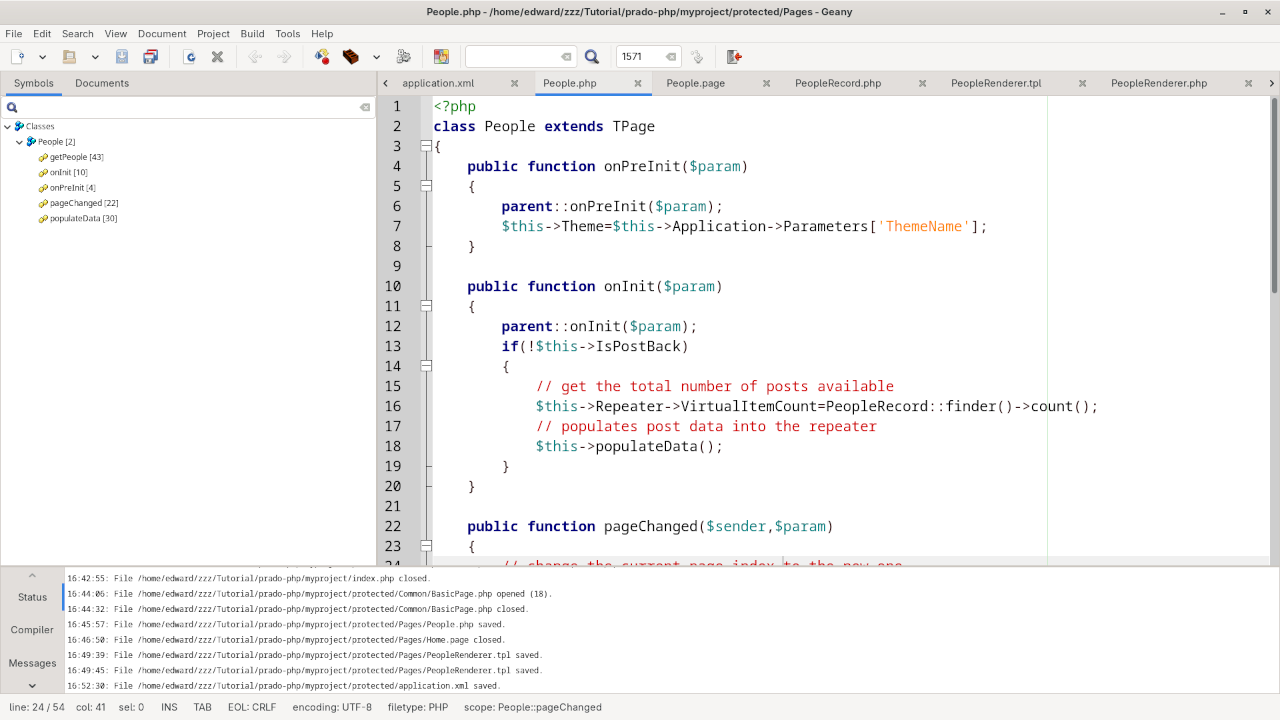
3. Create the Controller
Now, create a controller that will handle the user request and fetch the data from the database.
Create a new file in the /protected/Pages directory called UserController.php:
<?php
class UserController extends TPage
{
public function onLoad($param)
{
parent::onLoad($param);
$this->displayUsers();
}
public function displayUsers()
{
$users = User::finder()->findAll();
$output = "<ul>";
foreach ($users as $user) {
$output .= "<li>{$user->name} ({$user->email})</li>";
}
$output .= "</ul>";
$this->getResponse()->write($output);
}
}
4. Create the View
Prado views are HTML files with embedded Prado controls. For this example, we’ll create a view file to display the list of users.
Create a new view file called UserController.page in the /www directory:
<%@ Title="My Project Create Using Prado" %>
<com:TContent ID="Main">
<com:TRepeater ID="Repeater"
ItemRenderer="Application.Pages.PeopleRenderer"
AllowPaging="true"
AllowCustomPaging="true"
PageSize="5"
/>
<com:TPager ControlToPaginate="Repeater" OnPageIndexChanged="pageChanged" />
</com:TContent>
5. Update the Database Connection
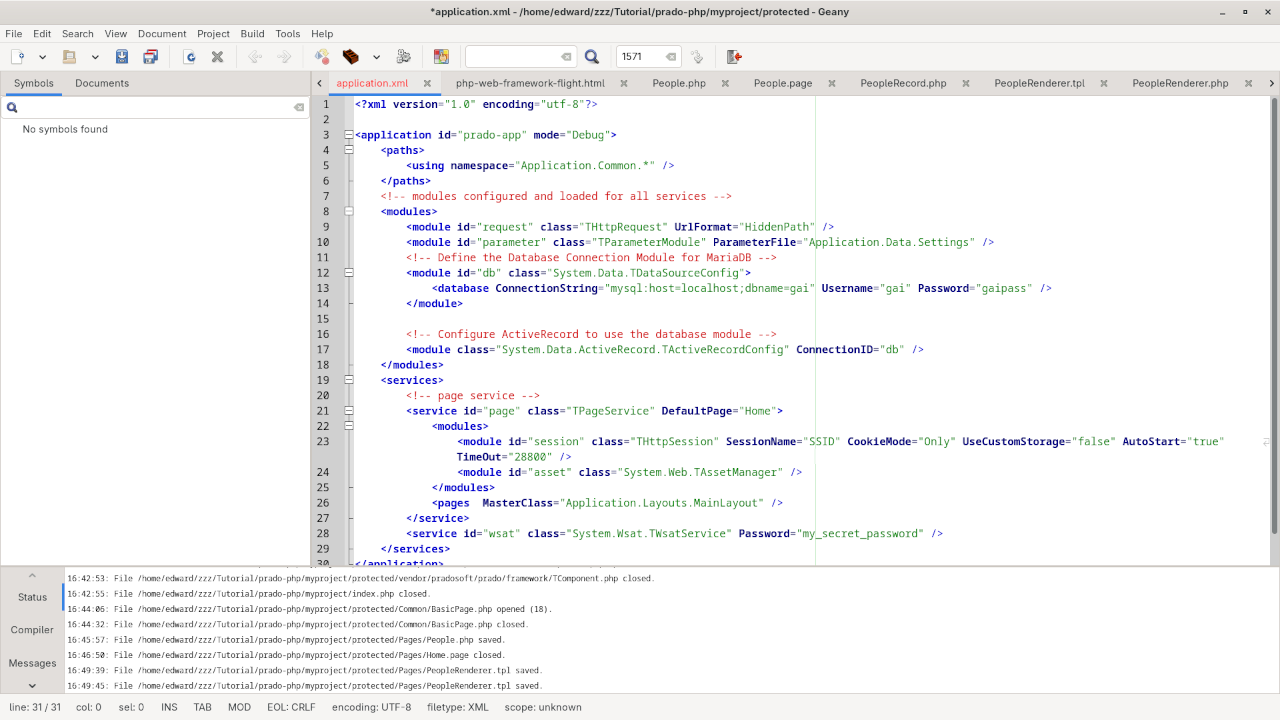
Make sure your /protected/application.xml file contains the correct database configuration:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<application id="prado-app" mode="Debug">
<paths>
<using namespace="Application.Common.*" />
</paths>
<!-- modules configured and loaded for all services -->
<modules>
<module id="request" class="THttpRequest" UrlFormat="HiddenPath" />
<module id="parameter" class="TParameterModule" ParameterFile="Application.Data.Settings" />
<!-- Define the Database Connection Module for MariaDB -->
<module id="db" class="System.Data.TDataSourceConfig">
<database ConnectionString="mysql:host=localhost;dbname=databasename" Username="databaseuser" Password="databasepassword" />
</module>
<!-- Configure ActiveRecord to use the database module -->
<module class="System.Data.ActiveRecord.TActiveRecordConfig" ConnectionID="db" />
</modules>
<services>
<!-- page service -->
<service id="page" class="TPageService" DefaultPage="Home">
<modules>
<module id="session" class="THttpSession" SessionName="SSID" CookieMode="Only" UseCustomStorage="false" AutoStart="true" TimeOut="28800" />
<module id="asset" class="System.Web.TAssetManager" />
</modules>
<pages MasterClass="Application.Layouts.MainLayout" />
</service>
<service id="wsat" class="System.Wsat.TWsatService" Password="my_secret_password" />
</services>
</application>
Running Your Application
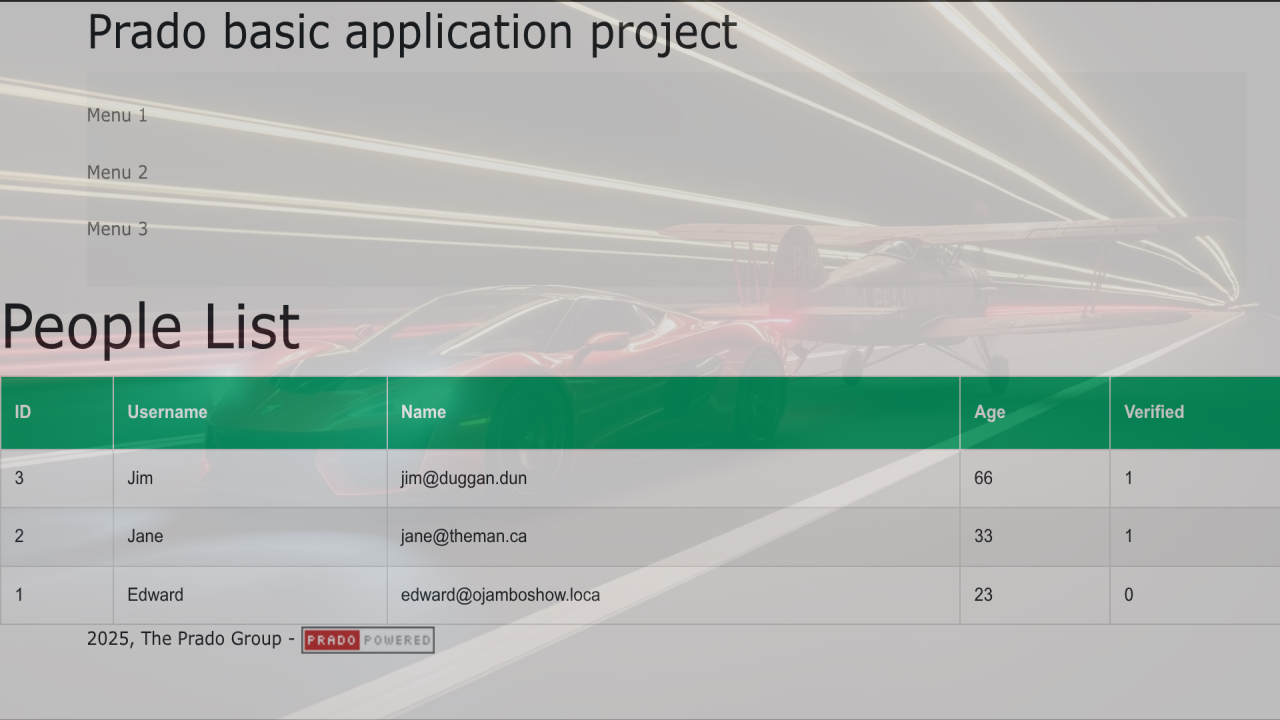
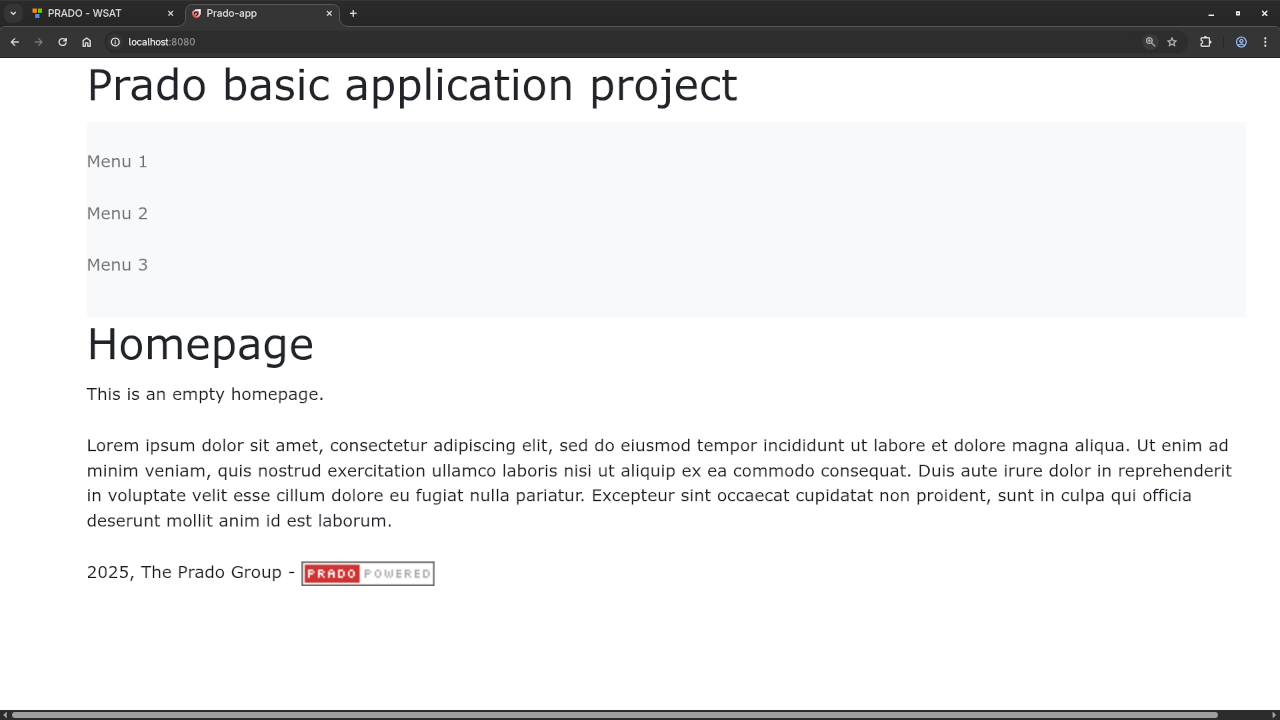
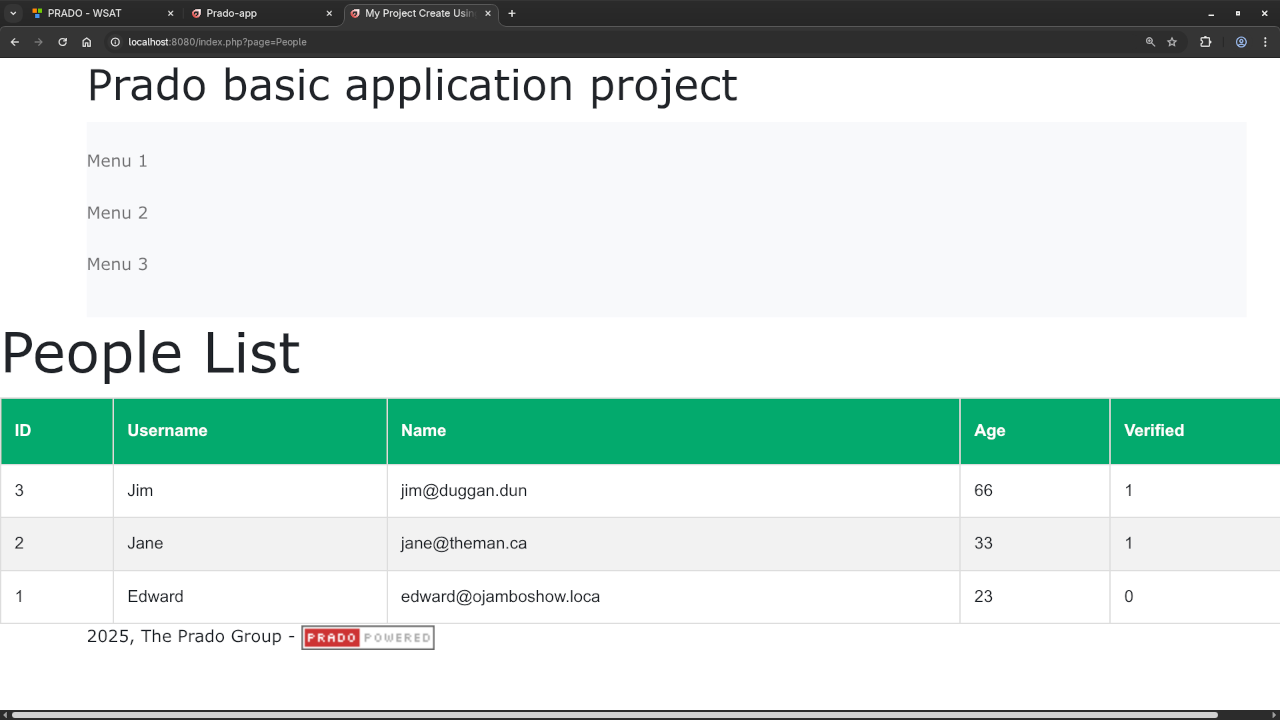
Now that everything is set up, you can run your Prado application by visiting the URL corresponding to your index.php file in your web browser.
If everything is set up correctly, you should see a list of users fetched from the MariaDB database and displayed as HTML.
Screenshots and a Screencast
Conclusion
With Prado PHP, you can easily build scalable and maintainable web applications using the MVC architecture. In this tutorial, you learned how to set up Prado PHP, connect it to a MariaDB database, and display data from a table in HTML. This is just a starting point-Prado offers a wealth of features that can help you build even more sophisticated applications.
Learn More
If you want to dive deeper into PHP, check out my book, Learning PHP and my Learning PHP course. You can also get in touch with me for one-on-one programming tutorials or assistance with Prado PHP updates or migrations.
Happy coding!
Disclaimer: This article provides an introductory guide to Prado PHP. For more advanced topics and in-depth tutorials, feel free to explore the documentation or reach out for personalized programming assistance.
🚀 Recommended Resources
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase at no extra cost to you.